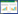文章信息
- 李国峰, 李祎
- LI Guofeng, LI Yi
- 六君子汤加减治疗稳定期慢性阻塞性肺疾病肺脾两虚证的Meta分析
- Meta-analysisof addition and subtraction of Liujunzi Decoction in the treatment of stable lung and spleen deficiency syndrome of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- 天津中医药, 2021, 38(10): 1305-1311
- Tianjin Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2021, 38(10): 1305-1311
- http://dx.doi.org/10.11656/j.issn.1672-1519.2021.10.17
-
文章历史
- 收稿日期: 2021-06-20
慢性阻塞性肺疾病(COPD)是一种以气道和肺实质慢性炎症引起的进行性气流受限为特征的疾病[1],它已成为21世纪的一个主要公共卫生问题。由于疾病频繁恶化和住院的风险增加,给患者和国家带来了巨大的经济负担[2-3]。按照世界卫生组织和慢性阻塞性肺疾病全球倡议组织(GOLD)的建议,药物疗法和非药物疗法经常被用来治疗COPD[4]。然而,这些疗法是否能抑制这种疾病的进展仍不清楚。因此,预防COPD发展的治疗方案是至关重要的。COPD属于中医“肺胀”的范畴[5],肺主气,主管全身之气与生成宗气。肺气虚可影响宗气生成,宗气减退是全身气虚的根本,可导致一身诸气均虚,故肺气虚日久,子病及母,可直接致脾气虚。脾气虚弱,谷气生成减少,影响宗气生成而致肺气虚,故肺虚、脾虚可相互影响,最终可致肺脾两虚证。在中国,许多传统的中药经常用于治疗COPD。多项临床试验[6-8]表明,中医药对COPD患者具有改善症状、改善生命质量、改善肺功能的作用。中国的经典方剂六君子汤能治疗肺脾两虚证,特别是在稳定期肺脾两虚型COPD具有很好的优势[9-11]。然而,这些试验的样本、用药频次、疗程不一,不利于当前的实践和指导制定新的治疗方案。因此,本研究就六君子汤加减治疗稳定期COPD肺脾两虚证的随机对照试验进行Meta分析,评价有效性及安全性,为临床提供参考依据。
1 资料与方法 1.1 检索策略计算机检索PubMed、Embase、Cochrane图书馆、中国知网、万方、维普、中国生物医学数据库,搜集六君子汤加减治疗稳定期COPD肺脾两虚证的随机对照试验,时间限定为建库至2019年3月。中文检索词为COPD、慢阻肺、慢性阻塞性肺疾病、六君子汤。英文检索词为COPD、Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease、COAD、Chronic Obstructive Airway Disease、Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease、Airflow Obstruction,Chronic、Airflow Obstructions,Chronic、Chronic Airflow Obstructions、Chronic Airflow Obstruction、liujunzi tang。
1.2 纳入标准1)研究类型:随机对照试验。2)研究对象:符合《慢性阻塞性肺疾病诊治指南(2013年修订版)》[12]的COPD诊断标准,COPD肺脾两虚证符合《中药新药临床研究指导原则》[13]及《中医虚证辨证参考标准》[14]。3)干预措施:对照组采用常规西医治疗方案,包括吸氧、茶碱制剂、糖皮质激素、支气管扩张剂、祛痰剂和抗生素等;试验组采用六君子汤加减+常规西医治疗方案。4)结局指标:①总有效率,参照《中药新药临床研究指导原则》[13]标准;②肺功能,包括用力肺活量(FVC)、第一秒用力呼气容积(FEV1)、第一秒用力呼气量占所有呼气量的比例(FEV1/FVC);③动脉血气分析,包括血氧饱和度(SaO2)、动脉血二氧化碳分压(PaCO2)、动脉血氧分压(PaO2);④中医症状积分,包括咳嗽、咳痰、气短、食少、腹胀;⑤运动耐力,采用6 min步行距离(6mWD);⑥体重指数(BMI);⑦呼吸困难量表(MMRC)。
1.3 排除标准1)综述。2)重复发表的文献。3)动物实验。4)数据无法提取。5)干预合并措施其他疗法。
1.4 资料提取文章数据由两名评作者独立使用EpiData 3.1进行录入。录入数据包括第一作者或信息提供者、出版日期、研究设计、样本量、干预方法、年龄、结局指标和疗程。
1.5 方法学质量评价Cochrane系统评价手册推荐的风险偏倚工具进行方法学质量评价。主要条目有:1)随机化方案。2)分组隐匿。3)盲法。4)不完全数据报告。5)选择性结局报告。6)其他偏倚来源。
1.6 统计学分析RevMan 5.3进行Meta分析。连续变量和二分类变量分别采用标准化均数差(SMD)和比值比(OR)及95%置信区间(CI)表示。采用χ2检验进行异质性检验,当P > 0.1和I2 < 50%时,研究之间没有统计学异质性,采用固定效应模型进行分析;若P < 0.1,I2 > 50%,则采用随机效应模型进行分析。如果研究之间存在显着的临床异质性,不进行合并,采用描述性分析。
2 结果 2.1 文献检索结果从相关数据库中获得文献261篇,Endnote去除重复文献90篇,然后阅读题目和摘要排除不相符文献篇,分别综述2篇、重复发表1篇、与主题不符合136篇、动物实验12篇;最后通过全文阅读,排除干预措施不符合2篇、研究对象不符合6篇、数据无法提取2篇,最终纳入文献10篇[9-11, 15-21]。文献筛选流程图详见图 1。
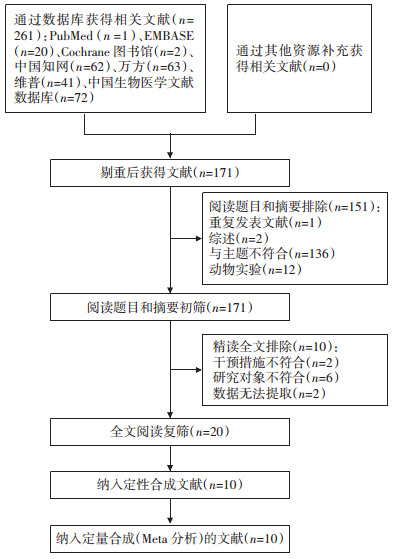
|
| 图 1 文献筛选流程图 Fig. 1 Literature screening and outcome |
纳入10篇文献[9-11, 15-21],共870例,其中试验组435例,对照组435例。样本量为60~112例。疗程为1周~3个月。对照组干预措施为常规西医治疗,试验组为六君子汤加减+常规西医治疗。见表 1。
纳入研究方法学质量评价结果。3项研究[9-10, 16]采用了正确的随机方法,7项研究[11, 15, 17-21]提及随机,但未明确何种随机方法。所有研究未报告分配隐匿。1项研究[10]对研究者和研究对象实施了盲法,其余未报告盲法。所有研究数据完整,无其他偏倚来源。2项研究[17, 19]数据完整性存在高风险偏倚。见图 2。
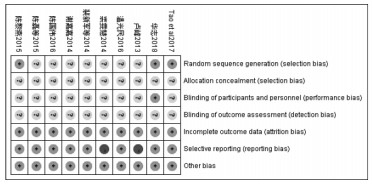
|
| 图 2 偏倚风险汇总图 Fig. 2 Risk of bias summary |
9篇文献[9-11, 15-18, 20-21]对总有效率进行了评价,无异质性(I2=0%,P=0.49),固定效应模型进行合并。结果提示与常规西药相比,六君子汤加减可提高稳定期COPD肺脾两虚证的总有效率[OR=3.10,95%CI(2.13,4.51),P < 0.000 01],差异有统计学意义。见图 3。
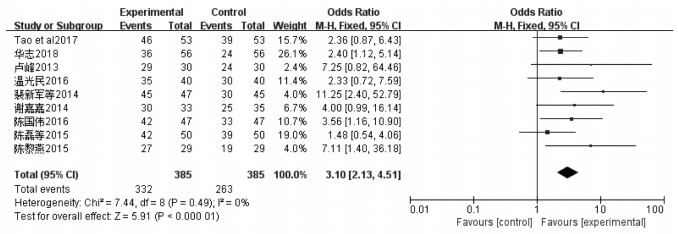
|
| 图 3 总有效率森林图 Fig. 3 Forest graph of Meta-analysis on the total effective rate |
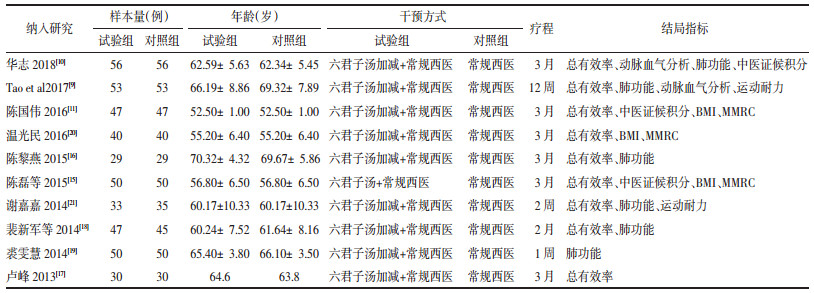
3篇文献[9-10, 19]比较了治疗前后FVC,6篇文献[9-10, 16-18, 19, 21]比较了治疗前后FEV1,5篇文献[9-10, 16, 18-19]比较了治疗前后FEV1 /FVC。结果提示六君子汤加减能改善稳定期COPD肺脾两虚证的部分肺功能指标FEV1[SMD=0.73,95%CI(0.29,1.18),P=0.001]、FEV1 /FVC[SMD=0.75,95%CI(0.41,1.09),P < 0.000 1];但FVC差异无统计学意义[SMD=0.28,95%CI(-0.24,0.81),P=0.27]。见表 2。
2篇文献[9-10]比较了治疗前后动脉血气分析指标。结果提示六君子汤加减能改善稳定期COPD肺脾两虚证的部分动脉血气分析指标SaO2 [SMD=0.94,95%CI(0.21,1.67),P=0.01]、PaCO2 [SMD=-1.71,95%CI(-2.02,-1.40),P < 0.000 01];但PaO2,差异无统计学意义[SMD=2.71,95%CI(-0.44,5.86),P=0.09]。见表 2。
2.4.4 中医症状积分3篇文献[10-11, 15]比较了治疗前后咳嗽证候积分,3篇文献[10-11, 15]比较了治疗前后咳痰证候积分,2篇文献[11, 15]比较了治疗前后气短症状积分,2篇文献[11, 15]比较了治疗前后食少症状积分,2篇文献[11, 15]比较了治疗前后腹胀症状积分。结果提示六君子汤加减能改善稳定期COPD肺脾两虚证的中医症状积分,包括咳嗽[SMD=-1.16,95% CI(-1.76,-0.55),P=0.000 2]、咳痰[SMD=-0.80,95%CI(-1.48,-0.13),P=0.02]、气短[SMD=-0.43,95%CI(-0.71,-0.14),P=0.003]、食少[SMD=-1.00,95%CI(-1.30,-0.70),P < 0.000 01]、腹胀[SMD=-1.09,95%CI(-1.39,-0.79),P < 0.000 01])。见表 2。
2.4.5 运动耐力2篇文献[9, 21]比较了治疗前后运动耐力的情况。结果提示六君子汤加减能提高稳定期COPD肺脾两虚证的运动耐力[SMD=0.94,95%CI(0.10,1.77),P=0.03]。见表 2。
2.4.6 BMI3篇文献[11, 15, 20]比较了治疗前后BMI的情况。结果提示两组差异无统计学意义[SMD=-0.41,95%CI(-1.37,0.55),P=0.41]。见表 2。
2.4.7 MMRC3篇文献[11, 15, 20]比较了治疗前后MMRC的情况。结果提示六君子汤加减能改善稳定期COPD肺脾两虚证的MMRC[SMD=-0.58,95%CI(-0.82,-0.34),P < 0.000 01]。见表 2。
2.4.8 不良反应10篇文献[9-11, 15-21]中未出现严重不良反应;1篇文献[9]提及试验组1例腹胀,2例皮疹,1例氨基转移酶升高;对照组1例胃部不适,2例头晕,2例腹胀;对症处理后没有影响正常治疗。
3 讨论本次Meta分析纳入文献为六君子汤加减+常规西医治疗对比常规西医治疗COPD稳定期肺脾两虚证随机对照试验。纳入文献患者的临床证候均为肺脾两虚证。本方以《医学正传》中的六君子汤为主,在《太平惠民和剂局方》中四君子汤的基础上加半夏、陈皮组成。其主要成分为党参、白术、茯苓、炙甘草、陈皮、半夏,具有益气健脾、燥湿化痰的作用。现代药理学证实党参能增强机体免疫力提高机体的抗应激和抗缺氧作用[22]。白术通过刺激机体的免疫系统,而起到抵抗疾病的作用[23]。茯苓能增强肿瘤坏死因子和自然杀伤细胞的活性,提高细胞免疫功能,且具有抑制慢性炎症的作用[24]。甘草具有抗过敏之效,保护发炎的气管黏膜等作用[25]。半夏中的总生物碱可以起到抵抗炎症的作用[26]。陈皮有扩张支气管及止咳平喘的作用,同时能促进消化酶的分泌,缓解胃肠内积气,调节胃肠功能,增强食欲[27];此外,陈皮提取物具有增强机体免疫,抗疲劳和对抗老化的作用[28-29]。因此,从六君子汤的主要成分进行的现代药理学分析结果进行推断,纳入的10篇文献的结果可信度较好。
在较长时间里,戒烟可以降低COPD病死率和FEV1下降率,是唯一影响COPD发展的方法。然而,对COPD的药物治疗在过去10年中有了很大的改进。吸入性糖皮质激素、吸入皮质类固醇激素、长效β受体激动剂、短效β受体激动剂、长效抗胆碱能、毒蕈碱类拮抗剂的利用使这些患者的预后比以前有了显著的改善。近年来,中医药治疗COPD的研究不断涌现,为这一问题提供了新的方案。本研究综合了六君子汤加减治疗COPD的最新证据。与传统西药治疗相比,六君子汤加减+常规西医可提高COPD的治疗效果,改善预后。
COPD的患者可能会出现咳嗽、呼吸困难、胸闷的症状[30-33]。慢性咳嗽、痰等的产生和FEV1已被证明与COPD频繁加重和住院的风险增加独立相关[34-35]。FEV1、FVC及FEV1/FVC是评价肺功能的重要指标。FEV1下降说明患者肺功能不佳;FEV1上升说明COPD肺功能有所改善;但单纯评价FEV1不能准确地评价患者肺部舒张后的反应。因此,采用FEV1、FVC及FEV1 /FVC更为准确的进行肺功能评价。本研究显示与单纯西医治疗相比,六君子汤加减+常规西医治疗改善COPD稳定期肺脾两虚证的肺功能指标,这与Tao等[9]研究结果一致。另外,患者咳嗽、咳痰、气短等中医证候积分明显得到了改善。此外,呼吸困难是患者COPD的症状之一,本次Meta分析评价了患者的呼吸困难指数,结果提示六君子汤加减+常规西医治疗能改善COPD的呼吸困难指数。六君子汤加减+常规西医治疗对肺功能的改善具有积极的意义和应用前景。同时,对运动耐力也有较好的促进作用。
Tao等[9]报告了不良反应,试验组1例腹胀,2例皮疹,1例氨基转移酶升高;对照组1例胃部不适,2例头晕,2例腹胀,对症处理后没有影响正常治疗;在这些试验中没有发生明显的不良事件。然而,由于符合条件的试验提供证据有限,不能从本次研究中确定具体的安全性结论,为了正确评估六君子汤的安全性,需要进行大规模的长期随访临床试验。
本研究存在一定局限性。首先,纳入文献方法学存在不同程度的偏倚,随机、分配隐匿及盲法不完善。部分研究样本量小,可能存在假阳性。同时,每个研究疗程不统一,随访时间短,不足以判断药物的远期疗效及安全性。其次,英文期刊上发表的六君子汤治疗COPD的相关文章较少,本研究仅检索到1篇,对在中国以外地区的评价有限,影响了六君子汤治疗COPD的外部有效性。
| [1] |
VESTBO J. COPD: definition and phenotypes[J]. Clinics in Chest Medicine, 2014, 35(1): 1-6. DOI:10.1016/j.ccm.2013.10.010 |
| [2] |
LOPEZ C J L, TAN W, SORIAN J B. Global burden of COPD[J]. Respirology, 2016, 21(1): 14-23. DOI:10.1111/resp.12660 |
| [3] |
CHAN K Y, LI X, CHEN W, et al. Prevalence of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) in China in 1990 and 2010[J]. Journal of Global Health, 2017, 7(2): 020704. DOI:10.7189/jogh.07.020704 |
| [4] |
YANGGE T, YA L, JIAN L, et al. Bufei Yishen Granules combined with acupoint sticking therapy suppress inflammation in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease rats: Via JNK/p38 signaling pathway[J]. Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine, 2017, 2017: 1-10. |
| [5] |
TIAN Y, LI Y, LI J. Bufei Yishen Granule combined with acupoint sticking improves pulmonary function and morphormetryin chronic obstructive pulmonary disease rats[J]. BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine, 2015, 15(1): 266. DOI:10.1186/s12906-015-0787-0 |
| [6] |
LI J S, LI S Y, YU X Q, et al. Bu-Fei Yi-Shen Granule combined with acupoint sticking therapy in patients with stable chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a randomized, double-blind, double-dummy, active-controlled, 4-center study[J]. Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 2012, 141(2): 584-591. DOI:10.1016/j.jep.2011.08.060 |
| [7] |
XIE Y, LI J S, YU X Q, et al. Effectiveness of Bufei Yishen Granule combined with acupoint sticking therapy on quality of life in patients with stable chronic obstructive pulmonary disease[J]. Chinese Journal of Integrative Medicine, 2013, 19(4): 260-268. DOI:10.1007/s11655-013-1438-2 |
| [8] |
LI S Y, LI J S, WANG M H, et al. Effects of comprehensive therapy based on traditional Chinese medicine patterns in stable chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a four-center, open-label, randomized, controlled study[J]. BMC Complementary & Alternative Medicine, 2012, 12(1): 197-197. |
| [9] |
TAO Y J, LIU X Y, QIU H, et al. Clinical efficacy of Liujunzi Decoction and its effect on lung function, exercise tolerance and blood gas analysis in COPD patients with symptoms of lung and spleen deficiency at stable stage[J]. Chinese Journal of Experimental Traditional Medical Formulae, 2017(22): 179-184. |
| [10] |
华志. 六君子汤治疗稳定期慢性阻塞性肺病肺脾两虚证的疗效及其对肺功能和血气分析的影响[J]. 河北医学, 2018, 24(12): 2098-2102. HUA Z. Effect of Liujunzi Decoction on lung and spleen deficiency syndrome in stable chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and its influence on lung function and blood gas analysis[J]. Hebei Medicine, 2018, 24(12): 2098-2102. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-6233.2018.12.042 |
| [11] |
陈国伟. 六君子汤联合西药治疗慢性阻塞性肺疾病稳定期临床研究[J]. 新中医, 2016, 48(12): 36-37. CHEN G W. Clinical study of Liujunzi Decoction combined with Western medicine in the treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease at stable period[J]. Journal of New Chinese Medicine, 2016, 48(12): 36-37. |
| [12] |
中华医学会呼吸病学分会慢性阻塞性肺疾病学组. 慢性阻塞性肺疾病诊治指南(2013年修订版)[J]. 中华结核和呼吸杂志, 2014, 36(2): 255-264. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Committee, Respiratory Society, Chinese Medical Association. Guidelines for diagnosis and treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (revised 2013)[J]. Chinese Journal of Tuberculosis and Respiratory Diseases, 2014, 36(2): 255-264. |
| [13] |
中华人民共和国卫生部. 中药新药临床研究指导原则[M]. 北京: 中国医药科技出版社, 2002: 54. Chinese Ministry of Health. Guiding principles of clinical research on new drugs of Chinese medicines[M]. Beijing: China Medical Science Press, 2002: 54. |
| [14] |
沈自尹, 王文健. 中医虚证辨证参考标准[J]. 中国中西医结合杂志, 1986, 6(10): 598-598. SHEN Z Y, WANG W J. Reference standard for syndrome differentiation of deficiency syndrome in traditional Chinese medicine[J]. Chinese Journal of Integrated Traditional and Western Medicine, 1986, 6(10): 598-598. |
| [15] |
陈磊, 张国龙, 陈敏, 等. 六君子汤治疗慢性阻塞性肺疾病稳定期肺脾两虚证的疗效观察[J]. 中医药导报, 2015, 21(2): 79-81. CHEN L, ZHANG G L, CHEN M, et al. Observation on therapeutic effect of Liujunzi Decoration on lung and spleen deficiency syndrome in stable stage of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease[J]. Guiding Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine and Pharmacy, 2015, 21(2): 79-81. |
| [16] |
陈黎燕, 徐武成, 葛敏捷. 六君子汤加减治疗慢性阻塞性肺疾病的疗效观察[J]. 中国生化药物杂志, 2015, 35(5): 140-142. CHEN L Y, XU W C, GE M J. Clinical efficacy of additive Liujunzi Decoration in treatment of chronic obstructive pneumonia[J]. Chinese Journal of Biochemical and Pharmaceutics, 2015, 35(5): 140-142. |
| [17] |
卢峰, 王世聪. 六君子汤对慢性阻塞性肺疾病患者内源性抗炎机制影响[J]. 辽宁中医药大学学报, 2013, 15(7): 161-163. LU F, WANG S C. Influence of Liujunzi Decoction on endogenous anti-inflammatory mechanisms in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease[J]. Journal of Liao Ning University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2013, 15(7): 161-163. |
| [18] |
裴新军, 陆云霞, 张连东, 等. 六君子汤加减治疗慢性阻塞性肺疾病稳定期患者呼吸肌疲劳临床观察[J]. 新中医, 2014, 46(11): 59-61. PEI X J, LU Y X, ZHANG L D, et al. Clinical observation of modified Liujunzi Decoration for respiratory muscle fatigue of stable phase patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease[J]. Journal of New Chinese Medicine, 2014, 46(11): 59-61. |
| [19] |
裘雯慧, 王洲峰. 六君子汤加味治疗肺脾气虚型慢性阻塞性肺疾病稳定期疗效观察[J]. 新中医, 2014, 46(11): 71-73. PEI W H, WANG Z F. Observation on therapeutic effect of modified Liujunzi Decoction on stable stage of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease with deficiency of lung-qi and spleen-qi[J]. Journal of New Chinese Medicine, 2014, 46(11): 71-73. |
| [20] |
温光民. 慢性阻塞性肺疾病稳定期肺脾两虚证给予六君子汤治疗的价值评价[J]. 全科口腔医学电子杂志, 2016, 3(24): 24-25. WEN G M. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease stabilizes lung and spleen two deficiency syndrome to give the value evaluation of the treatment of six gentlemen decoration[J]. General Journal of Stomatology, 2016, 3(24): 24-25. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.2095-7882.2016.24.016 |
| [21] |
谢嘉嘉, 叶仁群, 宋银枝, 等. 六君子汤治疗稳定期慢性阻塞性肺疾病疗效观察[J]. 新中医, 2014, 46(12): 63-65. XIE J J, YE R Q, SONG Y Z, et al. Observation on therapeutic effect of Liujunzi Decoction on stable chronic obstructive pulmonary disease[J]. Journal of New Chinese Medicine, 2014, 46(12): 63-65. |
| [22] |
黄圆圆, 张元, 康利平, 等. 党参属植物化学成分及药理活性研究进展[J]. 中草药, 2018, 49(1): 239-250. HUANG Y Y, ZHANG Y, KANG L P, et al. Research progress on chemical constituents and their pharmacological activities of plant from Codonopsis[J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs, 2018, 49(1): 239-250. |
| [23] |
黄丽亚. 白术注射液增强抗氧化酶作用的实验研究[J]. 时珍国医国药, 2006, 17(5): 758-759. HUANG L Y. Experimental research on the effect of strengthening anti-oxidase of atractyllismacrocephala Injection[J]. Li Shi Zhen Medicine and Material Research, 2006, 17(5): 758-759. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1008-0805.2006.05.036 |
| [24] |
林丽霞, 梁国瑞, 陈燕, 等. 茯苓多糖的免疫效应和抗肿瘤作用研究进展[J]. 环球中医药, 2015, 8(1): 112-115. LIN L X, LIANG G R, CHEN Y, et al. Immune effects and antitumor effect of pachyman: a research progress[J]. Global Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2015, 8(1): 112-115. |
| [25] |
蔡宛如, 钱华. 芍药甘草汤平喘和抗过敏作用的实验研究[J]. 中国中西医结合急救杂志, 2000, 7(6): 341-342. CAI W R, QIAN H. Experimental study on the anti-allergic and anti-asthmatic effects of peony-licorice decoction[J]. Chinese Journal of Integrated Traditional and Western Medicine in Intensive and Critical Care, 2000, 7(6): 341-342. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1008-9691.2000.06.013 |
| [26] |
周倩, 吴皓. 半夏总生物碱抗炎作用研究[J]. 中药药理与临床, 2006, 22(3): 87-89. ZHOU Q, WU H. The study of anti-inflammatory effect of total alkaloid form Banxia[J]. Pharmacology and Clinics of Chinese Materia Medica, 2006, 22(3): 87-89. |
| [27] |
王智磊, 张鑫, 刘素娟, 等. 陈皮"陈久者良"历史沿革和研究现状[J]. 中华中医药学刊, 2017, 35(10): 118-122. WANG Z L, ZHANG X, LIU S J, et al. Historical evolution and research status of Citrireticulatae pericarpium[J]. ChineseArchives of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2017, 35(10): 118-122. |
| [28] |
王姝梅, 何春美. 陈皮提取物清除氧自由基和抗脂质过氧化作用[J]. 中国药科大学学报, 1998, 29(6): 462-465. WANG S M, HE C M. Anti-lipid peroxidation and oxygen free radical scavenging activity of pericarpium Citrireticulatae extract[J]. Journal of China Pharmaceutical University, 1998, 29(6): 462-465. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1000-5048.1998.06.017 |
| [29] |
李庆耀, 梁生林. 陈皮的药用研究进展[J]. 中成药, 2008, 30(2): 246-248. LI Q Y, LIANG S L. Advances in medicinal research of citri[J]. Chinese Traditional Patent Medicine, 2008, 30(2): 246-248. |
| [30] |
BARNES P J, CELLI B R. Systemic manifestations and comorbidities of COPD[J]. European Respiratory Journal, 2009, 33(5): 1165-1185. |
| [31] |
STOCKLEY R A. Progression of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: impact of inflammation, comorbidities and therapeutic intervention[J]. Current Medical Research and Opinion, 2009, 25(5): 1235-1245. |
| [32] |
BURGEL P R, NESME M P, CHANEZ P, et al. Cough and sputum production are associated with frequent exacerbations and hospitalizations in COPD subjects[J]. Chest, 2009, 135(4): 975-982. |
| [33] |
刘亚茹, 刘玉静, 纪品川. 补肺活血汤治疗稳定期慢性阻塞性肺疾病的临床观察[J]. 天津中医药, 2019, 36(7): 650-654. LIU Y R, LIU Y J, JI P C. Clinical observation of Bufei Huoxue Decoction in the treatment of stable chronic obstructive pulmonary disease[J]. Tianjin Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2019, 36(7): 650-654. |
| [34] |
李群, 徐鹏, 熊明. 百令胶囊对慢性阻塞性肺疾病患者健商指数、CAT评分的影响[J]. 天津中医药, 2018, 35(9): 664-666. LI Q, XU P, XIONG M. Effect of Bailing Capsule on health quotient index and CAT score in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease[J]. Tianjin Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2018, 35(9): 664-666. |
| [35] |
孔令宜, 李桂伟. 右美托咪定用于慢性阻塞性肺疾病急性加重期肺肾两虚型患者无创辅助通气镇静的临床观察[J]. 天津中医药, 2016, 33(6): 339-342. KONG L Y, LI G W. Clinical observation on dexmedetomidine for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease with acute exacerbation of lung and kidney deficiency type two patients with of noninvasive ventilation sedation[J]. Tianjin Journal of traditional Chinese Medicine, 2016, 33(6): 339-342. |
 2021, Vol. 38
2021, Vol. 38