文章信息
- 葛凯杰, 孟佳, 王化强
- GE Kaijie, MENG Jia, WANG Huaqiang
- 不同剂量的血必净注射液对急性胰腺炎患者肺损伤的保护作用及临床疗效观察
- Effect and the clinical efficacy of Xuebijing Injection with different doses on lung functions in severe acute pancreatitis
- 天津中医药, 2022, 39(9): 1114-1117
- Tianjin Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 39(9): 1114-1117
- http://dx.doi.org/10.11656/j.issn.1672-1519.2022.09.08
-
文章历史
- 收稿日期: 2022-03-30
急性胰腺炎是一种全身性疾病,常常继发全身性炎症反应综合征和多器官功能障碍综合征。在早期胰外器官损伤中,以急性肺损伤最为突出。急性肺损伤是指氧合指数小于300,与非急性肺损伤患者相比,急性肺损伤患者的严重程度指数、住院天数和感染并发症的发生率显著增高[1],更有研究显示急性胰腺炎合并急性肺损伤的患者病死率高达为30%~60%[2-3]。临床研究表明,血必净注射液可显著改善急性胰腺炎患者体内氧化应激状态,抑制炎症反应,并具有潜在肺功能保护作用[4-6]。本研究观察了不同剂量的血必净注射液对重症胰腺炎患者肺损伤的保护作用及临床疗效。
1 资料与方法 1.1 研究对象选取2021年3月—2022年3月在许昌市中心医院重症医学科、消化内科及肝胆外科住院的急性胰腺炎合并肺损伤的患者160例作为研究对象,其中男98例,女62例,年龄22~75岁,平均年龄(53.92±3.67)岁。纳入标准:年龄>18周岁,诊断符合2019中国急性胰腺炎诊治指南[7],并合并肺损伤及胸腔积液者。排除标准:入院即存在严重感染,胸腔积液过少不能行诊断性穿刺或行胸腔闭式引流者。本研究经许昌市中心医院伦理委员会审理批准。
1.2 研究方法 1.2.1 分组按照随机数字表法将患者分为:血必净注射液50 mL每日两次(A组)、血必净注射液100 mL每日两次(B组)、血必净注射液100 mL每日3次(C组);以及基础治疗的对照组,各40例。
1.2.2 治疗方法在分别应用基础治疗和血必净注射液治疗前及治疗3 d后进行急性生理学与慢性健康状况评分系统Ⅱ(APACHEⅡ)评分、急性胰腺炎严重程度床边指数(BISAP)评分、B线评分、计算氧合指数(PaO2/FiO2),检测胸水中白介素-6(IL-6)及肿瘤坏死因子-α(TNF-α)水平。比较不同组别间监测指标的差异。
1.2.3 监测指标治疗前及治疗后的APACHEⅡ评分、BISAP评分、B线评分、PaO2/FiO2、胸水中IL-6及TNF- α水平。
1.3 统计学方法应用IBM SPSS 22.0软件进行数据分析,计量资料以均值±标准差(x±s)表示,计数资料以率(%)表示。各组正态分布计量资料间的比较采用单因素方差分析,组间比较采用多重检验(LSD-t);各组计数资料的比较Pearson χ2检验或Fisher精确检验,P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
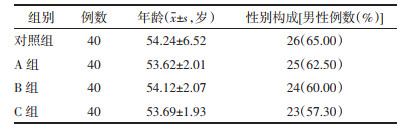
2 结果 2.1 各组患者治疗前一般资料比较各组患者的年龄、性别构成差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。见表 1。
|
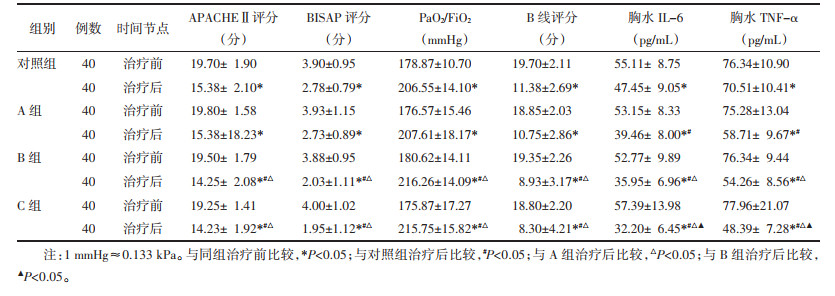
各组患者治疗前APACHEⅡ评分、BISAP评分、PaO2/FiO2、B线评分、胸水IL-6及TNF-α水平比较,差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05)。即各组在治疗前的病情严重程度具有可比性。结果表明,各组患者APACHEⅡ评分、BISAP评分、PaO2/FiO2、B线评分、胸水IL-6及TNF-α水平在治疗前后比较,差异均具有统计学意义(P < 0.05),见表 2。与基础治疗对照组比较,胸水IL-6及TNF-α水平在A组均低于对照组,且差异具有统计学意义(P < 0.05),B组、C组中的各指标改善均优于对照组,表明血必净的治疗效果优于基础治疗组。A和B组之间的APACHEⅡ评分、BISAP评分、PaO2/FiO2、B线评分、胸水IL-6及TNF-α水平比较,均存在统计学差异,说明B组治疗改善效果优于A组。C组与A组、B组比较,胸水IL-6及TNF-α水平比较,均存在统计学差异(P < 0.05),且表达水平均表现为低于A组和B组,即治疗改善效果优于A组和B组;治疗3 d后,C组APACHEⅡ评分、BISAP评分、PaO2/FiO2、B线评分与A组比较,均存在统计学差异(P < 0.05),但与B组比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。即C组在APACHEⅡ评分、BISAP评分、PaO2/FiO2、B线评分的治疗效果优于A组,但与B组比较,这4个指标的治疗效果无统计学差异。见表 2。
|
急性胰腺炎病情进展快,预后差,APACHEⅡ评分、BISAP评分、B线评分、PaO2/FiO2等从不同角度反映了急性胰腺炎及急性肺损伤的严重程度[8-9]。急性胰腺炎合并急性肺损伤的机制极为复杂,是多种炎症细胞、炎症因子和细胞因子等相互作用的结果。TNF-α和IL-6是急性胰腺炎局部炎症反应发展为严重的全身炎症反应的重要炎症介质[10-11]。
以上有关急性胰腺炎及急性肺损伤的研究从不同角度证实了全身炎症可对肺部造成的严重损伤,且伴有急性肺损伤的急性胰腺炎患者预后较差,而IL-6和TNF-α、C-反应蛋白(CRP)等炎症因子可以早期预测急性胰腺炎及急性肺损伤的严重程度,具有重要的预后评估价值。血清中的炎症因子水平反应的是全身的炎症反应程度,本研究为了探索不同剂量的血必净注射液对重症胰腺炎患者肺损伤的保护作用及临床疗效,采用抽检胸水中的IL-6、TNF-α水平,以直接反应肺部的炎症反应程度和损伤的严重程度,进而间接观察治疗效果。
血必净已被批准用于治疗重症患者的严重感染(中国食品药品监督管理局;中国北京,编号Z20040033),由当归、红花、川芎、赤芍、丹参5味活血化瘀中药组成,主要成分为羟基红花黄A、芍药苷、仙京素Ⅰ和苯甲酰芍药苷[12]。红花作为主药,活血化瘀,而赤芍和川芎作为主药,具有凉血化瘀、解毒的功效。丹参和当归补血化瘀,可以显著改善脏器微循环[13],抑制了重症急性胰腺炎患者的氧化应激状态及炎症因子的产生[14],还与抗内毒素、恢复凝血和免疫功能调节有关[15-16]。有证据表明血必净可能调节细胞因子的产生,特别是已知与炎症反应有关的TNF-α和IL-6[17]。刘丽丽等[18]研究表明血必净注射液对重症急性胰腺炎患者的肺损伤具有保护作用。董小鹏等[19]通过动物实验也表明血必净注射液可能通过抑制肺组织炎症反应,减少Toll样受体4(TLR4)、核因子κB(NF-κB)、TNF-α表达水平,从而对急性胰腺炎肺损伤大鼠产生一定保护作用。
在本研究中,不仅应用APACHEⅡ评分及BISAP评分作为治疗效果的衡量指标,而且检测了胸水中的IL-6、TNF-α水平,以此直接反应肺部的局部炎症反应。以前的多项研究表明血必净注射液对重症急性胰腺炎的肺损伤具有保护作用,但不同的剂量可能有不同的保护作用。本研究根据应用不同剂量的血必净注射液将重症急性胰腺炎患者分为A、B、C 3组,同时设置基础治疗的对照组,研究表明,血必净的治疗效果优于基础治疗组;同时,与A、B两组对比,C组的APACHEⅡ、PaO2/FiO2及胸水中的炎症因子水平均有改善,这也说明不同剂量的血必净注射液对肺具有不同的保护作用。一项真实世界的研究,血必净相关的药物不良反应(ADRs)发生率是偶然的(0.3%),和剂量之间的相关性无统计学意义(P=0.743),且大多数ADRs是相对轻微或不严重的[20]。本研究亦有一定的局限与不足,临床病例数仍偏少,期待有更大样本的研究来进一步证明。
| [1] |
MOKRÁ D. Acute lung injury-from pathophysiology to treatment[J]. Physiological Research, 2020, 69(suppl 3): S353-S366. |
| [2] |
SCHEPERS N J, BAKKER O J, BESSELINK M G, et al. Impact of characteristics of organ failure and infected necrosis on mortality in necrotising pancreatitis[J]. Gut, 2019, 68(6): 1044-1051. DOI:10.1136/gutjnl-2017-314657 |
| [3] |
杨林, 陈培莉, 刘永生. 老年重症急性胰腺炎合并急性肺损伤/急性呼吸窘迫综合征的临床特点和预后相关因素分析[J]. 中国医学工程, 2022, 30(3): 36-39. YANG L, CHEN P L, LIU Y S. Clinical characteristics and prognostic factors of severe acute pancreatitis with ALI/ARDS in elderly patients[J]. China Medical Engineering, 2022, 30(3): 36-39. |
| [4] |
陈加链, 蔡燕杏, 陈科署, 等. 血必净注射液对重症急性胰腺炎氧化应激的影响及肺损伤的作用[J]. 中国现代普通外科进展, 2018, 21(12): 992-994. CHEN J L, CAI Y X, CHEN K S, et al. Effect of Xuebijing Injection on oxidative stress to protect lung in severe acute pancreatitis[J]. Chinese Journal of Current Advances in General Surgery, 2018, 21(12): 992-994. |
| [5] |
余国栋. 血必净注射液治疗重症急性胰腺炎对炎性因子的干预效果[J]. 临床合理用药杂志, 2019, 12(11): 58-59. YU G D. Intervention effect of Xuebijing Injection on inflammatory factors in the treatment of severe acute pancreatitis[J]. Chinese Journal of Clinical Rational Drug Use, 2019, 12(11): 58-59. |
| [6] |
窦志敏, 尹超, 李斌, 等. 血必净对重症急性胰腺炎患者氧化应激的影响[J]. 中国中西医结合消化杂志, 2018, 26(3): 289-292. DOU Z M, YIN C, LI B, et al. Effects of Xuebijing on oxidative stress in patients with severe acute pancreatitis[J]. Chinese Journal of Integrated Traditional and Western Medicine on Digestion, 2018, 26(3): 289-292. |
| [7] |
杜奕奇, 陈其奎, 李宏宇, 等. 中国急性胰腺炎诊治指南(2019年, 沈阳)[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2019, 35(12): 2706-2711. DU Y Q, CHEN Q K, LI H Y, et al. Chinese guidelines for the management of acute pancreatitis (Shenyang, 2019)[J]. Journal of Clinical Hepatology, 2019, 35(12): 2706-2711. |
| [8] |
HARSHIT KUMAR A, SINGH GRIWAN M. A comparison of APACHEⅡ, BISAP, Ranson's score and modified CTSI in predicting the severity of acute pancreatitis based on the 2012 revised Atlanta Classification[J]. Gastroenterology Report, 2017, 6(2): 127-131. |
| [9] |
ZHENG L, HONG W, GENG W, et al. A comparison of the BISAP score and Amylase and BMI(CAB) score versus for predicting severe acute pancreatitis[J]. Acta Gastro-Enterologica Belgica, 2019, 82(3): 397-400. |
| [10] |
ZHANG H, NEUHÖFER P, SONG L, et al. IL-6 trans-signaling promotes pancreatitis-associated lung injury and lethality[J]. The Journal of Clinical Investigation, 2013, 123(3): 1019-1031. |
| [11] |
SCHWEDE M, WILFONG E M, ZEMANS R L, et al. Effects of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal cells on gene expression in human alveolar type Ⅱ cells exposed to TNF-α, IL-1β, and IFN-γ[J]. Physiological Reports, 2018, 6(16): e13831. |
| [12] |
ZUO L H, SUN Z, HU Y R, et al. Rapid determination of 30 bioactive constituents in Xuebijing Injection using ultra high performance liquid chromatography-high resolution hybrid quadrupole-orbitrap mass spectrometry coupled with principal component analysis[J]. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis, 2017, 137: 220-228. |
| [13] |
刘艳春, 张雪梅, 李英, 等. 血必净联合阿托伐他汀对糖尿病肾病患者氧化应激水平的影响[J]. 微循环学杂志, 2017, 27(3): 62-67. LIU Y C, ZHANG X M, LI Y, et al. Effects of Xuebijing combined with atorvastatin on oxidative stress level of patients with diabetic kidney disease[J]. Chinese Journal of Microcirculation, 2017, 27(3): 62-67. |
| [14] |
JIANG Y, ZOU L H, LIU S L, et al. GC/MS-based metabonomics approach reveals effects of Xuebijing Injection in CLP induced septic rats[J]. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, 2019, 117: 109163. |
| [15] |
CHEN S G, DAI G X, HU J W, et al. Discovery of Xuebijing Injection exhibiting protective efficacy on sepsis by inhibiting the expression of HMGB1 in septic rat model designed by cecal ligation and puncture[J]. American Journal of Therapeutics, 2016, 23(6): e1819-e1825. |
| [16] |
SONG Y L, YAO C, YAO Y M, et al. Xuebijing Injection versus placebo for critically ill patients with severe community-acquired pneumonia: a randomized controlled trial[J]. Critical Care Medicine, 2019, 47(9): e735-e743. |
| [17] |
CHEN X, FENG Y X, SHEN X Y, et al. Anti-Sepsis protection of Xuebijing injection is mediated by differential regulation of pro- and anti-inflammatory Th17 and T regulatory cells in a murine model of polymicrobial Sepsis[J]. Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 2018, 211: 358-365. |
| [18] |
刘丽丽, 洪路贤, 屈苗. 血必净注射液对重症急性胰腺炎患者肺损伤的保护作用[J]. 中国现代普通外科进展, 2020, 23(1): 54-56. LIU L L, HONG L X, QU M. Effect of Xuebijing Injection on lung functions in severe acute pancreatitis[J]. Chinese Journal of Current Advances in General Surgery, 2020, 23(1): 54-56. |
| [19] |
董小鹏, 王丽娟, 赵春霖, 等. 血必净注射液对急性胰腺炎大鼠肺损伤及肺组织TLR4、NF-κB、TNF-α表达的影响[J]. 中成药, 2020, 42(11): 3025-3030. DONG X P, WANG L J, ZHAO C L, et al. Effects of Xuebijing Injection on lung injury and expression of TLR4, NF-κB and TNF-α in lung tissue in rats with acute pancreatitis[J]. Chinese Traditional Patent Medicine, 2020, 42(11): 3025-3030. |
| [20] |
ZHENG R, WANG H, LIU Z, et al. A real-world study on adverse drug reactions to Xuebijing Injection: hospital intensive monitoring based on 93 hospitals (31 913 cases)[J]. Annals of translational medi- cine, 2019, 7(6): 117. |
 2022, Vol. 39
2022, Vol. 39