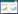文章信息
- 陈硕, 苏轶男, 王凯, 王燕
- CHEN Shuo, SU Yinan, WANG Kai, WANG Yan
- 中药保留灌肠联合针刺治疗在结直肠癌术后的临床运用
- Clinical study in the postoperative treatment of colorectal cancer: the combined application of the retention enema with traditional Chinese medicine and acupuncture
- 天津中医药, 2022, 39(6): 746-749
- Tianjin Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 39(6): 746-749
- http://dx.doi.org/10.11656/j.issn.1672-1519.2022.06.15
-
文章历史
- 收稿日期: 2021-12-02
2. 上海市浦东新区人民医院中医科,上海 201299
结直肠癌是目前相对常见的消化道恶性肿瘤。根据2020年《临床医师癌症杂志》发布的全球癌症统计报告,全球结直肠癌的发病率列第3位,病死率列第2位[1]。中国结直肠癌标化发病率高于全球平均水平,且呈年轻态趋势[2-3]。目前,根治性手术是结直肠癌治疗的最主要手段,然而术后常见并发症,特别是胃肠功能紊乱影响着患者短期预后[4-5]。在外科快速康复和中西医结合治疗理念[6]的指导下,本院结合自身优势,采用中药保留灌肠联合针刺的术后治疗方案,以促进患者早期排气排便。本研究旨在探讨加味大承气汤保留灌肠联合针刺治疗的临床疗效及其对胃肠激素的影响,现报告如下。
1 资料与方法 1.1 纳入标准本研究经天津市人民医院伦理委员会审批通过,批件号:(2019)年快审第(B02)号。患者符合原发性结直肠癌诊断标准,无远处转移,并于天津市人民医院接受根治性手术;年龄区间18~65岁,性别不限;首次接受术后中医治疗;心、肺、肝、肾功能基本正常;预期生存时间大于3个月;自愿入组参加,依从性好;签署书面的知情同意书。
1.2 排除标准出现严重合并症者;精神障碍患者;存在严重感染者。
1.3 一般资料选择2019年10月—2020年10月入组病例共80例,按照随机数字表法进行完全随机分组,分为治疗组和对照组,每组40例。两组患者术前均无严重合并症,在性别、年龄、肿瘤大小方面比较,差异均无统计学意义(P > 0.05),具有可比性。见表 1。
直肠癌根治术30例,乙状结肠癌根治术20例,右半结肠癌根治术18例,左半结肠癌根治术12例。
1.5 剔除标准中途失访者;依从性极差者;受访者中途要求退出;试验过程出现严重不良事件,研究者认为不宜进一步参与研究的患者;出现严重并发症或短期行2次手术的患者;术后继发基础性疾病,健康状况不允许继续参加的患者;误诊、误纳;无法依从,或违背研究方案的患者。
1.6 治疗方法术后,治疗组采用中药保留灌肠联合针刺进行治疗。具体方法为:予加味大承气汤高位保留灌肠。方药组成[7-8]:大黄30 g,厚朴20 g,芒硝20 g(冲兑),枳实15 g,木香10 g,莱菔子20 g,黄芪30 g,丹参15 g,党参15 g。以上诸药煎药200 mL,去渣过滤,至温度36~38 ℃时使用一次性灌肠管插入肛门25 cm灌入,嘱患者静卧保留灌肠液2 h。每日灌肠2次,在术后12 h以内进行第1次灌肠。另在术后12 h取足三里、上巨虚、天枢以及中脘穴行中医针刺治疗,用2寸(50 mm)毫针进针,然后提插捻转,予以强刺激,出现酸、麻、胀视为得气,针刺治疗每日1次,每次30 min。对照组予以同温生理盐水保留灌肠。灌肠开始时间及次数、灌肠管插入位置均同治疗组。7 d为1个疗程,连续治疗1个疗程后评价疗效。
1.7 观察指标记录患者首次肠鸣音出现时间、肠鸣音恢复正常时间、首次排气时间、首次排便时间,同期监测患者血清胃动素和生长抑素水平变化。疗效标准:1)痊愈:患者24 h内出现首次排气,肠鸣音恢复正常,3次/分以上,正常进食后3 d,无腹痛、腹胀和恶心等不良表现。2)好转:患者24~48 h出现首次排气,肠鸣音正常或略弱,2~3次/分以上,正常进食后3 d,无腹痛、腹胀和恶心等不良表现,或有轻度腹痛、腹胀和恶心等不良表现。3)无效:患者术后48 h以后仍未排气,无肠鸣音或肠鸣音微弱,进食后存在严重的腹痛、腹胀和恶心等不良表现。
1.8 统计学方法采用SPSS 23.0统计软件分析数据,计量资料以均数±标准差(x±s)表示,组间数据比较采用独立样本t检验,重复测量资料采用重复测量方差分析。计数资料采用例数、构成比或率表示,组间比较采用卡方检验,等级资料组间比较采用非参数检验,P < 0.05表示差异有统计学意义。
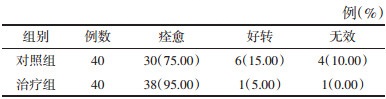
2 结果 2.1 两组临床效果比较两组临床效果采用非参数检验,整体疗效方面治疗组高于对照组,并且两组差异有统计学意义(Z=7.391,P < 0.01)。见表 2。
|
治疗组首次肠鸣音出现时间、肠鸣音恢复正常时间、首次排气排便时间均早于对照组(P < 0.05),说明中药保留灌肠联合针刺治疗促进肠道蠕动,恢复排气排便。见表 3。

|
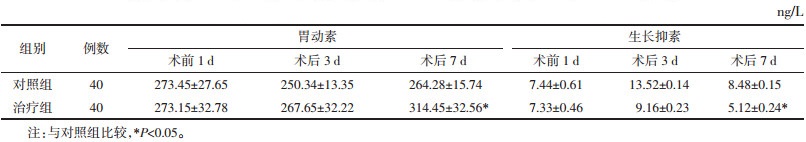
重复测量方差分析结果显示,胃动素和生长抑素均符合球形检验,分析发现对照组和治疗组患者术后第3天的胃动素水平均降低,说明行结直肠癌根治性手术会抑制胃动素的分泌。治疗组较对照组患者术后第7天的胃动素水平显著提高(P < 0.05)。此外,两组患者术后第3天的生长抑素水平均升高,符合生长抑素能够抑制胃肠道运动的研究报道,而术后第7天生长抑素水平又降低,且治疗组较对照组降低更为显著(P < 0.05)。见表 4。以上结果说明加味大承气汤保留灌肠联合针刺治疗,可能通过调节胃动素和生长抑素的水平促进肠道运动的恢复。
|
行外科根治性手术的患者在术后易出现胃肠功能紊乱和功能抑制,肠道蠕动减慢,甚至会引起肠粘连、肠梗阻、感染加重、肠黏膜屏障受损等并发症。尽管当前腹腔镜手术的普及极大地缩短了手术时间,降低了术后机体炎症状态,但仍难以完全避免胃肠功能障碍的发生。在临床上,常用的干预术后排气、排便功能障碍的方式多数为开塞露纳肛刺激肛门以增强排便反射,胃肠减压以减轻上段胃肠道压力,新斯的明肌肉注射以缓解肠麻痹并加速肠蠕动,生理盐水灌肠等。近年来,中医辅助策略在结直肠癌患者的术后康复中得到了越来越多的应用。
中药保留灌肠是中医外治法之一,将药液通过肛门灌入并在直肠内留置,使得药物经直肠黏膜吸收,不仅能够直达病灶,还能避免口服药物的首关消除效应,提高局部的血药浓度,从而有效缓解病情。大黄为君药泻热通便,芒硝为臣药软坚润燥,具有活血化瘀、行气散结等功效,在促进胃肠道功能恢复方面具有优势,其所含电解质、单多糖化合物等成分还可以营养肠道黏膜,稳固肠黏膜屏障[9]。
针刺能够灵活地调整患者气血和脏腑功能,从而改善胃肠运动能力[10]。研究表明,针刺足三里能够通过提高括约肌收缩频率,增加胃肠道蠕动强度有效降低微酸分泌和胃内压力[11]。针刺上巨虚具有保护肠黏膜,减轻黏膜的炎性反应、水肿、渗出等功能[12]。对天枢穴的刺激能够有效提高患者术后胃肠动力及炎症因子表达[13]。而针刺中脘,可以松弛胃部痉挛,调节胃肠蠕动节律,开放幽门[14]。本研究以中药保留灌肠联合针刺上述穴位,取得了良好的治疗效果。
为了进一步评价患者早期胃肠道功能恢复情况及相关调控机制,笔者还监测了参与胃肠道调控的相关指标胃动素和生长抑素的水平。结果表明,患者术后普遍胃动素水平降低而生长抑素水平升高,与对照组比较,患者经加味大承气汤中药保留灌肠配合针刺治疗7 d后,胃动素水平显著提高且生长抑素水平降低(P < 0.05)。有研究指出,加味大承气汤保留灌肠能够通过调节血清血管活性肠肽、生长抑素和胃动素水平改善患者胃肠动力障碍。田丰等[15]发现针刺上巨虚等穴位能够有效调节胃动素、胃泌素和生长抑素水平,进而改善老年性便秘患者症状,与本研究结论一致。因此,加味大承气汤保留灌肠联合针刺治疗能够通过调节胃肠道相关激素水平达到治疗效果。
综上所述,在快速康复理念的指导下,结合中西医治疗,患者术后短期予以中药保留灌肠联合针刺治疗,可以短期促进胃肠道蠕动,恢复肠道功能,促进患者早期进食,或可以降低围手术期肠梗阻的发生,减少住院时间,降低住院花费。值得临床进一步研究与运用。
| [1] |
刘宗超, 李哲轩, 张阳, 等. 2020全球癌症统计报告解读[J]. 肿瘤综合治疗电子杂志, 2021, 7(2): 1-14. LIU Z C, LI Z X, ZHANG Y, et al. Interpretation on the report of global cancer statistics 2020[J]. Journal of Multidisciplinary Cancer Management (Electronic Version), 2021, 7(2): 1-14. |
| [2] |
袁蕙芸, 蒋宇飞, 谭玉婷, 等. 全球癌症发病与死亡流行现状和变化趋势[J]. 肿瘤防治研究, 2021, 48(6): 642-646. YUAN H Y, JIANG Y F, TAN Y T, et al. Current status and time trends of cancer incidence and mortality worldwide[J]. Cancer Research on Prevention and Treatment, 2021, 48(6): 642-646. DOI:10.3971/j.issn.1000-8578.2021.20.1533 |
| [3] |
王一冲, 尹腾飞, 彭红叶, 等. 生活方式对结直肠癌发生发展的影响[J]. 医学综述, 2021, 27(13): 2577-2582. WANG Y C, YIN T F, PENG H Y, et al. Lifestyle influence on occurrence and development of colorectal cancer[J]. Medical Recapitulate, 2021, 27(13): 2577-2582. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-2084.2021.13.014 |
| [4] |
金国梁, 王哲鹏, 段树全, 等. 加速康复外科在腹腔镜结直肠癌根治术中的应用[J]. 包头医学院学报, 2021, 37(5): 75-79. JIN G L, WANG Z P, DUAN S Q, et al. Application of accelerated rehabilitation surgery in laparoscopic radical resection of colorectal cancer[J]. Journal of Baotou Medical College, 2021, 37(5): 75-79. |
| [5] |
王国福, 魏建龙. 开腹术与腹腔镜治疗结直肠癌对其有效率和并发症率的对比观察[J]. 新疆医学, 2021, 51(5): 569-571. WANG G F, WEI J L. Comparative analysis about the effective rate and complication rate of laparotomy and laparoscopic in the treatment of colorectal cancer[J]. Xinjiang Medical Journal, 2021, 51(5): 569-571. |
| [6] |
梁伟健, 贾勇, 杨得振, 等. 中医外治法干预结直肠癌围手术期研究进展[J]. 河北中医, 2021, 43(2): 341-344, 348. LIANG W J, JIA Y, YANG D Z, et al. Research progress on the intervention of TCM external therapy in perioperative period of colorectal cancer[J]. Hebei Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2021, 43(2): 341-344, 348. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1002-2619.2021.02.037 |
| [7] |
谢峰. 大承气汤加减保留灌肠治疗不全性肠梗阻临床疗效分析[J]. 中医临床研究, 2019, 11(31): 102-104. XIE F. Efficacy of Enema with the Dachengqidecoction on incomplete intestinal obstruction[J]. Clinical Journal of Chinese Medicine, 2019, 11(31): 102-104. |
| [8] |
方荣臻, 林少露. 腹部手术后应用大承气汤保留灌肠联合针刺对患者胃肠功能恢复的影响[J]. 当代医学, 2021, 27(11): 74-76. FANG R Z, LIN S L. Effect of Dachengqi decoction retention Enema combined with acupuncture on gastrointestinal function recovery after abdominal operation[J]. Contemporary Medicine, 2021, 27(11): 74-76. |
| [9] |
余吉平, 袁玥旻, 裘建明, 等. 加味大承气汤对直肠肿瘤患者术后肠功能恢复的影响[J]. 中国中西医结合杂志, 2017, 37(4): 419-421. YU J P, YUAN Y M, QIU J M, et al. Effect of modified Dachengqi Decoction on recovery of gastrointestinal function after surgery in patients with rectal cancer[J]. Chinese Journal of Integrated Traditional and Western Medicine, 2017, 37(4): 419-421. |
| [10] |
边屯. 中药保留灌肠联合穴位注射治疗溃疡性结肠炎临床研究[J]. 新中医, 2015, 47(12): 53-55. BIAN T. Clinical research of Chinese medicine retention Enema combined with acupoint injection in treating ulcerative colitis[J]. Journal of New Chinese Medicine, 2015, 47(12): 53-55. |
| [11] |
李雯, 韩旭, 余芝, 等. 电针、温和灸足三里穴区对大鼠胃运动及迷走神经胃支放电频率的影响[J]. 中华中医药杂志, 2021, 36(4): 1921-1925. LI W, HAN X, YU Z, et al. Effects of electroacupuncture and mild moxibustion stimulation at Zusanli(ST 36) on gastric motility and vagus nerve gastric branch in rats[J]. China Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine and Pharmacy, 2021, 36(4): 1921-1925. |
| [12] |
TAN J Q. Effects of acupuncture on the expression of IL-1β, IL-6 and eNOs in serum of rats with incomplete intestinal obstruction[J]. Changsha: Hunan University of Chinese Medicine, 2020. |
| [13] |
黄金, 杨静雯, 林璐璐, 等. 不同频率电针天枢穴对术后肠麻痹小鼠胃肠动力和炎症因子的影响[J]. 辽宁中医杂志, 2021, 48(11): 192-194. HUANG J, YANG J W, LIN L L, et al. Effects of electroacupuncture at Tianshu(ST25)with different frequencies on intestinal motility and inflammatory factors in murine model with postoperative ileus[J]. Liaoning Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2021, 48(11): 192-194. |
| [14] |
陈美华. 温针灸足三里、中脘促进腹部术后胃肠功能恢复护理[J]. 中医临床研究, 2019, 11(3): 14-15. CHEN M H. The effect of warm acupuncture on Zusanli and Zhongwan on the recovery of gastrointestinal function after abdominal surgery and its effect on the nursing[J]. Clinical Journal of Chinese Medicine, 2019, 11(3): 14-15. |
| [15] |
田丰, 石宁, 王培育. 针灸推拿对老年性便秘患者血清MLT、GAS、SS水平及预后的影响[J]. 现代医学与健康研究电子杂志, 2020, 4(23): 66-68. TIAN F, SHI N, WANG P Y. Effects of acupuncture and massage on serum MLT, GAS and SS levels and prognosis of senile constipation[J]. Modern Medicine and Health Research Electronic Journal, 2020, 4(23): 66-68. |
2. Department of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai Pudong New Area People's Hospital, Shanghai 201299, China
 2022, Vol. 39
2022, Vol. 39