文章信息
- 何俊, 樊瑜琪, 杨丰文, 黄明, 张俊华, 张伯礼
- HE Jun, FAN Yuqi, YANG Fengwen, HUANG Ming, ZHANG Junhua, ZHANG Boli
- 马鞭草化学成分及药理活性研究进展
- Research advances on chemical components and pharmacological activities of Verbena officinalis
- 天津中医药, 2020, 37(11): 1205-1212
- Tianjin Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2020, 37(11): 1205-1212
- http://dx.doi.org/10.11656/j.issn.1672-1519.2020.11.02
-
文章历史
- 收稿日期: 2020-03-08
马鞭草(Verbenae Herba)为马鞭草科植物马鞭草Verbena officinalis L.的干燥地上部分[1],始载于《名医别录》,又名风颈草、铁马鞭、紫顶龙芽、红藤草、野荆芥等。马鞭草为多年生草本植物,于每年6~8月花期采收,在全球有较广的分布,在中国主要分布于湖北、江苏、广西、贵州,此外,安徽、新疆、浙江、四川等地亦有分布。马鞭草味苦,性凉,归肝、脾经,具有活血散瘀、清热解毒、利水、退黄、截疟等功效,广泛用于治疗外感发热、流感、水肿、疟疾、黄疸、咽喉肿痛、牙周炎、经闭、白喉等病症。
马鞭草主要含有黄酮类、环烯醚萜类、苯乙醇苷类、三萜类、甾醇类、挥发油类等化学成分。现代药理研究表明,其具有抗菌、抗病毒、抗炎镇咳、抗肿瘤、抗早孕、神经保护、调节免疫活性等作用。马鞭草作为传统中药材之一,在中国汉族、傣族、彝族等20多个民族当中应用广泛。更加值得注意的是,在2020年抗击新型冠状病毒肺炎疫情防控的过程中,马鞭草作为常用中药材之一在中国工程院院士张伯礼教授抗新型冠状病毒肺炎的临床验方中得以良好的应用。笔者现对近20年来国内外所开展的马鞭草化学成分、药理及毒性相关研究进行综述,为马鞭草进一步的研究及临床应用提供参考。
1 化学成分研究马鞭草因其在临床上应用广泛,早在1908年便有学者对其化学成分展开了相关研究。马鞭草化学成分主要为黄酮类、环烯醚萜类、苯乙醇苷类、三萜类、二萜酚类、甾醇类、挥发油类等,其中环烯醚萜类是马鞭草的特征性成分。马鞭草主要化学成分综述如下。
1.1 黄酮类成分黄酮类成分为马鞭草的主要成分,研究表明马鞭草中的黄酮类化合物具有抑菌、抗炎、镇咳等作用[2]。主要有甘草素、栗苷、蒿亭、胡麻素、Nepetin、木犀草素、山柰酚、槲皮素、异鼠李素、芹菜素、杨梅素、杨梅苷、蒿黄素、香叶木素、4′-羟基汉黄芩素、木犀草素-7-O-葡萄糖苷、芹菜素-7-O-葡萄糖苷、槲皮素-3-O-葡萄糖苷、胡麻黄素-6-O-葡萄糖苷、金合欢素-7-O-芸香糖苷和8-羟基-柚皮素-4′-甲基醚等[3-10]。
1.2 环烯醚萜类成分环烯醚萜类成分是马鞭草的特征性成分,研究表明马鞭草中的环烯醚萜类成分具有较好的抗炎、镇咳、抗菌、抗病毒、抗早孕等作用[2]。主要有马鞭草苷、9-羟基木犀苷、戟叶马鞭草苷、3,4-二氢马鞭草苷、5-羟基马鞭草苷、钩吻醇、三叶草苷、当药苦苷、龙胆苦苷、桃叶珊瑚苷、大叶苷、3′-acetylsweroside等[3-4, 11-14]。
1.3 三萜类及二萜酚类成分马鞭草中三萜类成分主要为熊果酸、齐墩果酸、马尾柴酸、3α,24-二羟基齐墩果酸、熊果酸内酯、3-表熊果酸、3-表齐墩果酸、3α,24-二羟基熊果酸、羽扇豆醇等,其中熊果酸和齐墩果酸为2015版《中华人民共和国药典》中马鞭草含量测定的指标性成分。除三萜类成分外,马鞭草中还含有鼠尾草酚、鼠尾草酸、迷迭香酚、异迷迭香酚、迷迭香酸等二萜酚类成分[1, 4, 8-9, 11, 15]。
1.4 苯乙醇苷类及甾醇类成分近年来,由于马鞭草中所含有的二乙酰基苯乙醇类化合物具有较强的抗肿瘤活性,使得苯乙醇苷类成分也日益成为了马鞭草化学成分的研究热点。其代表性成分主要有毛蕊花糖苷、异毛蕊花糖苷、阿克替苷、马替诺皂苷、3,4二羟基-苯乙醇、Cistanoside E、Parvifloroside B、Campneoside Ⅰ、3"",4""-diacetyl-O-betonysoside A、3,4-diacetyl-O-isoverbascoside等。此外,马鞭草中的甾醇类成分β-谷甾醇、7α,22S-二羟基谷甾醇、β-谷甾醇-β-D-葡萄糖苷等也受到了研究人员的关注[4, 8, 15-18]。
1.5 挥发性化学成分研究表明,马鞭草中的挥发油类成分主要为萜类、烷烃类和杂环类成分,具有较强的抗菌作用。其中含量较高的成分为乙酸、芳樟醇、律草烯、大根香叶烯-d、α-依兰烯、十五烷、反-石竹烯、α-姜黄烯、γ-芹子烯、反-β-金合欢烯、紫惠槐烯、1-乙基-2-甲基环癸烷、白菖蒲油烯、β-榄香烯、β-没药烯、顺-α-没药烯、(-)-石竹烯氧化物、β-杜松烯、α-雪松醇等化合物[19]。
1.6 其他成分除上述成分外,研究人员还从马鞭草中分离得到了十六酸、十六酸甲酯、十六酸乙酯、鞣质、腺苷、苦杏仁酶、强心苷、水苏碱、β-胡萝卜素、二氢咖啡酸丙酯、2-羟基-3-甲氧基蒽醌、苦味酸、verbean A、Acteoside、Eukovoside等化学成分[5, 8-9, 11, 17, 20-21]。
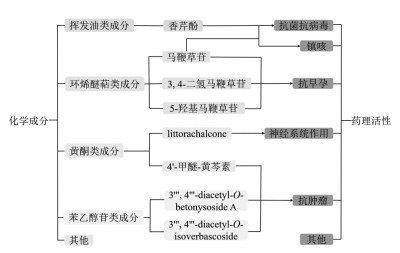
2 药理作用马鞭草作为中国传统中药,古籍中就已明确记载了其具有“清热解毒、活血散瘀、利水消肿”等多种功效。现代药理学研究表明,马鞭草中所含化学成分具有抗病毒、抗菌、镇咳、抗炎、镇痛及抗肿瘤等多种药理活性。近年来,随着人们对马鞭草化学成分及药理作用研究的日益深入,马鞭草已引起了国内外学者的广泛关注。马鞭草化学成分的药理活性见图 1。
|
| 图 1 马鞭草成分的药理活性 Fig. 1 The pharmacological activity of Verbena officinalis components |
马鞭草对多种致病细菌都有较强的抑制作用。研究表明马鞭草中的黄酮类成分对革兰氏阴性菌(如大肠杆菌)和革兰氏阳性细菌(如金黄色葡萄球菌、白假丝酵母菌)具有明显的抑制作用[22]。此外,马鞭草的醇提取液对假单胞菌和匍枝根霉也具有较强抑制活性,其咖啡酰衍生物段对于假单胞菌和根霉菌的生长的抑制率可达87.4%及79.1%,表明其咖啡酰衍生物段可能存在单体化合物之间的协同抑菌作用[23]。研究人员在对马鞭草的研究中还发现,其挥发油类成分对于蜡状芽孢杆菌和铜绿假单胞菌有较强的抑制作用,且所含有的单体成分香芹酚能够完全抑制橘青霉菌[24]。
马鞭草及其提取物还具有抗病毒的作用。研究发现马鞭草能抑制乙型肝炎病毒(HBV)和乙肝表面抗原(HBsA)[25],其在治疗病毒性乙型肝炎方面有着显著的疗效[26]。此外,临床研究表明马鞭草对于病毒性疱疹也具有较好的治疗作用[27]。
2.2 镇咳作用咳嗽是呼吸系统的常见疾病,研究发现马鞭草水煎剂具有镇咳作用,其中马鞭草苷为马鞭草镇咳的有效成分[28]。任非等[29]通过小鼠氨水引咳及豚鼠枸橼酸引咳实验发现马鞭草水提取液、醇提取液、乙酸乙酯萃取液、正丁醇萃取液都具有显著的镇咳作用,且其作用具有一定的浓度依赖性。临床研究也表明,马鞭草对于治疗百日咳具有良好的疗效[30]。
2.3 抗炎镇痛作用马鞭草提取物具有抗炎活性[10]。任非等[29]通过小鼠二甲苯耳肿胀法研究发现马鞭草总提物、马鞭草醇提取液、乙酸乙酯萃取液、正丁醇萃取液都具有显著的抗炎作用。其中马鞭草醇提液的抗炎作用可能与抑制组胺及5-羟色胺的合成与释放有关[31]。而王琳琳等[18]在马鞭草总苷对慢性非细菌性前列腺炎模型鼠的研究中发现,马鞭草总苷治疗大鼠前列腺炎的机制可能与抑制前列腺局部白细胞介素-2(IL-2)、肿瘤坏死因子-α(TNF-α)、白细胞介素-1β(IL-1β)等促炎性细胞因子的产生有关。除此之外,临床研究也证实了马鞭草对支原体肺炎、化脓性胸膜炎、慢性肾炎、慢性前列腺炎、牙龈炎以及口腔黏膜炎等多种炎症类疾病都具有良好的治疗作用[32-35]。
除抗炎作用外,马鞭草还被证明具有镇痛的作用。王振富[36]通过热板法和醋酸扭体实验证实了马鞭草能够提高小鼠热板所致痛阈值,对醋酸所致小鼠扭体反应有明显对抗作用。而王琳琳等[37]也在研究中发现马鞭草总苷能明显抑制醋酸导致的小鼠扭体反应,提高小鼠对热刺激的痛阈值,表明马鞭草总苷对急性锐痛和慢性钝痛均有抑制作用。此外,Calvo[38]通过观察马鞭草甲醇提取物制成的外用制剂对角叉菜胶所致大鼠跖肿胀部及局部注射甲醛大鼠舔脚背的次数的影响,发现马鞭草甲醇提取物的外用制剂与吡罗昔康抗炎效果一致,镇痛效果低于水杨酸甲酯。
2.4 增强免疫作用马鞭草及其提取物还具有增强免疫的功效。用马鞭草醇提物对小鼠进行腹腔注射后,发现马鞭草醇提物对小鼠T淋巴细胞增殖能力、抗体形成细胞分泌抗体的能力具有明显的增强效应,对小鼠吞噬细胞功能则具有明显的抑制效应[39]。并且马鞭草醇提物腹腔注射对小鼠IL-2生物活性具有明显的增强作用,且与剂量呈正相关,提示马鞭草在机体的抗感染、抗肿瘤作用可能与其免疫增强作用有关[40]。另有临床研究表明,以马鞭草为主的方药狼疮饮在治疗免疫系统相关疾病系统性红斑狼疮时疗效显著[41]。同时,刘玉琴[42]也通过对免疫性不孕患者进行治疗时发现马鞭草具有显著的免疫调节作用。
2.5 抗肿瘤作用 2.5.1 抗绒毛膜癌作用近年来,大量的研究证明马鞭草具有较强的抗绒毛膜癌潜力。用马鞭草醇提液分别作用于体外培养的绒毛膜癌JAR细胞、人肝癌SMMC-7721细胞及人胚肺二倍体成纤维细胞(2BS)后,发现其对体外培养的绒毛膜癌JAR细胞有明显抑制作用,且具有特异性,这一作用可能与抑制表皮生长因子受体(EGFR)的表达有关[43]。徐昌芬等[44]通过四甲基偶氮唑盐微量酶反应比色法(MTT)实验以人早孕分离纯化的绒毛膜滋养层细胞和人绒毛膜癌JAR细胞对马鞭草醇提液有效部位进行筛选,发现其氯仿部位能明显抑制两种细胞的增殖。在对其作用机制的进一步研究中发现,马鞭草可以抑制JAR细胞人绒毛膜促性腺激素(hCG)的分泌,并通过改变B淋巴细胞B-2蛋白(Bcl-2)和Bcl-2相关X蛋白(Bax),下调Fasl的表达,诱导JAR细胞发生凋亡[45-46]。同时,流式细胞仪检测结果还发现马鞭草提取物可以诱导细胞发生G2/M期阻滞[47]。
4′-甲醚-黄芩素是马鞭草中的单体成分,实验发现其对JAR细胞具有增殖抑制作用,可以通过提高细胞内Ca2+浓度、降低端粒酶逆转录酶(hTERT)mRNA的表达以及上调Bax、细胞色素C(cytochrome C)、半胱天冬酶9(Caspase-9)、半胱天冬酶3(Caspase-3)的表达,激活p38MAPK信号通路及抑制生存素蛋白(Survivin)表达,降低原癌基因(c-myc)的表达等机制诱导JAR细胞发生凋亡[48-49]。研究还发现,4′-甲醚-黄芩素对人绒毛膜癌多药耐药细胞株JAR/VP16有耐药逆转作用,其机制可能是抑制耐药细胞生长及诱导细胞凋亡下调多药耐药基因1(MDR1)mRNA、肺耐药蛋白(LRP)mRNA及相应产物P糖蛋白(P-gp)和LRP的表达[50]。
2.5.2 抗肝癌作用研究发现,马鞭草总黄酮可以显著抑制人肝癌HepG-2细胞增殖、降低HepG-2细胞的侵袭力,其机制可能与下调HepG-2细胞内基质金属蛋白酶-9(MMP-9)和血管内皮生长因子(VEGF)表达水平有关[51]。RT-PCR,Western blot分析结果表明马鞭草总黄酮通过下调肝癌HepG-2细胞IL-6、JAK2、STAT3水平来抑制细胞增殖[52]。在进一步研究中发现,马鞭草总黄酮可以通过促进IκB-α蛋白表达,下调NF-κBp65蛋白表达,抑制TopoⅡ活性并激活Bcl-2 /Bax /Caspase-3信号通路级联反应,增加活性氧(ROS)水平、降低线粒体膜电位,并同时上调Caspase-3、Caspase-9、P53蛋白水平诱导肝癌细胞发生凋亡,从而发挥其抗肿瘤作用[53-54]。曹志然等[55]通过研究发现,马鞭草水提物和醇提物可以明显抑制H22荷瘤小鼠体内肿瘤的生长。Kou等[56]同样通过建立H22小鼠移植瘤模型检测发现马鞭草提取物具有体内抗肿瘤作用,且其在抗肿瘤的同时对小鼠免疫系统无损伤。此外,还有研究表明,马鞭草水提物与顺铂联合应用具有协同抗肝癌的作用[57]。
2.5.3 对其他肿瘤作用除了绒毛膜癌和肝癌以外,马鞭草对其他种类的肿瘤细胞也有一定的增殖抑制作用。研究发现马鞭草水提物对人结肠癌HCT116细胞具有增殖抑制作用[58]。马鞭草经皮透过液对B16黑色素瘤细胞的增殖具有抑制性[59]。此外,徐华娥等[60]通过研究还发现马鞭草醇提液在小剂量时能够显著增加紫杉醇的抗小鼠肉瘤活性。
2.6 抗早孕作用大量的实验研究及临床应用已证实马鞭草具有明显的抗早孕作用。为了探讨马鞭草抗早孕的作用机制,徐昌芬等[61]、卢小东等[62]观察了马鞭草乙醇提取液对体外培养的绒毛滋养层细胞形态及功能的影响,发现马鞭草提取液以剂量依赖方式直接损伤滋养层细胞,抑制hCG的合成和分泌,抑制滋养层琥珀酸脱氢酶(SDH)从而终止早孕。其还通过给早孕小鼠灌服马鞭草提取液探讨了马鞭草的体内抗早孕作用可能与抗孕酮作用有关[63]。张曙萱等[64]研究发现马鞭草抗早孕机制可能与抑制蜕膜细胞生长及促进其凋亡相关。张涛等[65]发现马鞭草甲醇总提取物对雌性SD大鼠具有明显的抗早孕作用,并在进一步的研究中发现,马鞭草中的环烯醚萜苷类成分能兴奋大鼠离体子宫肌条,其抗早孕功效可能与此相关。
2.7 对神经系统的作用马鞭草对于神经系统类疾病也有一定的功效。刘佳等[66]发现马鞭草对中枢神经系统具有一定的作用,但其作用机制及用量还需要进一步的深入研究。马鞭草醇提液还具有明显的抗脑水肿作用,其作用机制可能与抑制脑组织AQP4的表达有关[67]。此外,AD小鼠模型实验证明了马鞭草水煎液可以提高模型鼠的学习和记忆能力,其作用机制可能与马鞭草水提物可以降低β淀粉样蛋白表达水平相关[68]。从马鞭草中分离得到的littorachalcone也被证实具有促进神经生长因子介导的轴突生长的作用[69]。另外,Waheed等[70]、Rashidian等[71]还发现马鞭草醇提物具有抗惊厥、抗焦虑、镇静等作用,其抗惊厥作用的机制可能与增强GABAergic神经元系统相关。
2.8 其他作用近年来,Sisay等[72]在研究中发现,马鞭草的甲醇提液具有止泻活性。马鞭草注射液对60Co照射小鼠有一定的保护作用[73]。此外,还有文献报道了马鞭草中的黄酮类化合物具有抗氧化及保护小鼠肝肺损伤的功效[74-75]。马鞭草提取液还能抑制大鼠肾草酸钙晶体形成,用来防止尿结石,临床应用也证明了马鞭草在防治尿石症时具有良好的疗效[76-77]。部分临床研究表明马鞭草还可用于治疗乳痈、围绝经期功能不良性子宫出血及热证哮喘[78-80]。
3 毒性研究马鞭草毒性较低,不溶血。Fateha等[81]发现给怀孕大鼠灌服马鞭草提取液会影响其繁殖能力,因此孕妇应尽量避免使用马鞭草。同时其还通过研究证实了马鞭草对大鼠没有致死作用及骨髓毒性,在实际应用中,马鞭草的应用优势远大于应用风险[82]。
4 结语与展望综上所述,马鞭草药源丰富、价格低廉且毒性较低,所含有的黄酮类、环烯醚萜类、苯乙醇苷类、三萜类、挥发油类等成分具有多种药理活性,其中黄酮类、环烯醚萜类和挥发油类等成分为其抗菌、抗病毒、抗炎、镇咳作用的主要药效成分。
肺炎作为一种常见疾病,严重威胁着儿童及老年人的健康。近年来,随着人们对肺炎研究的深入,病毒病原体越来越被认为是导致肺炎的重要病因,目前已有超过20种病毒被证实与社区获得性肺炎有关[83]。马鞭草具有抗炎镇痛、广谱抗菌、抗病毒、镇咳的作用。目前,临床上应用马鞭草及其制剂治疗咳喘、肺炎已有相关报道,且疗效确切。因此,将马鞭草用于肺炎的相关治疗必将取得新的研究进展,其应用前景也将非常广阔。
| [1] |
国家药典委员会.中华人民共和国药典一部[S].北京: 中国医药科技出版社, 2015: 52. Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission. Pharmacopoeia of people's republic of China[S]. Beijing:China Medical Science Press, 2015:52. |
| [2] |
刘素香, 白雪, 刘毅, 等. 马鞭草HPLC指纹图谱建立及指标性成分的测定[J]. 中草药, 2016, 47(12): 2069-2073. LIU S X, BAI X, LIU Y, et al. Establishment of HPLC fingerprint of Verbenae officinalis and determination of multi-components[J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs, 2016, 47(12): 2069-2073. |
| [3] |
田菁.马鞭草活性成分研究[D].北京: 军事医学科学院, 2005. TIAN J. Study on the active ingredients of Verbena officinalis[D]. Beijing: Academy of Military Medical Sciences, 2005. |
| [4] |
孙玉明, 王月月, 蔡蕊, 等. 高效液相色谱-光电二极管阵列-高分辨质谱联用鉴定马鞭草提取物中的化学成分[J]. 色谱, 2017, 35(9): 987-994. SUN Y M, WANG Y Y, CAI R, et al. Identificantion of the chemical compositions of Verbena officinalis L. extract by high performaceliquid chromatography-photodiode array-high resolution mass spectrometry[J]. Chinese Journal of Chromatography, 2017, 35(9): 987-994. |
| [5] |
马金华, 杨勇勋. 马鞭草的化学成分研究[J]. 西南民族大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 45(6): 579-582. MA J H, YANG Y X. Studies on chemical constituents from whole plants of Verbena officinalis L[J]. Journal of Southwest Minzu University (Natural Science Edition), 2019, 45(6): 579-582. |
| [6] |
陈改敏, 张建业, 张向沛, 等. 马鞭草黄酮类化学成分的研究[J]. 中药材, 2006, 29(7): 677-679. CHEN G M, ZHANG J Y, ZHANG X P, et al. Studies on chemical constituents of flavonoid from Verbena officinals[J]. Journal of Chinese Medicinal Materials, 2006, 29(7): 677-679. |
| [7] |
陈丽花, 李志军, 王定勇. 马鞭草抗乙肝有效部位化学成分研究[J]. 广东药学院学报, 2009, 25(3): 242-244. CHEN L H, LI Z J, WANG D Y. Chemical constituents in the anti-HBV active fraction of Verbena officinalis[J]. Journal of Guangdong Pharmaceutical College, 2009, 25(3): 242-244. |
| [8] |
张玉雪.马鞭草的活性成分研究[D].上海: 上海交通大学, 2010. ZHANG Y X. Study on the active ingredients of Verbena officinalis[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 2010. |
| [9] |
张建业.马鞭草化学成分及红花指纹图谱的研究[D].郑州: 郑州大学, 2005. ZHANG J Y. Studies on chemical constituents of Verbena officinalis L. and Fingerprint Analysis of Flos Carthami[D]. Zhengzhou: Zhengzhou University, 2005. |
| [10] |
DEEPAK M, HANDA S S. Antiinflammatory activity and chemical composition of extracts of Verbena officinalis L.[J]. Phytotherapy Research, 2000, 14(6): 463-465. DOI:10.1002/1099-1573(200009)14:6<463::AID-PTR611>3.0.CO;2-G |
| [11] |
訾佳辰, 李玉山, 刘兴国, 等. 马鞭草化学成分的分离与鉴定[J]. 沈阳药科大学学报, 2005, 22(2): 105-109. ZI J C, LI Y S, LIU X G, et al. Isolation and identification of the chemical constituents of Verbena officinalis L[J]. Journal of Shenyang Pharmaceutical University, 2005, 22(2): 105-109. |
| [12] |
王华, 任非, 段坤峰, 等. 高效液相色谱-串联质谱法同时测定马鞭草中5种糖苷类成分的含量[J]. 现代中西医结合杂志, 2015, 24(3): 235-237, 241. WANG H, REN F, DUAN K F, et al. Simultaneous determination of five glycosides in Verbena officinalis L. by HPLC-MS/MS[J]. Modern Journal of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine, 2015, 24(3): 235-237, 241. |
| [13] |
张涛, 阮金兰, 吕子敏. 马鞭草环烯醚萜苷类成分的研究[J]. 中草药, 2000, 31(10): 721-723. ZHANG T, RUAN J L, LYU Z M. Studies on iridoid glucosides from Verbena officinalis[J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs, 2000, 31(10): 721-723. |
| [14] |
徐伟, 辛菲, 刘明, 等. 马鞭草裂环环烯醚萜苷类成分的分离与鉴定[J]. 沈阳药科大学学报, 2010, 27(10): 793-796. XU W, XIN F, LIU M, et al. Isolation and identification of chemical constituents of secoiridoid glycosides from the aerial parts of Verbena officinalis L[J]. Journal of Shenyang Pharmaceutical University, 2010, 27(10): 793-796. |
| [15] |
刘宏民, 鲍峰玉, 阎学斌. 马鞭草化学成分的研究[J]. 中草药, 2002, 33(6): 492-494. LIU H M, BAO Y F, YAN X B. Studies on chemical constituents of Verbena officinalis[J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs, 2002, 33(6): 492-494. |
| [16] |
田菁, 赵毅民, 栾新慧. 马鞭草的化学成分研究(Ⅱ)[J]. 天然产物研究与开发, 2007, 19(2): 247-249. TIAN J, ZHAO Y M, LUAN X H. Chemical constituents of Verbena officinalis L. (Ⅱ)[J]. Nature Product Research and Development, 2007, 19(2): 247-249. |
| [17] |
辛菲, 金艺淑, 沙沂, 等. 马鞭草化学成分研究[J]. 中国现代中药, 2008, 10(10): 21-23. XIN F, JIN Y S, SHA Y, et al. Study on the chemical constituents of Verbena officinalis[J]. Modern Chinese Medicine, 2008, 10(10): 21-23. |
| [18] |
王琳琳, 李寒冰, 苗明三. 马鞭草总苷对大鼠慢性非细菌性前列腺炎的干预作用[J]. 中国医药导报, 2016, 13(16): 4-7. WANG L L, LI H B, MIAO M S. Effect of total glucosides of Verbena officinalis L. on rat model for chronic nonbacterial prostatitis[J]. China Medical Herald, 2016, 13(16): 4-7. |
| [19] |
杨再波. 顶空萃取-气相色谱-质谱法分析马鞭草的挥发油组分[J]. 理化检验(化学分册), 2008, 44(6): 514-516. YANG Z B. Head-space extraction-GC/MS determination of chemical components of volatile oil from Verbena[J]. Physical Testing and Chemical Analysis (Part B:Chemical Analysis), 2008, 44(6): 514-516. |
| [20] |
张涛, 谢虹, 阮金兰. 马鞭草化学成分的分离与鉴定(Ⅰ)[J]. 武汉市职工医学院学报, 2000, 28(1): 27-29. ZHANG T, XIE H, RUAN J L. Separation and identification of the chemical constituents from the aerial parsts of Verbena officinalis L. (Ⅰ)[J]. Journal of Wuhan Medical College for Staff and Workers, 2000, 28(1): 27-29. |
| [21] |
訾佳辰.马鞭草的化学成分研究[D].沈阳: 沈阳药科大学, 2004. ZI J C. Studies on chemical constituents from whole plants of Verbena officinalis L.[D]. Shenyang: Shenyang Pharmaceutical University, 2004. |
| [22] |
HERNANDEZN E, TERESCHUK M L, ABDALA L R. Antimicrobial activity of flavonoids in medicinal plants from Tafidel Valle (Tucuman, Argentina)[J]. Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 2000, 73(1): 317-322. |
| [23] |
CASANOVA E, GARCíA J M, CALVO M I. Antioxidant and antifungal activity of Verbena officinalis L. leaves[J]. Plant Foods for Human Nutrition, 2008, 63(3): 93-97. DOI:10.1007/s11130-008-0073-0 |
| [24] |
DE M L, DE F V, FRATIANNI F, et al. Chemistry, antioxidant, antibacterial and antifungal activities of volatile oils and their components[J]. Natural Product Communications, 2009, 4(12): 1741-1750. |
| [25] |
钟有添, 王小丽, 辜宝祥. 中医药治疗病毒性乙型肝炎研究进展[J]. 赣南医学院学报, 2004, 26(2): 224-227. ZHONG Y T, WANG X L, GU B X. Research progress of traditional Chinese medicine in treatment of viral hepatitis B[J]. Journal of Gannan Medical University, 2004, 26(2): 224-227. |
| [26] |
李彦卿. 马鞭草治疗病毒性乙型肝炎[J]. 中医杂志, 2001, 42(7): 392. LI Y Q. Verbena in the treatment of viral hepatitis B[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2001, 42(7): 392. |
| [27] |
蓝正字. 马鞭草善治病毒性疱疹[J]. 中医杂志, 2001, 42(6): 13. LAN Z Y. Verbena is good at treating viral herpes[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2001, 42(6): 13. |
| [28] |
桂承会, 唐人九. 马鞭草镇咳有效成分的研究[J]. 中药通报, 1985, 10(10): 37. GUI C H, TANG R J. Study on the effective components of verbena for antitussive[J]. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica, 1985, 10(10): 37. |
| [29] |
任非, 袁志芳, 段坤峰, 等. 马鞭草提取物的镇咳、抗炎和祛痰作用研究[J]. 中国药房, 2013, 24(31): 13-16. REN F, YUAN Z F, DUAN K F, et al. Study on antitussive, anti-inflammatory and expectorant effects of the extracts from Verbena officinalis[J]. China Pharmacy, 2013, 24(31): 13-16. |
| [30] |
董映枢. 马鞭草能疗百日咳[J]. 中医杂志, 2001, 42(6): 13. DONG Y S. Verbena can treat whooping cough[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2001, 42(6): 13. |
| [31] |
谭文波, 李奉权. 马鞭草醇提液的抗炎作用与组胺、5-羟色胺的关系[J]. 中国医药指南, 2012, 10(9): 405-406. TAN W B, LI F Q. The relationship between the anti-inflammatory effect of verbena alcohol extract and histamine and 5-hydroxytryptamine[J]. Guide of China Medicine, 2012, 10(9): 405-406. |
| [32] |
杨水秀, 胡茶花, 陈晓亮, 等. 马鞭草防治放射性口腔炎的临床观察[J]. 现代肿瘤医学, 2013, 21(11): 2437-2438. YANG S X, HU C H, CHEN X L, et al. Clinical application of verbena to prevent and treat radioactive stomatitis[J]. Journal of Modern Oncology, 2013, 21(11): 2437-2438. |
| [33] |
周中山. 马鞭草汤治疗支原体肺炎临床观察[J]. 湖南中医学院学报, 2001, 21(1): 51. ZHOU Z S. Clinical observation on the treatment of mycoplasma pneumonia with Verbena Decoction[J]. Journal of Hunan College of Chinese Medicine, 2001, 21(1): 51. |
| [34] |
张允学, 吴东伟. 重用马鞭草善治慢性肾炎和慢性前列腺炎[J]. 中医临床研究, 2012, 4(19): 103. ZHANG Y X, WU D W. Treating chornic nephritis and chornic prostatitis with verbena[J]. Clinical Journal of Chinese Medicine, 2012, 4(19): 103. |
| [35] |
ELSABAA, HEBA M, ABDEL R, et al. Short-term effects of Verbena officinalis Linn decoction on patients suffering from chronic generalized gingivitis:Double-blind randomized controlled multicenter clinical trial[J]. Quintessence International, 2016, 47(6): 491-498. |
| [36] |
王振富. 马鞭草镇痛作用的实验研究[J]. 中国民族民间医药, 2009, 18(17): 35-36. WANG Z F. Study on analgesic effect of Verbena officinalis[J]. Chinese Journal of Ethnomedicine and Ethnopharmacy, 2009, 18(17): 35-36. |
| [37] |
王琳琳, 王灿, 苗明三. 马鞭草总苷对大鼠慢性非细菌性前列腺炎的影响及其抗炎、镇痛作用研究[J]. 中国药房, 2016, 27(19): 2608-2611. WANG L L, WANG C, MIAO M S. Effects of total glucosides of Verbena officinalis on chornic nonbacterial prostatitis in mice and its anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects study[J]. China Pharmacy, 2016, 27(19): 2608-2611. |
| [38] |
CALVO M I. Anti-inflammatory and analgesic activity of the topical preparation of Verbena officinalis L[J]. Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 2006, 107(3): 380-382. DOI:10.1016/j.jep.2006.03.037 |
| [39] |
王文佳, 王平, 俞琦, 等. 马鞭草醇提物免疫活性的初步研究[J]. 贵阳中医学院学报, 2008, 30(4): 17-18. WANG W J, WANG P, YU Q, et al. Preliminary study on the immune activity of Verbena ethanol extract[J]. Journal of Guiyang College of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2008, 30(4): 17-18. |
| [40] |
王文佳, 王平, 俞琦, 等. 马鞭草醇提物对小鼠IL-2生物活性的影响[J]. 甘肃中医学院学报, 2008, 25(4): 14-15. WANG W J, WANG P, YU Q, et al. The effects of alcohol extract from Verbena officinalis L. on biological activity of IL-2 in mice[J]. Journal of Gansu College of Chinese Medicine, 2008, 25(4): 14-15. |
| [41] |
眭书魁, 高建华, 马秀清, 等. 狼疮饮治疗系统性红斑狼疮的临床研究[J]. 河北中医, 2000, 22(2): 85-89. XU S K, GAO J H, MA X Q, et al. Clinical research on Langchuang Yin for the treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus[J]. Hebei Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2000, 22(2): 85-89. |
| [42] |
刘玉琴. 中西医结合治疗女性免疫性不孕645例效果分析[J]. 中原医刊, 2004, 34(18): 32-33. LIU Y Q. Analysis of the effect of integrated traditional Chinese and western medicine on 645 cases of female immune infertility[J]. Chinese Journal of Practical Medicine, 2004, 34(18): 32-33. |
| [43] |
徐珊, 焦中秀, 徐小晶, 等. 马鞭草醇提液对绒毛膜癌JAR细胞增殖及表皮生长因子受体表达的影响[J]. 中国药科大学学报, 2000, 45(4): 43-46. XU S, JIAO Z X, XU X J, et al. Effects of alcohol extract of Verbena officinalis on Proli-feration and EGFR expression of choriocarcinoma JAR cells[J]. Journal of China Pharmaceutical University, 2000, 45(4): 43-46. |
| [44] |
徐昌芬, 曾群, 徐珊, 等. 马鞭草醇提液中有效部位的提取及筛选[J]. 交通医学, 2003, 17(5): 604. XU C F, ZENG Q, XU S, et al. Extraction and screening of effective parts in Verbena alcohol extract[J]. Medical Journal of Communications, 2003, 17(5): 604. |
| [45] |
张立平, 徐昌芬. 马鞭草诱导人绒毛膜癌JAR细胞凋亡作用观察[J]. 现代预防医学, 2009, 36(8): 1523-1527. ZHANG L P, XU C F. Observation on the inhibition effect of Verbena officinalis on human choriocarcinoma JAR cells[J]. Modern Preventive Medicine, 2009, 36(8): 1523-1527. |
| [46] |
王家俊, 罗莉, 张立平, 等. 马鞭草C部位对人绒癌JAR细胞hCG分泌的影响和作用机制[J]. 中国药科大学学报, 2004, 61(6): 88-91. WANG J J, LUO L, ZHANG L P, et al. Effect of Verbena officinals on inhibiting secretion of hCG and intriguring apoptosis of JAR cell[J]. Journal of China Pharmaceutical University, 2004, 61(6): 88-91. |
| [47] |
王家俊, 罗莉, 张立平, 等. 马鞭草C部位使人绒癌JAR细胞阻滞于G2/M期并诱导细胞凋亡[J]. 南京医科大学学报(自然科学版), 2004, 49(6): 49-52. WANG J J, LUO L, ZHANG L P, et al. Blockage in G2/M phase and induction apoptosis on human choriocarcinoma JAR cells by Verbena officinals C[J]. Journal of Nanjing Medical University (Natural Science), 2004, 49(6): 49-52. |
| [48] |
杨最素, 冯播, 徐昌芬. 4'-甲醚-黄芩素对绒毛膜癌JAR细胞c-myc表达的影响[J]. 中药新药与临床药理, 2011, 22(5): 501-505. YANG Z S, FENG B, XU C F. Effect of 4'-Methery-scutellarein on c-myc Expression in Human Choriocarcinoma JAR Cells[J]. Traditional Chinese Drug Research and Clinical Pharmacology, 2011, 22(5): 501-505. |
| [49] |
杨最素, 冯播, 徐昌芬. 4'-甲醚-黄芩素诱导人绒毛膜癌细胞凋亡的信号转导机理研究[J]. 中药药理与临床, 2011, 27(5): 20-23. YANG Z S, FENG B, XU C F. The signal transduction mechanism of induced apoptotic effects of 4'-methylether-scutellarein on human choriocarcinoma cells[J]. Pharmacology and Clinics of Chinese Materia Medica, 2011, 27(5): 20-23. |
| [50] |
李卓, 朱利群, 张燕, 等. 4'-甲醚-黄芩素对耐药性人绒毛膜癌的耐药逆转作用[J]. 中国肿瘤生物治疗杂志, 2016, 23(2): 182-187. LI Z, ZHU L Q, ZHANG Y, et al. Reversal effect of 4'-methylether-scutellarein on multidrug resistance of human choriocarcinoma[J]. Chinese Journal of Cancer Biotherapy, 2016, 23(2): 182-187. |
| [51] |
任丽平, 李先佳, 朱宝安. 马鞭草总黄酮对HepG-2细胞增殖及侵袭力影响[J]. 中国公共卫生, 2016, 32(7): 935-937. REN L P, LI X J, ZHU B A. Impact of total flavonoids of Verbena officinalis L. on proliferation and invasiveness of human hepatocellular carcinoma HepG-2 cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Public Health, 2016, 32(7): 935-937. |
| [52] |
李永明, 李先佳. 马鞭草总黄酮对肝癌HepG-2细胞IL-6、JAK2、STAT3水平的影响[J]. 河南科技大学学报(医学版), 2017, 35(3): 169-171. LI Y M, LI X J. Effect of total flavonoids of Verbena officinalis on IL-6, JAK2, STAT3 level of human hepatocellular carcinoma HepG-2 cells[J]. Journal of Henan University of Science and Technology (Medical Edition), 2017, 35(3): 169-171. |
| [53] |
李先佳, 任丽平, 金少举. 马鞭草总黄酮靶向拓扑异构酶Ⅱ诱导肝癌HepG-2细胞凋亡[J]. 中国药理学通报, 2017, 33(8): 1147-1152. LI X J, REN L P, JIN S J. Apoptosis of human hepatocellular carcinoma HepG-2 cells induced by total flavonoids of Verbena officinalis L. through targeting topoisomerase Ⅱ[J]. Chinese Pharmacological Bulletin, 2017, 33(8): 1147-1152. |
| [54] |
李先佳, 任丽平, 金少举. 马鞭草总黄酮诱导肝癌HepG-2细胞凋亡及可能机制[J]. 国际药学研究杂志, 2017, 44(8): 790-794. LI X J, REN L P, JIN S J. Apoptosis of HepG-2 cells induced by total flavonoids of Verbena officinalis L. and possible mechanism[J]. Journal of International Pharmaceutical Research, 2017, 44(8): 790-794. |
| [55] |
曹志然, 王蓓, 戎瑞雪, 等. 马鞭草水提取物对荷瘤小鼠抑瘤作用及免疫功能影响[J]. 军医进修学院学报, 2009, 30(4): 545-546. CAO Z R, WANG B, RONG R X, et al. Effect of wate extract from verbena on tumor and immunological function of tumor-bearing mice[J]. Academic Journal of Chinese PLA Medical School, 2009, 30(4): 545-546. |
| [56] |
KOU W Z, YANG J, YANG Q H, et al. Study on in-vivo anti-tumor activity of Verbena officinalis extract[J]. African Journal of Traditional, Complementary and Alternative Medicines, 2013, 10(3): 512-517. |
| [57] |
李小龙, 曹志然. 马鞭草对肝癌小鼠抑瘤作用及IL-2生物活性的影响[J]. 河北医药, 2011, 33(2): 234-235. LI X L, CAO Z R. Effect of Verbena on tumor inhibition and IL-2 biological activity of hepatocarcinoma mice influences[J]. Hebei Medical Journal, 2011, 33(2): 234-235. |
| [58] |
ENCALADA M A, REHECHO S, ANSORENA D, et al. Antiproliferative effect of phenylethanoid glycosides from Verbena officinalis L. on colon cancer cell lines[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology, 2015, 63(2): 1016-1022. |
| [59] |
郭殷锐, 李沁莹, 张广唱, 等. 马鞭草经皮透过液对B16黑色素瘤细胞的作用[J]. 中药新药与临床药理, 2016, 27(1): 19-22. GUO Y R, LI Q Y, ZHANG G C, et al. Effect of herba Verbena percutaneous fluid on B16 melanoma cells[J]. Traditional Chinese Drug Research and Clinical Pharmacology, 2016, 27(1): 19-22. |
| [60] |
徐华娥, 袁红宇, 欧宁. 马鞭草醇提液小剂量时能显著增加紫杉醇的抗肿瘤活性[J]. 南京医科大学学报(自然科学版), 2008, 53(10): 1275-1278. XU H E, YUAN H Y, OU N. Synergistic anti-tumor effect of alcohol extract of Verbena officinalis and paclitaxel[J]. Journal of Nanjing Medical University (Natural Science), 2008, 53(10): 1275-1278. |
| [61] |
徐昌芬, 卢小东, 周亚东, 等. 人早孕绒毛滋养层细胞的分离纯化及马鞭草抗早孕机理的初步研究[J]. 解剖学杂志, 1999(2): 137-140. XU C F, LU X D, ZHOU Y D, et al. Trophoblast cells isolated from human villi of early pregnancy and study on mechanism of abortifacient effect by verbena officinalis[J]. Chinese Journal of Anatomy, 1999(2): 137-140. |
| [62] |
卢小东, 焦中秀, 徐昌芬. 马鞭草醇提液对滋养层细胞SDH抑制作用的研究[J]. 江苏中医药, 2001, 46(5): 44. LU X D, JIAO Z X, XU C F. Study on the inhibitory effect of verbena extract on SDH of trophoblast cells[J]. Jiangsu Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2001, 46(5): 44. |
| [63] |
欧宁, 王海琦, 袁红宇, 等. 马鞭草抗早孕作用的动物实验研究[J]. 中国药科大学学报, 1999, 43(3): 49-51. OU N, WANG H Q, YUAN H Y, et al. The animal study of Verbena officinalis on anti-early-pregnancy[J]. Journal of China Pharmaceutical University, 1999, 43(3): 49-51. |
| [64] |
张曙萱, 王海琦, 欧宁. 马鞭草提取液对体外培养人早孕蜕膜细胞的影响[J]. 中国天然药物, 2004, 2(4): 52-56. ZHANG S X, WANG H Q, OU N. Studies on the effect of Verbena offcinalis extract on decidual stromal cells of early pregnancy in vitro[J]. Chinese Journal of Natural Medicines, 2004, 2(4): 52-56. |
| [65] |
张涛, 李万, 阮金兰. 马鞭草化学成分对大鼠离体子宫平滑肌条作用的研究[J]. 中国中医药科技, 2001, 8(5): 313. ZHANG T, LI W, RUAN J L. Study on the effect of the chemical constituents of verbena on the isolated rat uterine smooth muscle strips[J]. Chinese Journal of Traditional Medical Science and Technology, 2001, 8(5): 313. |
| [66] |
刘佳, 张大方, 李丽静, 等.马鞭草不同提取物对小鼠中枢神经系统作用的初步探讨[A].中华中医药学会中药实验药理分会第八届学术会议论文摘要汇编[C].2009. LIU J, ZHANG D F, LI L J, et al. Preliminary study on the effects of different extracts of verbena on the central nervous system of mice[A]. Compilation of abstracts of the eighth academic conference of the Chinese Medicine Experimental Pharmacology Branch of the Chinese Society of Chinese Medicine[C]. 2009. |
| [67] |
谭文波, 谭刚. 马鞭草醇提液对大鼠局灶性缺血再灌注后脑水肿的影响[J]. 中国老年学, 2013, 33(12): 2815-2817. TAN W B, TAN G. Effect of Verbena officinalis alcohol extract on brain edema after focal ischemia-reperfusion in rats[J]. Chinese Journal of Gerontology, 2013, 33(12): 2815-2817. |
| [68] |
LAI S, YU M, YUEN W, et al. Novel neuroprotective effects of the aqueous extracts from Verbena officinalis Linn[J]. Neuropharmacology, 2006, 50(6): 641-650. DOI:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2005.11.009 |
| [69] |
汤树良. 马鞭草中促进神经生长因子介导的轴突生长的新成分littorachalcone[J]. 国外医学(中医中药分册), 2004, 27(3): 176-177. TANG S L. Litorachalcone, a new component of Verbena officinalis, which promotes nerve growth factor mediated axonal growth[J]. International Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2004, 27(3): 176-177. |
| [70] |
WAHEED K A, ARIF-ULLAK K, TOUQEER A. Anticonvulsant, anxiolytic, and sedative activities of Verbena officinalis[J]. Frontiers in Pharmacology, 2016, 7: 499. |
| [71] |
RASHIDIAN A, KAZEMI F, MEHRZADI S, et al. Anticonvulsant effects of aerial parts of Verbena officinalis extract in mice:involvement of benzodiazepine and opioid receptors[J]. Journal of Evidence-Based Integrative Medicine, 2017, 22(4): 632-636. |
| [72] |
SISAY M, BUSSA N, GASHAW T. Evaluation of the antispasmodic and antisecretory activities of the 80% methanol extracts of Verbena officinalis Linn:Evidence from in-vivo antidiarrheal study[J]. Journal of Evidence-Based Integrative Medicine, 2019, 24(1): 1-9. |
| [73] |
许建安. 马鞭草对(60)Co照射小鼠保护作用的研究[J]. 医学信息(上旬刊), 2011, 24(5): 2550-2552. XU J A. Research on the radio protective effect of Verbena on (60)Co-irradiated mice[J]. Medical Information, 2011, 24(5): 2550-2552. |
| [74] |
高涵, 任梦瑶, 汪莎莎, 等. 马鞭草中多酚类物质的提取及抗氧化活性检测[J]. 现代食品, 2018, 34(18): 125-128. GAO H, REN M Y, WANG S S, et al. Extraction and antioxidation of polyphenol from Verbena[J]. Modern food, 2018, 34(18): 125-128. |
| [75] |
宋兆华, 朱宝安. 马鞭草总黄酮对大鼠脓毒性急性肺损伤的保护机制[J]. 医药导报, 2014, 33(4): 429-433. SONG Z H, ZHU B A. Protection mechanism of the total flavonoids from Verbena on rats with septic acute lung injury[J]. Herald of Medicine, 2014, 33(4): 429-433. |
| [76] |
王海燕, 杨静. 马鞭草提取液抑制鼠草酸钙结石形成的实验研究[J]. 四川中医, 2011, 29(7): 58-59. WANG H Y, YANG J. Experimental study on Verbena extract inhibiting the formation of calcium murinate stone[J]. Journal of Sichuan of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2011, 29(7): 58-59. |
| [77] |
韦耀力, 胡俊杰. 重用马鞭草治疗泌尿系结石124例[J]. 中国中医急症, 2010, 19(11): 1971-1972. WEI Y L, HU J J. Treatment of 124 cases of urinary calculi with Verbena[J]. Journal of Emergency in Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2010, 19(11): 1971-1972. |
| [78] |
王月秋. 马鞭草治疗乳痈30例[J]. 中国民间疗法, 2009, 17(11): 71. WANG Y Q. Treating 30 cases of mammary carbuncle with Verbena[J]. China's Naturopathy, 2009, 17(11): 71. |
| [79] |
巩翠玉. 复方马鞭草汤治疗围绝经期功血的临床疗效探讨[J]. 中国社区医师(医学专业), 2012, 14(26): 195-196. GONG C Y. Study on the clinical effect of Fufang Mabiancao Decoction on perimenopausal uterine bleeding[J]. Chinese Community Doctors, 2012, 14(26): 195-196. |
| [80] |
常开诚. 马鞭草治疗热证哮喘[J]. 中医杂志, 2001, 42(7): 392. CHANG K C. Verbena officinalis in the treatment of febrile asthma[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2001, 42(7): 392. |
| [81] |
FATEHA A H, MOHAMEDA Z, CHIKA Z, et al. Prenatal developmental toxicity evaluation of Verbena officinalis during gestation period in female Sprague-Dawley rats[J]. Chemico-Biological Interactions, 2019, 304: 28-42. DOI:10.1016/j.cbi.2019.02.016 |
| [82] |
FATEHA A H, MOHAMEDA Z, CHIKA Z, et al. Mutagenicity and genotoxicity effects of verbena officinalis leaves extract in Sprague-Dawley rats[J]. Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 2019, 235: 88-99. DOI:10.1016/j.jep.2019.02.007 |
| [83] |
索涛, 范慧, 陈国忠. 病毒性肺炎治疗的研究进展[J]. 武汉大学学报(医学版), 2020, 41(3): 378-383. SUO T, FAN H, CHEN G Z. Advances in the treatment of viral pneumonia[J]. Medical Journal of Wuhan University, 2020, 41(3): 378-383. |
 2020, Vol. 37
2020, Vol. 37