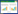文章信息
- 冯超男, 胡海殷, 季昭臣, 欧益, 强晓钰, 吴晓蕾, 张俊华, 曹璐佳
- FENG Chaonan, HU Haiyin, JI Zhaochen, OU Yi, QIANG Xiaoyu, WU Xiaolei, ZHANG Junhua, CAO Lujia
- 血塞通软胶囊治疗脑梗死有效性和安全性的系统评价
- Systematic evaluation of effectiveness and safety of Xuesaitong Soft Capsule in treating cerebral infarction
- 天津中医药, 2022, 39(7): 893-900
- Tianjin Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 39(7): 893-900
- http://dx.doi.org/10.11656/j.issn.1672-1519.2022.07.16
-
文章历史
- 收稿日期: 2022-02-17
脑梗死又称缺血性卒中,中医称之为卒中或中风。本病系由各种原因所致的局部脑组织区域血液供应障碍,好发于50岁以上的中、老年人[1]。脑梗死的前驱症状无特殊性,往往由于持续时间较短且程度轻微而被患者及家属忽略[2]。脑梗死发病起病急,其临床症状在发病后数小时或1~2 d达到高峰[3-5]。在中国,脑梗死(Stroke)是造成中国寿命年损失的第一位病因[6],造成了沉重的经济和社会负担[7]。
现在国际上针对急性脑梗死的治疗仍然以血管再通(溶栓、血管内介入治疗)为主,但由于受时间窗、费用及医疗水平等因素限制,实际受益人群仍然很少[8-9]。与此同时,众多临床工作者总结长期工作经验发现,中国部分传统中药有活血化瘀作用及明显抗血小板聚集作用[10]。近年来,血塞通软胶囊与西药联合使用防治脑梗死的实例频频出现,并且大多疗效显著[11-13]。
目前,血塞通软胶囊广泛应用于各种心脑血管疾病,并有一定数量的血塞通软胶囊治疗脑梗死的临床研究陆续报道。本研究立足于中医理论基础,使用循证医学方法,对中药成方血塞通软胶囊治疗脑梗死进行文献定量与定性综合分析,旨在为临床提供循证依据。
1 资料与方法 1.1 纳入标准 1.1.1 研究类型随机对照试验(RCT)。
1.1.2 研究对象纳入受试者明确诊断为脑梗死且未伴有明显合并症(非心系疾病等)的研究。诊断标准参照《中国急性缺血性脑卒中诊治指南2018》[14]。
1.1.3 干预措施治疗组应用血塞通软胶囊或者在常规治疗的基础上联用血塞通软胶囊;对照组采用常规治疗;如研究为加载设计,则两组常规治疗方案须保持一致,常规治疗用药在不同研究间可以不同,但在同一研究中须完全一致。
1.1.4 结局指标临床疗效、美国国立卫生院神经功能缺损评分(NIHSS)、Barthel指数、血浆黏度、全血黏度;报告上述结局指标之一,即可纳入。
1.2 排除标准排除单一病例研究、会议摘要、消息、书信、临床调查,无法获取测量指标数据的研究等。
1.3 文献检索检索中国知网、万方数据库、维普数据库、中国生物医学文献数据库(SinoMed)、PubMed及Embase数据库,检索时间为建库至2021年8月。中文检索词包括脑梗死,脑梗,缺血性脑卒中,脑卒中,缺血性卒中,中风,卒中,血塞通软胶囊,随机对照试验。英文检索词包括cerebral infarction,infarct of brain,cerebral ischemic stroke,ischemia stroke,ischemic cerelral infarction和Xuesaitong soft capsule,xuesaitong softcapsule,XST,Xuesaitong,RCT。
1.4 文献筛选、资料提取文献筛选及资料提取均由两人独立进行,如遇分歧交由第三方裁定。根据预先设计好的资料提取表进行数据提取。提取信息主要包括:1)纳入研究的基本信息,包括文题、作者、单位、发表杂志等。2)研究对象的基线特征,包括人口学特征如例数、年龄、性别等,以及临床特征如病程、中医证候等。3)干预措施,包括药物名称、疗程、频次、用量等。4)结局指标。
1.5 质量评价采用Cochrane Handbook 5.0推荐的“偏倚风险评估”工具对纳入的RCT进行质量评价。根据随机方法、分配隐藏、受试者盲法、结果评价盲法、数据完整性、选择性报告、其他偏倚等7个方面评价研究质量。方法运用正确为低风险(Low risk),方法运用描述不清楚为不明风险(Unclear risk),方法运用不正确为高风险(High risk)。两名研究者独立进行质量评价,然后交叉核对,若存在分歧则通过咨询第三方解决。
1.6 统计方法应用Revman 5.3软件进行数据统计分析。计数资料采用比值比(OR),计量资料采用均数差(MD),两者均计算95%置信区间(95% CI)。Mantel-Haenszel方法用于二分变量,DerSimonian和Laird逆方差方法用于连续变量。合并统计量之前采用卡方(χ2)检验进行异质性分析,并结合I2值(异质性定量统计值)估计异质性的大小,当P > 0.05且I2 < 50%时认为研究间异质性较小,采用固定效应模型合并效应量;当P≤0.05或I2≥50%时认为异质性较大,则首先查找异质性来源,若不能用临床异质性解释者,指标效应量的合并选用随机效应模型,必要时进行亚组分析或采用描述性分析。采用倒漏斗图分析潜在的发表偏倚。
2 结果 2.1 文献检索结果初步检索获得文献683篇。通过查重、阅读标题和摘要,排除文献656篇,阅读全文排除不符合标准的文献后排除11篇,最终筛选出符合纳入排除标准的文献16篇[15-30]。文献筛选流程图,见图 1。
|
| 图 1 文献筛选流程图 Fig. 1 Literature screening flow chart |
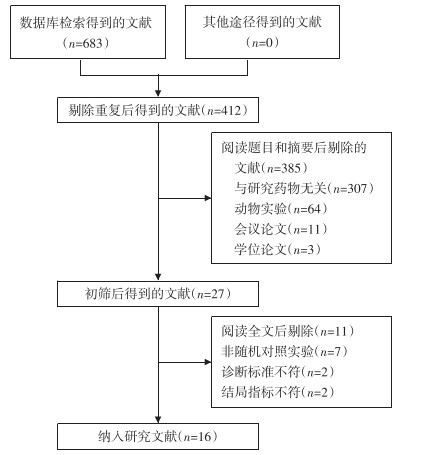
共纳入16项研究,均为中文文献,其中最早发表于2005年,最晚发表于2021年。16项研究共纳入1 973例脑梗死患者,其中试验组1 024例,对照组949例。其中涉及干预措施为血塞通软胶囊+常规治疗VS常规治疗,其中常规疗法包括:阿司匹林、拜阿司匹林、阿托伐他汀片、单唾液酸四己糖神经节苷脂钠注射液、阿司匹林肠溶片等。研究对象数量介于64~277个之间。纳入研究的基本特征,见表 1。
|
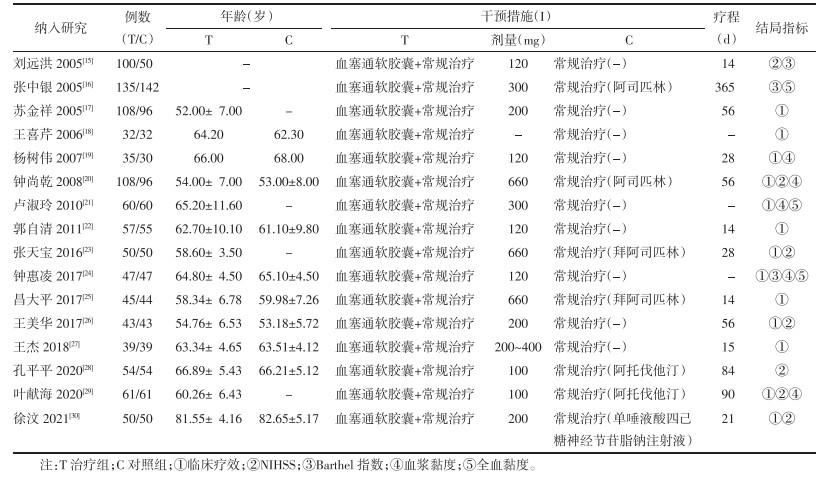
随机方法:16项研究中,有4项研究[15, 23, 28, 30]报告并使用了正确的随机方法,评为Low risk;6项研究[17, 20, 24-25, 27, 29]报告以入院顺序作为随机方法,评为High risk;其余6项研究仅提及“随机”但并未描述具体方法,评为Unclear risk。分配隐藏:14项研究未提分配隐藏,评为Unclear risk。有2项研究[26-27]报告并使用了分配隐藏方法,评为Low risk。受试者盲法:14项研究均未提及受试者盲法,评价为High risk。有2项研究[26-27]报告并使用了受试者盲法,评为Low risk。结果评价盲法:10项研究报告主观和客观结局指标,评为Unclear risk。5项研究[17-18, 22-23, 27]报告仅主观结局指标,评为High risk;1项研究[15]仅报告客观结局指标,评为Low risk。结果数据完整性:16项研究病例数据均完整,评为Low risk。选择性报告:因无法获取16项RCT的注册方案,考虑以文章方法学部分与结果部分进行对应查看,其中1项研究[17]方法学部分的设计未能在结果部分充分报告,评为High risk;其余15项研究均进行了完整报告,评为Low risk。其他偏倚:因15项纳入研究的报告均未进行试验注册及方案审批,评为High risk;1项研究[26]仅报告方案审批,评为Unclear risk。结果见图 2。
|
| 图 2 纳入RCT质量评价 Fig. 2 RCT quality evaluation was included |
13项研究[17-27, 29-30]报告了血塞通软胶囊联合常规治疗对脑梗死患者临床疗效的影响,共纳入患者1 438例,其中治疗组735例,对照组703例。统计分析显示存在中度异质性(P=0.005,I2=58%),故采用随机效应模型进行Meta分析,结果显示:在临床疗效方面,常规治疗基础上联用血塞通软胶囊,疗效明显优于常规治疗,[OR=3.51(2.01,6.12),P < 0.05],差异具有统计学意义。结果见图 3。
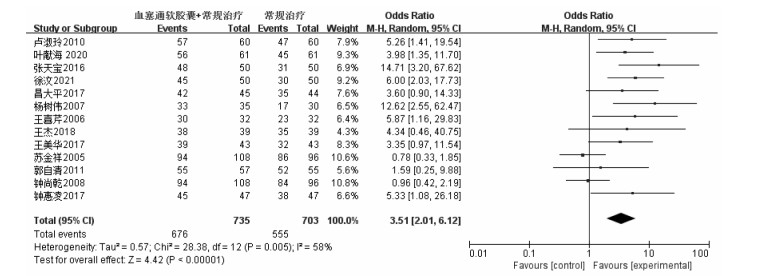
|
| 图 3 血塞通软胶囊治疗脑梗死的临床症状比较森林图 Fig. 3 Comparison of clinical symptoms of Xuesaitong Soft Capsule in the treatment of cerebral infarction forest diagram |
NIHSS用于评估卒中患者神经功能缺损程度,治疗后可以定期评估治疗效果。7项研究[15, 20, 23, 26, 28-30]报告了血塞通软胶囊联合常规治疗对脑梗死患者NIHSS评分的影响,共纳入患者870例,其中治疗组466例,对照组404例。统计分析显示异质性较小(P=0.78,I2=0%),故采用固定效应模型进行Meta分析,结果显示:在NIHSS评分方面,常规治疗基础上联用血塞通软胶囊,疗效明显优于常规治疗,[MD=-3.29(-3.89,-2.70),P < 0.05],组间比较差异具有统计学意义。结果见图 4。
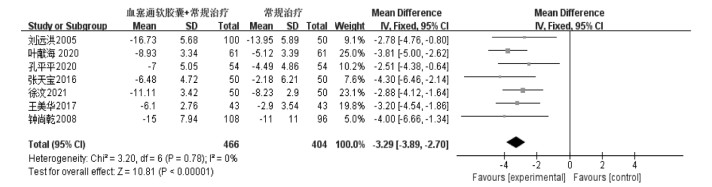
|
| 图 4 血塞通软胶囊治疗脑梗死的NIHSS评分森林图 Fig. 4 NIHSS score forest map of Xuesaitong Soft Capsule in the treatment of cerebral infarction |
3项研究[15-16, 24]报告了血塞通软胶囊联合常规治疗脑梗死对Barthel指数影响,共纳入患者521例,其中治疗组282例,对照组239例。经过统计学分析后异质性大(P < 0.000 01,I2=98%),故采用随机效应模型进行Meta分析。通过敏感性分析查找异质性来源,无法找到来源,采用描述性分析,结果见图 5。
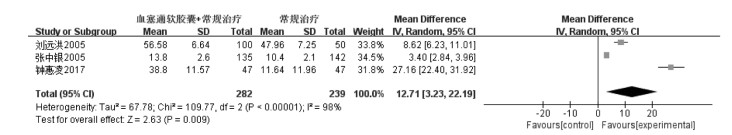
|
| 图 5 血塞通软胶囊治疗脑梗死的Barthel指数森林图 Fig. 5 Barthel index forest map of Xuesaitong Soft Capsule in the treatment of cerebral infarction |
1篇研究[15]报告了血塞通软胶囊联合西医常规治疗脑梗死对Barthel指数的影响,其结果显示,治疗14 d时Barthel指数升高,差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05),治疗90 d后明显优于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。
1篇研究[16]报告了血塞通软胶囊联合阿司匹林治疗脑梗死对Barthel指数的影响,其结果显示,治疗组优于对照组,各组间差异具有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。
1篇研究[24]报告了血塞通软胶囊联合西医常规治疗脑梗死对Barthel指数的影响,其结果显示,治疗前两组Barthel评分差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05),治疗后观察组评分高于对照组,差异具有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。
2.4.4 血浆黏度结果5项研究[19-21, 24, 29]报告了血塞通软胶囊联合常规治疗脑梗死对血浆黏度影响,共纳入患者592例,其中治疗组304例,对照组288例。经过统计学分析后异质性大(P < 0.000 01,I2=99%),故采用随机效应模型进行Meta分析。结果显示:在血浆黏度方面,常规治疗基础上联用血塞通软胶囊,疗效明显优于常规治疗,[MD=-1.17(-1.64,-0.71),P < 0.05],组间比较差异具有统计学意义。结果见图 6。
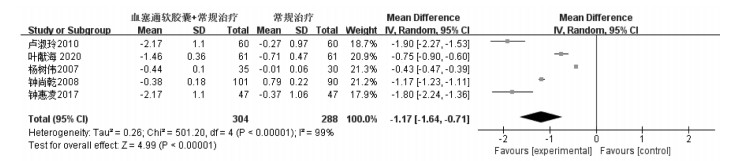
|
| 图 6 血塞通软胶囊治疗脑梗死的血浆黏度森林图 Fig. 6 Forest map of plasma viscosity in the treatment of cerebral infarction with Xuesaitong Soft Capsule |
3项研究[16, 21, 24]报告了血塞通软胶囊联合常规治疗脑梗死对全血黏度影响,共纳入患者491例,其中治疗组242例,对照组249例。经过统计学分析后异质性大(P < 0.000 01,I2=99%),故采用随机效应模型进行Meta分析。结果显示:在全血黏度方面,常规治疗基础上联用血塞通软胶囊,疗效明显优于常规治疗,[MD=-4.88(-9.09,-0.67),P < 0.05],组间比较差异具有统计学意义。结果见图 7。

|
| 图 7 血塞通软胶囊治疗脑梗死的全血黏度森林图 Fig. 7 Forest diagram of whole blood viscosity of Xuesaitong Soft Capsule in the treatment of cerebral infarction |
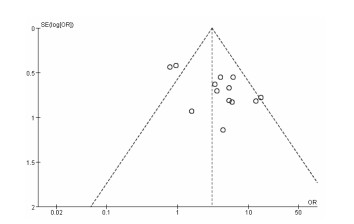
基于血塞通软胶囊联合常规治疗对比常规治疗临床疗效改善总有效率方面漏斗图显示,纳入的研究在漏斗图顶端集中,但个别研究未呈对称分布,说明有可能存在发表偏倚。结果见图 8。
|
| 图 8 血塞通软胶囊治疗脑梗死的临床症状比较漏斗图分析 Fig. 8 Funnel plot analysis of clinical symptoms of Xuesaitong Soft Capsule in treating cerebral infarction |
纳入的研究中,4项研究[18-19, 22, 26]报告“未发生不良事件”,1项研究[28]报告不良事件为:试验组出现咽干、恶心各1例,对照组出现恶心、呕吐各1例。其余研究均未针对安全性进行报告。
3 讨论脑血管病是威胁人类健康的最严重的疾病之一,虽然脑梗死病死率低于脑出血,但其致残率高,约20%的幸存者1~2年内会出现再中,严重影响患者的生存质量。血塞通软胶囊原料为名贵道地药材文三七,显著发挥临床作用的活性成分是三七总皂苷,对脑梗死时有一定的治疗效果。该药对血管具有扩张作用,加快微动脉和微静脉之间的血液循环速度,改善脑血管的收缩与舒张障碍,使脑血流量增加,提高病灶附近供血能力。对血脂进行调节,减少动脉血管壁上附着脂肪的量[31]。另外,三七总皂苷中含有大量人参二醇与三醇,经过药品加工能够分解为Rc等多种单体物质,在最短时间内将药效发挥出来。其中含有的活性成分可以显著增加大脑皮层组织的血流量与ATP的量,并提高脑细胞膜与血管膜的通透性,缓解脑细胞由于钠与水滞留引发的细胞毒性水肿,增强脑细胞对缺血的耐受能力,加强脑梗死后脑细胞应对缺血的能力,尽快恢复损坏的神经功能[32-34]。
本研究主要对血塞通软胶囊联合常规治疗治疗脑梗死的疗效进行系统评估,通过系统全面的检索及文献筛选,最终纳入16项研究,Meta分析的结果表明,在临床疗效、临床症状,血流动力学指标方面,均优于对照组。
本次研究存在一定的局限性:纳入研究质量不高,且14篇均未对分配隐藏、盲法及其他偏倚进行报告,存在选择性偏倚、实施偏倚和测量偏倚的可能性。个别纳入研究的基本信息报告不清,如患者性别、年龄等。部分结果的临床异质性明显,在诊断标准基本一致的情况下,其原因可能是纳入患者的病情、病程差异以及对照组的用药差异导致。漏斗图显示,纳入的文献可能存在一定的发表偏倚。
综上,数据分析显示在常规治疗基础上,加用血塞通软胶囊可提高脑梗死临床疗效,可为临床血塞通软胶囊治疗脑梗死提供借鉴。但由于纳入文献的数量和质量等问题,尚需结合中医药的特点,改进创新研究方法与思路,建立相应的规范或标准,按照科学的方法评价中医药的适用性、安全性、有效性和经济性,促进中医药临床疗效的科学表达[35]。本研究结论尚需开展更多高质量的RCT研究予以验证,为血塞通软胶囊治疗脑梗死的有效性和安全性提供更可靠的证据,进一步推动临床诊疗方案改善与提升。
| [1] |
LI Z X, WANG C J, ZHAO X Q, et al. Substantial progress yet significant opportunity for improvement in stroke care in China[J]. Stroke, 2016, 47(11): 2843-2849. DOI:10.1161/STROKEAHA.116.014143 |
| [2] |
WANG W Z, JIANG B, SUN H X, et al. Prevalence, incidence, and mortality of stroke in China: results from a nationwide population-based survey of 480-687 adults[J]. Circulation, 2017, 135(8): 759-771. DOI:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.116.025250 |
| [3] |
聂兰敏. 急性脑梗死的中医药治疗进展[J]. 大众科技, 2015, 17(11): 82-83. NIE L M. Progress in treatment of acute cerebral infarction[J]. Popular Science&Technology, 2015, 17(11): 82-83. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1008-1151.2015.11.031 |
| [4] |
李晓, 李金成, 苏业军, 等. 中医药治疗急性脑梗死研究进展[J]. 亚太传统医药, 2015, 11(9): 54-55. LI X, LI J C, SU Y J, et al. Research progress of Chinese medicine in the treatment of acute cerebral infarction[J]. Asia-Pacific Traditional Medicine, 2015, 11(9): 54-55. |
| [5] |
徐兴培. 中医药治疗急性脑梗死的的临床研究进展[J]. 转化医学电子杂志, 2015, 2(4): 134-135. XU X P. Clinical research progress of TCM in the treatment of acute cerebral infarction[J]. E-Journal of Translational Medicine, 2015, 2(4): 134-135. |
| [6] |
钟迪, 张舒婷, 吴波. 《中国急性缺血性脑卒中诊治指南2018》解读[J]. 中国现代神经疾病杂志, 2019, 19(11): 897-901. ZHONG D, ZHANG S T, WU B. Interpretation of "Chinese guidelines for diagnosis and treatment of acute ischemic stroke 2018"[J]. Chinese Journal of Contemporary Neurology and Neurosurgery, 2019, 19(11): 897-901. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1672-6731.2019.11.015 |
| [7] |
LEES K R, EMBERSON J, BLACKWELL L, et al. Effects of alteplase for acute stroke on the distribution of functional outcomes: a pooled analysis of 9 trials[J]. Stroke, 2016, 47(9): 2373-2379. DOI:10.1161/STROKEAHA.116.013644 |
| [8] |
解小龙, 孟甜甜, 李婷婷, 等. 三七类口服制剂治疗急性脑梗死的网状Meta分析[J]. 中草药, 2021, 52(14): 4277-4288. XIE X L, MENG T T, LI T T, et al. Panax notoginseng oral preparations for acute cerebral infarction: a network meta-analysis[J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs, 2021, 52(14): 4277-4288. DOI:10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2021.14.020 |
| [9] |
POWERS W J, DERDEYN C P, BILLER J, et al. 2015 American heart association/American stroke association focused update of the 2013 guidelines for the early management of patients with acute ischemic stroke regarding endovascular treatment: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American heart association/American stroke association[J]. Stroke, 2015, 46(10): 3020-3035. DOI:10.1161/STR.0000000000000074 |
| [10] |
桂树华, 胡玲玲, 王挺刚, 等. 血塞通软胶囊联合阿司匹林治疗老年慢性脑梗死对颈动脉斑块稳定性及机体抗氧化功能的影响[J]. 贵州医药, 2017, 41(10): 1059-1061. GUI S H, HU L L, WANG T G, et al. Effect of Xuesaitong soft capsule combined with aspirin on carotid plaque stability and antioxidant function in elderly patients with chronic cerebral infarction[J]. Guizhou Medical Journal, 2017, 41(10): 1059-1061. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-744X.2017.10.020 |
| [11] |
李薇, 魏毅. 血塞通软胶囊联合阿托伐他汀应用于急性缺血性中风患者的疗效观察[J]. 中南医学科学杂志, 2018, 46(4): 405-407, 427. LI W, WEI Y. Clinical effects of Xuesaitong soft capsule combined with atorvastatin in treating stroke patient and the effect on the PCSK9 thereof[J]. Medical Science Journal of Central South China, 2018, 46(4): 405-407, 427. |
| [12] |
王晓聪. 血塞通软胶囊联合阿司匹林治疗老年慢性脑梗死的效果分析[J]. 中医临床研究, 2020, 12(9): 24-25. WANG X C. Analysis of the effect of Xuesaitong soft capsule combined with aspirin in the treatment of elderly patients with chronic cerebral infarction[J]. Clinical Journal of Chinese Medicine, 2020, 12(9): 24-25. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1674-7860.2020.09.010 |
| [13] |
董子洵, 韩晟, 林丽开, 等. 血塞通软胶囊综合评价研究[J]. 中国临床药理学杂志, 2021, 37(12): 1612-1624. DONG Z X, HAN S, LIN L K, et al. Comprehensive evaluation of Xuesaitong soft capsule[J]. The Chinese Journal of Clinical Pharmacology, 2021, 37(12): 1612-1624. |
| [14] |
中华医学会神经病学分会, 中华医学会神经病学分会脑血管病学组. 中国急性缺血性脑卒中诊治指南2018[J]. 中华神经科杂志, 2018, 51(9): 666-682. Neurology Branch of Chinese Medical Association, Chinese Medical Association Neurology Branch Cerebrovascular Disease Group. Chinese guidelines for diagnosis and treatment of acute ischemic stroke 2018[J]. Chinese Journal of Neurology, 2018, 51(9): 666-682. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.1006-7876.2018.09.004 |
| [15] |
刘远洪, 葛晓航, 梁金花, 等. 血塞通软胶囊治疗急性脑梗死100例疗效观察[J]. 云南中医中药杂志, 2005, 26(4): 51. LIU Y H, GE X H, LIANG J H, et al. Therapeutic effect of Xuesaitong soft capsule on 100 cases of acute cerebral infarction[J]. Yunan Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine and Materia Medica, 2005, 26(4): 51. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1007-2349.2005.04.053 |
| [16] |
张中银, 郑德清, 庄闪花. 血塞通软胶囊在脑卒中康复期的应用[J]. 中国康复理论与实践, 2005, 11(7): 538-539. ZHANG Z Y, ZHENG D Q, ZHUANG S H. Effect of Xuesaitong Capsule on stroke during recovery phase[J]. Chinese Journal of Rehabilitation Theory&Practice, 2005, 11(7): 538-539. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-9771.2005.07.018 |
| [17] |
苏金祥, 孙延芹, 孙立靖, 等. 血塞通软胶囊辅助治疗急性脑梗死108例疗效观察[J]. 山东医药, 2005, 45(2): 3. SU J X, SUN Y Q, SUN L J, et al. Clinical observation of Xuesaitong Soft capsule in adjuvant treatment of 108 cases of acute cerebral infarction[J]. Shandong Medical Journal, 2005, 45(2): 3. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1002-266X.2005.02.023 |
| [18] |
王喜芹. 血塞通软胶囊治疗急性脑梗死32例[J]. 云南中医中药杂志, 2006, 27(3): 29. WANG X Q. Treatment of acute cerebral infarction with Xuesaitong soft capsule[J]. Yunnan Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine and Materia Medica, 2006, 27(3): 29. |
| [19] |
杨树伟. 血塞通软胶囊治疗脑梗死临床观察[J]. 现代中西医结合杂志, 2007, 16(21): 2993-2994. YANG S W. Clinical observation of Xuesaitong soft capsule in treatment of cerebral infarction[J]. Modern Journal of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine, 2007, 16(21): 2993-2994. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1008-8849.2007.21.017 |
| [20] |
钟尚乾, 张焕风, 黄永禄, 等. 血塞通软胶囊治疗急性脑梗死及对血液流变学的影响[J]. 中国药物与临床, 2008, 8(1): 68-69. ZHONG S Q, ZHANG H F, HUANG Y L, et al. Xuesaitong soft capsule in the treatment of acute cerebral infarction and its effect on hemorheology[J]. Chinese Remedies&Clinics, 2008, 8(1): 68-69. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1671-2560.2008.01.025 |
| [21] |
卢淑玲. 血塞通软胶囊治疗腔隙性脑梗死的临床疗效[J]. 中国医药指南, 2010, 8(33): 216-217. LU S L. The clinical effect of Xuesaitong soft capsule treat lacunar infarction[J]. Guide of China Medicine, 2010, 8(33): 216-217. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1671-8194.2010.33.153 |
| [22] |
郭自清, 柳四新, 陈雪莲, 等. 血塞通软胶囊联合奥扎格雷钠治疗急性脑梗死112例疗效观察[J]. 中国实用医药, 2011, 6(3): 162-163. GUO Z Q, LIU S X, CHEN X L, et al. Clinical observation of Xuesaitong soft capsule combined with Ozaggrel sodium in the treatment of 112 cases of acute cerebral infarction[J]. China Practical Medicine, 2011, 6(3): 162-163. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1673-7555.2011.03.132 |
| [23] |
张天宝. 血塞通联合拜阿司匹林在急性脑梗死中的临床疗效[J]. 航空航天医学杂志, 2016, 27(4): 428-429. ZHANG T B. The clinical effect of Xuesaitong combined with aspirin in acute cerebral infarction[J]. Journal of Aerospace Medicine, 2016, 27(4): 428-429. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.2095-1434.2016.04.011 |
| [24] |
钟惠凌, 李林锋, 李红. 血塞通软胶囊治疗脑梗死的临床效果观察[J]. 内蒙古中医药, 2017, 36(15): 73-74. ZHONG H L, LI L F, LI H. Clinical observation of Xuesaitong soft capsule in the treatment of cerebral infarction[J]. Nei Mongol Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2017, 36(15): 73-74. |
| [25] |
昌大平, 何庆华. 血塞通软胶囊佐治对脑梗死患者神经功能及生活质量的影响[J]. 海峡药学, 2017, 29(8): 134-136. CHANG D P, HE Q H. Effect of Xuesaitong soft capsule on neurological function and quality of life in patients with cerebral infarction[J]. Strait Pharmaceutical Journal, 2017, 29(8): 134-136. |
| [26] |
王美华, 翁秋燕, 查芹, 等. 血塞通软胶囊对急性腔隙性梗死合并脑微出血患者临床疗效的评价[J]. 中国临床药理学与治疗学, 2017, 22(5): 574-579. WANG M H, WENG Q Y, ZHA Q, et al. Effect of Xuesaitong soft capsule on acute lacunar cerebral infarction combined with cerebral microbleeds[J]. Chinese Journal of Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics, 2017, 22(5): 574-579. |
| [27] |
王杰. 血塞通软胶囊联合西药治疗脑梗死的临床效果[J]. 中国社区医师, 2018, 34(9): 98-99. WANG J. Clinical effect of Xuesaitong soft capsule combined with western medicine in the treatment of cerebral infarction[J]. Chinese Community Doctors, 2018, 34(9): 98-99. |
| [28] |
孔平平, 张守成. 血塞通胶囊联合阿托伐他汀对脑梗死恢复期患者神经功能影响分析[J]. 现代养生, 2020, 20(21): 77-79. KONG P P, ZHANG S C. Effect of Xuesaitong capsule combined with atorvastatin on neurological function of convalescent patients with cerebral infarction[J]. Health Protection and Promotion, 2020, 20(21): 77-79. |
| [29] |
叶献海. 血塞通胶囊联合阿托伐他汀对脑梗死恢复期患者神经功能及血液流变学的影响[J]. 河南医学研究, 2020, 29(17): 3201-3203. YE X H. Effects of Xuesaitong capsule combined with atorvastatin on neurological function and hemorheology in convalescent patients with cerebral infarction[J]. Henan Medical Research, 2020, 29(17): 3201-3203. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1004-437X.2020.17.060 |
| [30] |
徐汶. 血塞通软胶囊联合单唾液酸四己糖神经节苷脂钠对老年脑梗死患者神经功能与炎性状态的影响[J]. 现代医学与健康研究电子杂志, 2021, 5(4): 67-69. XU W. Effects of Xuesaitong soft capsule combined with sodium monosialate tetrohexose ganglioside on neurological function and inflammatory state in elderly patients with cerebral infarction[J]. Modern Medicine and Health Research Electronic Journal, 2021, 5(4): 67-69. |
| [31] |
贾宁, 王美霞, 逯鹏飞, 等. 补阳还五汤加减合血塞通注射液治疗脑梗死后遗症38例临床效果观察[J]. 实用中西医结合临床, 2015, 15(4): 46-47. JIA N, WANG M X, LU P F, et al. Clinical effect of Buyang Huanwu Decoction plus Jianhe Xuesaitong Injection on 38 cases of Sequelae of cerebral infarction[J]. Practical Clinical Journal of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine, 2015, 15(4): 46-47. |
| [32] |
董子洵, 韩晟, 林丽开, 等. 血塞通软胶囊综合评价研究[J]. 中国临床药理学杂志, 2021, 37(12): 1612-1624. DONG Z X, HAN S, LIN L K, et al. Comprehensive evaluation of Xuesaitong soft capsule[J]. The Chinese Journal of Clinical Pharmacology, 2021, 37(12): 1612-1624. |
| [33] |
杨媛媛, 孙玉坤, 姚辉. 棓丙酯联合血塞通治疗急性脑梗死的效果观察[J]. 中国当代医药, 2015, 22(31): 141-142, 145. YANG Y Y, SUN Y K, YAO H. Efficacy of Propyl gallate combined with Xuesaitong Injection for the treatment of acute cerebral infarction[J]. China Modern Medicine, 2015, 22(31): 141-142, 145. |
| [34] |
魏士贤, 崔欣, 王雪笠, 等. 血塞通软胶囊应用于脑梗死治疗中的效果评价[J]. 世界最新医学信息文摘, 2015, 15(89): 85-86. WEI S X, CUI X, WANG X L, et al. Effect evaluation of Xuesaitong soft capsule in the treatment of cerebral infarction[J]. World Latest Medicine Information, 2015, 15(89): 85-86. |
| [35] |
张俊华, 李幼平, 张伯礼. 循证中医药学: 理论与实践[J]. 中国中药杂志, 2018, 43(1): 1-7. ZHANG J H, LI Y P, ZHANG B L. Evidence-based Chinese medicine: theory and practice[J]. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica, 2018, 43(1): 1-7. |
 2022, Vol. 39
2022, Vol. 39