文章信息
- 李志鹏, 赵少莉, 曹世杰, 等.
- LI Zhipeng, ZHAO Shaoli, CAO Shijie, et al.
- 基于CiteSpace和Vosviewer知识图谱对中医湿热证基础研究的可视化分析
- Visualization analysis of knowledge graph of traditional Chinese medicine literature about damp-heat syndrome based on CiteSpace and Vosviewer
- 天津中医药, 2023, 40(10): 1253-1262
- Tianjin Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 40(10): 1253-1262
- http://dx.doi.org/10.11656/j.issn.1672-1519.2023.10.06
-
文章历史
- 收稿日期: 2023-06-28
2. 天津中医药大学现代中药国家重点实验室, 天津 301617;
3. 天津中医药大学中药学院, 天津 301617
湿热首见于《素问·生气通天论》,其称“困于湿,首如裹,湿热不攘,大筋软短,小筋弛长,软短为拘,弛长为痿”。湿热证[1]是指由湿热邪气引发,表现为湿邪和热邪的相互搏结,如清代医家薛生白曾言“热得湿而热愈炽,湿得热而湿愈横。湿热两分,其病轻而缓;湿热两合,其病重而速”。朱丹溪言“六气之中,湿热为患,十之八九”,体现了湿热证发病具有致病广泛、病症繁多的特点。湿热证在临床上常表现为慢性浅表性胃炎、慢性乙型肝炎、尿路感染、2型糖尿病、肾功能衰竭等多种疾病,包含脾胃湿热、脾虚湿热、下焦湿热、肝胆湿热等多个证型[2]。湿热证以头身重痛、身热不扬、四肢倦怠乏力、口不仁面垢、口渴或不渴、小便黄、大便黏滞不爽、舌红苔黄腻为主要临床表现。薛生白在《湿热病篇》中认为,湿热证的发病是由“内外相引”而造成的;此外,清·叶天士《温热论》中提及湿热证是内外合邪发为病,“外邪入里,里湿为合”,外湿是疾病发生的主要原因,内湿是发病的内在依据。因现代人嗜食肥甘厚味,脾胃运化吸收不及则内生湿邪,如《仁斋直指方》有“饮食失调而生湿热”,在脾胃内湿的基础之上,加之外感湿热之邪,内外合邪,蕴久化为湿热。正如薛生白在《湿热病篇》中提及“太阴内伤,湿邪停聚,客邪再至,内外相引,故病湿热。”正是因为在嗜食肥甘厚味的饮食习惯与湿热外邪环境的共同影响下,导致近年来湿热证相关疾病的患者数量在不断增加。
近年来不断有学者对湿热证进行探索研究,但是尚缺乏对中医湿热证基础研究文献的计量学分析。而研究通过CiteSpace5.8.R1和Vosviewer软件进行演算,对中医湿热证基础研究相关文献进行可视化分析,从而探讨湿热证研究的热点、前沿及趋势,为中医湿热证进一步的深入研究提供借鉴意义。
CiteSpace和VOSviewer软件可通过可视化方法呈现出科学知识的结构、规律和分布情况,被应用于科学文献中识别并显示科学发展新趋势和新动态[3-4],在中医药领域多被应用于分析中医药防治疾病的研究进展[5-6]。
1 资料与方法 1.1 数据采集文章数据来源于中国知网(CNKI)、万方、维普数据库,检索方式为“主题”,检索词选定为“湿热”“湿热证”,检索时间为2000年1月—2021年12月。纳入标准:研究内容涉及中医湿热证基础研究相关文献。研究共纳入360篇文献。
1.2 数据处理将纳入的文献以Refworks格式导出,并以“download_***”的格式命名,导出的文献记录包含作者、研究机构、题名、摘要、关键词、发表年份等。通过CiteSpace和Vosviewer软件对作者、机构和关键词进行可视化分析。
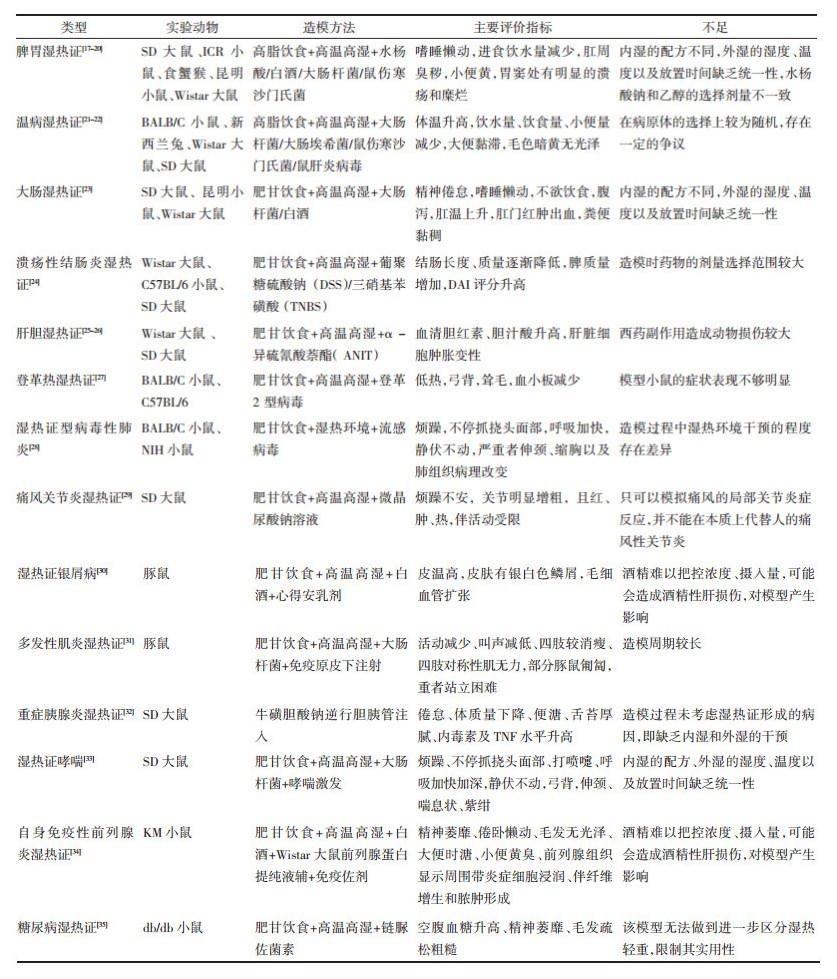
2 结果 2.1 文献发表时间文献发表数量的历年变化情况代表了该领域学术理论水平和发展情况[7]。排除不相关的文献后,共纳入中医湿热证基础研究文献360篇,年度发文量如图 1所示,以2000—2012年为第一阶段,发文量整体呈现上涨趋势,其中2000年发文量2篇为最低值,2012年达到最高值30篇,说明中医湿热证研究取得突破性进展,引起行业广泛关注。2012—2016年期间发文量逐渐下降,但是自2016—2021年之间再次快速上涨,说明湿热证的研究逐渐被重新重视,已成为当前研究的热点。
|
| 图 1 文献发表时间分布 Fig. 1 Time distribution of literature publication |
对作者共现分析[8],如图 2所示,N表示节点/数量,E表示节点间对象之间的连线,作者合作可视化图谱中N=357,E=508,表明本研究纳入的360篇文献共由357名作者完成,作者之间合作了508次,说明作者之间的联系较为紧密。主要形成了以文小敏、惠华英、林培政为主的核心研究团队,其中文小敏团队侧重探讨中药在脾胃湿热证大鼠模型中的应用,惠华英团队主要集中于研究葛根芩连汤对肠道湿热证泄泻小鼠模型的影响,林培政团队则开展了中药对病毒感染湿热证模型疗效的研究。
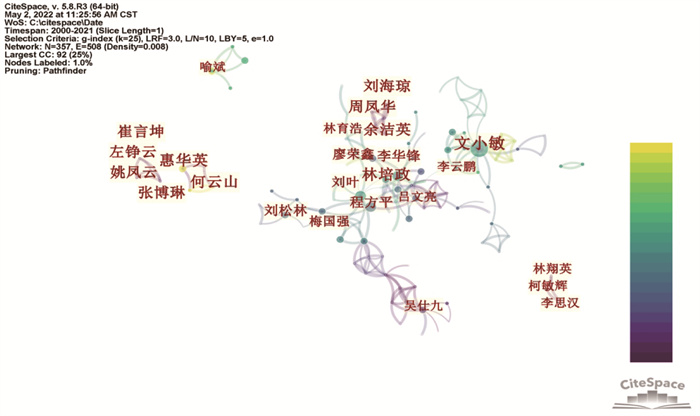
|
| 图 2 作者合作网络知识图谱 Fig. 2 Author collaboration network knowledge graph |
对机构合作网络的可视化图谱分析,节点之间的连线粗细代表不同机构之间的合作强度。如图 3所示,得到的可视化图谱中共包含225家研究机构,合作了204次,网络密度为0.008 1。主要形成了以南方医科大学中医药学院、湖南中医药大学、广州中医药大学为主的研究机构。

|
| 图 3 研究机构合作网络知识图谱 Fig. 3 Knowledge graph of research institution collaboration network |
论文中高频关键词分析以图谱的形式呈现出来,可以借此寻找该领域的研究热点[9]。中医药防治湿热证基础研究的关键词如图 4所示,排名前10的高频关键词见于表 1。Vosviewer软件对关键词进行共现分析,标签越大,说明关键词出现的频次越高。在湿热证型方面,脾胃湿热证、温病湿热证、大肠湿热证为当前主要的研究热点;中药复方研究方面,三仁汤、葛根芩连汤、王氏连朴饮、甘露消毒丹、灭幽汤为当前研究热点;此外,湿热证动物模型的建立也成为当前中医药防治湿热证的研究重点。
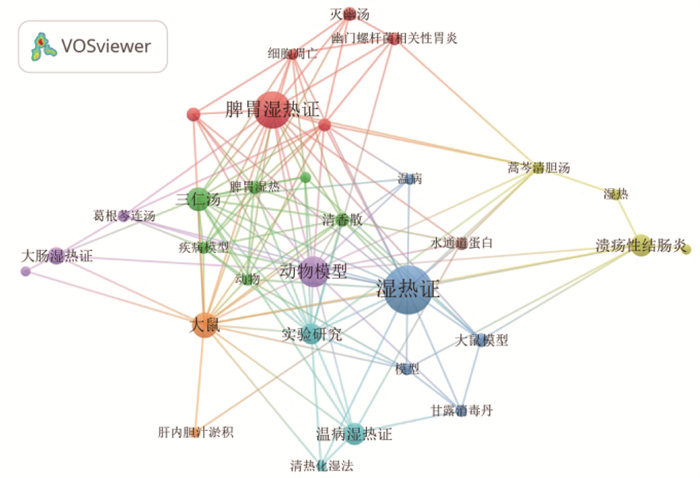
|
| 图 4 关键词共现图谱 Fig. 4 Keyword co-occurrence graph |
关键词聚类分析通过对具有多项指标的信息数据按照信息程度进行分类,能够反映该领域研究文献的集中程度[10-11]。一般认为,聚类模块值(Q) > 0.3,提示聚类结构显著;平均轮廓值(S) > 0.7意味着聚类是令人信服的[12]。如图 5所示,聚类Q值为0.8301,S值为0.9518,提示本研究聚类显著且真实可信。共得到10个聚类,分别是“#0脾胃湿热证”“#1大鼠模型”“#2动物模型”“#3大肠杆菌”“#4葛根芩连汤”“#5 ntcp”“#6肠道菌群”“#7清化理气通便法”“#8实验研究”“#9 aqp4”。聚类标签(#)的数字越小,代表该聚类规模越大。

|
| 图 5 关键词聚类图谱 Fig. 5 Keyword clustering graph |
综合分析高频次以及关键词聚类结果,可以基本确定近21年来中医湿热证的基础研究与湿热证动物模型的构建、湿热证型的探索以及复方药理作用的研究等领域关系密切。
2.4.3 关键词突现分析关键词突现分析是指关键词在短时间内使用频次显著增加,通过对关键词进行突显分析,可以有效反映某段时间内关注度较高的研究内容,显示不同研究热点的转移,判断潜在的发展趋势和研究前沿[13]。“Begin”和“End”为突变开始和结束的时间,“Strength”为关键词突现的强度,强度越高表示其影响力越大。如图 6所示,对文献中前8个突现词进行分析,发现每个时间阶段的研究重点各有不同,而从肠道菌群和炎症因子方面考察中药复方对湿热证的治疗成为未来一段时间的研究热点。
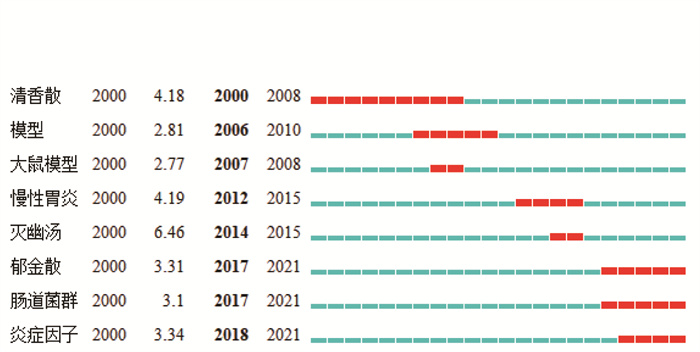
|
| 图 6 关键词突现图谱(排名前8) Fig. 6 Keyword emergence graph (top 8) |
相关文献时间分布结果表明,2005年之后中医湿热证的研究逐渐受到关注,并保持一定的研究热度。作者合作网络图谱得到以文小敏、惠华英、林培政为主的核心研究团队,作为该领域的学术引领者,团队之间的合作较为紧密,使得中医药治疗湿热证研究有了长足的发展。多所中医药大学及其附属医院对于湿热证研究做出了较为突出的贡献,尤其以南方学术机构对湿热证的研究居多,这种情况的出现或许与岭南地区独特的气候和地理环境易造成湿热证患者数量较多有关。然而,目前缺乏跨地域之间的交流与合作,导致研究相对分散,地域发展不平衡。未来须突破地域障碍,通过加强区域合作,加大研究成果交流,以推动该领域的学术进步与发展。
3.2 湿热证的研究现状关键词是对文献研究的高度概括,通过对关键词的偶联分析可以了解某个领域的发展态势,而高频关键词常被用来揭示该领域的研究热点和前沿[14]。通过对高频关键词以及关键词聚类进行综合分析,发现中医湿热证的动物模型、湿热证型、复方药理作用成为当前中医药防治湿热证基础研究的主要内容。
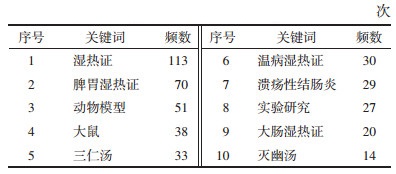
研究所纳入的中医湿热证动物模型的分类整理详见图 7、表 2(其中有的研究涉及两种实验动物)。根据湿热证的研究现状,发现当前研究过程中用于湿热证造模的实验动物种类繁多,造模方法多样化,导致同一种疾病无法建立起具有统一评价标准的动物模型[15-16]。同时,在建立动物模型的过程中,存在实验人员的主观性强的问题,最终导致同类文章之间缺乏可比性。而缺乏合理的实验模型,便不能更好地反映中医证候学的特点,很难与中医的传统病因病机、辨证论治相结合。因此,对于不同疾病所需要的中医湿热证的动物模型尚需进一步研究,在模型的选取上多依据中医传统理论“外邪入里,里湿为合”的原则,模拟临床疾病的病因,结合动物的行为学改变和微观生化病理指标,建立起具有客观评价标准的动物模型,这将对于进一步阐释中医药防治湿热证的作用机制具有重要的方法学意义。
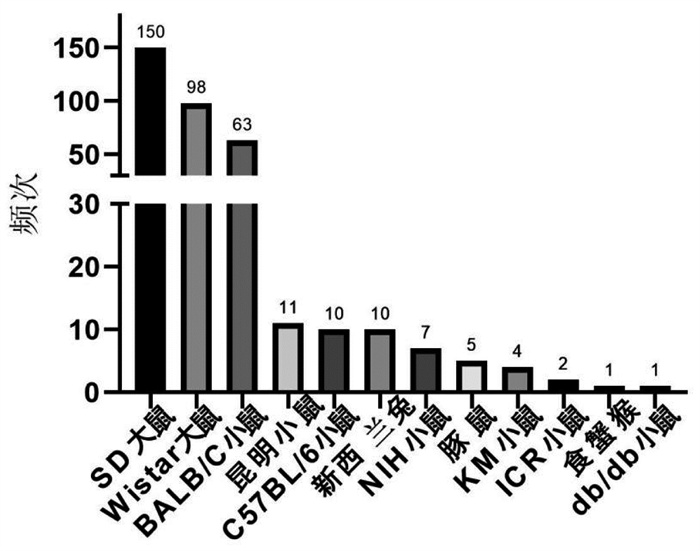
|
| 图 7 湿热证动物模型使用频次 Fig. 7 Frequency of using animal models of dampness heat syndrom |
此外,研究纳入的文献以脾胃湿热证(109篇)、温病湿热证(67篇)、溃疡性结肠炎湿热证(33篇)、大肠湿热证(28篇)为主要研究证型,涉及到消化系统和代谢系统等方面的疾病。然而,中医湿热证的证型较为丰富,目前的研究方向存在过于集中的现象,导致其余临床常见湿热证型,如肝胆湿热证、膀胱湿热证等证型的研究相对较少。由于湿热证的各种证型之间存在一定的关联性,因此为进一步丰富中医湿热证的科学内涵,理应在拓宽湿热证研究方向的基础上,加强湿热证不同证型之间的相互比较。通过采用多因素比较的方法,发现相关证型之间的联系,利用不同证候和微观指标的关系来充分发挥中医辨证论治的优势,有助于使中医湿热证的研究工作更加深入。
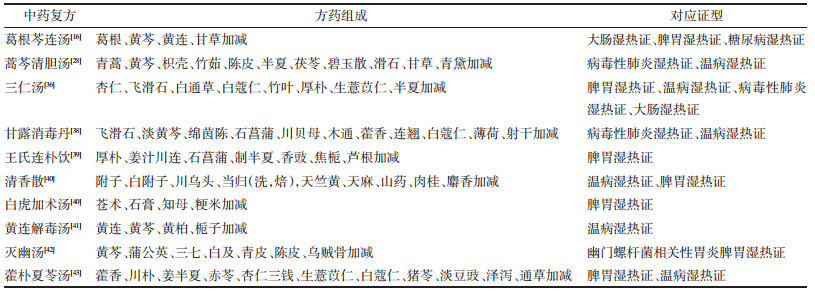
在中药复方药理作用方面,研究纳入的文献共涉及57种中药复方,其中以三仁汤(45篇)、王氏连朴饮(28篇)、蒿芩清胆汤(23篇)、清香散(18篇)、甘露消毒丹(15篇)、黄连解毒汤(15篇)、灭幽汤(14篇)、葛根芩连汤(13篇)等中药复方药理作用的研究最为常见,如表 3所示。此前有学者发现中药复方对湿热证的治疗有积极的推动作用,如三仁汤通过纠正脾胃湿热证大鼠胃黏膜上皮细胞增殖与凋亡的失衡、降低炎症反应程度,从而促进胃黏膜损伤修复[36]。葛根芩连汤可以调控肠道微生态平衡,恢复湿热证泄泻小鼠肠道菌群的物种多样性,并且可以调整细菌不同物种之间的相对含量[37]。甘露消毒丹可以通过影响炎性相关因子的含量以及AQP1的表达,从而抑制湿热证病毒性肺炎小鼠的炎症反应,此外,还可以抑制流感病毒核酸mRNA的表达[38]。因为中药复方治疗湿热证具有靶点多、途径多、层次多的特点,通过药理、病理、生化、免疫等多学科的交叉研究,引入新技术和新方法,深入探究中药复方治疗湿热证的作用机制,才能更好地佐证中药复方的疗效,完善中药复方的理论基础,以便于更好地应用于临床。
|
对关键词的突现结果进行分析及文献回顾,可预测中医湿热证领域研究的热点与前沿。发现从肠道菌群和炎症因子这两方面探索中药治疗湿热证的作用机制将成为未来研究的趋势。肠道菌群通过免疫、内分泌和代谢等途径参与调节机体的生理功能,而肠道菌群的紊乱则会导致机体内环境稳态的失衡,使生理功能发生失调。现有的实验数据已经证实湿热证可以影响肠道菌群多样性和丰度的改变,但是中医药在肠道微生态方面的研究存在着明显的不足,即缺乏深入的分子生物学机制研究,若通过多靶点、多途径研究,深入探索中医湿热证与肠道微生态之间的关系,可以丰富和发展中医证候学中微生态的科学内涵。
炎症反应是自我防御的体现,但是过度炎症反应的发生会对机体造成一定的损伤,而湿热证的形成与机体的炎症反应有关。现代研究表明湿热证促进多种炎症细胞因子基因的表达,导致严重的炎症反应,因而,从改善炎症角度探讨中药治疗湿热证的作用机制,可以为中药治疗湿热证的现代应用提供实验依据。由于中药复方制剂的有效成分并非是单药有效成分的相互叠加,因此其具体的作用机制还需要进一步地挖掘与探索。
4 结论近年来,大量学者参与中医湿热证的基础研究工作,拓宽了湿热证研究的思路,为揭示中医药治疗湿热证的疗效提供了理论依据。虽然湿热证的研究取得了一定成果,但是尚未取得突破性进展,其重要原因是缺乏合理的动物模型,现有的湿热证动物模型无法明确湿热证的生物学基础,影响中医药治疗湿热证的作用机制阐明。因此须建立起具有统一评价标准的动物模型,并从肠道菌群和炎症因子层次,深入探讨中药复方治疗湿热证的作用机制,将会成为未来一段时间内该领域的研究热点。
| [1] |
商俊芳, 刘宝厚, 魏锦慧. 刘宝厚教授从湿热辨治肾脏病的经验[J]. 时珍国医国药, 2015, 26(10): 2524-2525. SHANG J F, LIU B H, WEI J H. Professor Liu Baohou's experience in treating kidney disease from dampness and heat[J]. Lishizhen Medicine and Materia Medica Research, 2015, 26(10): 2524-2525. |
| [2] |
林育, 项磊, 肖雪, 等. 基于临床研究的湿热证文本信息挖掘[J]. 广东药科大学学报, 2017, 33(5): 654-658. LIN Y, XIANG L, XIAO X, et al. Information mining of damp-heat syndrome based on clinical research[J]. Journal of Guangdong Pharmaceutical University, 2017, 33(5): 654-658. |
| [3] |
王龙, 代彦林, 韩姗姗, 等. 基于CiteSpace的中医"病证结合"文献知识图谱可视化分析[J]. 时珍国医国药, 2021, 32(1): 242-244. WANG L, DAI Y L, HAN S S, et al. Visualization analysis of traditional Chinese medicine literature knowledge map of "combination of disease and syndrome" based on CiteSpace[J]. Lishizhen Medicine and Materia Medica Research, 2021, 32(1): 242-244. |
| [4] |
韩姗姗, 代彦林, 丁樱, 等. 雷公藤毒性研究进展的CiteSpace知识图谱分析[J]. 中国中药杂志, 2022, 47(4): 1085-1094. HAN S S, DAI Y L, DING Y, et al. CiteSpace knowledge map analysis of research progress on Tripterygium wilfordii toxicity[J]. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica, 2022, 47(4): 1085-1094. DOI:10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20211108.501 |
| [5] |
余泽芸, 武平, 胡远樟, 等. 基于CiteSpace分析针灸在治疗类风湿性关节炎中的应用[J]. 世界科学技术-中医药现代化, 2020, 22(8): 2758-2763. YU Z Y, WU P, HU Y Z, et al. Application of acupuncture and moxibustion in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis based on CiteSpace[J]. Modernization of Traditional Chinese Medicine and Materia Medica-World Science and Technology, 2020, 22(8): 2758-2763. |
| [6] |
王艳秋, 孟翔鹤, 秦静波, 等. 基于Citespace的中医药治疗过敏性紫癜可视化分析[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志, 2020, 26(10): 173-179. WANG Y Q, MENG X H, QIN J B, et al. Visualization analysis of henoch-schonlein Purpura treated by traditional Chinese medicine based on citespace[J]. Chinese Journal of Experimental Traditional Medical Formulae, 2020, 26(10): 173-179. |
| [7] |
熊金璐, 于迪, 宋来辉, 等. 基于CiteSpace的矿物药研究现状可视化分析[J]. 中草药, 2021, 52(4): 1105-1116. XIONG J L, YU D, SONG L H, et al. Visualization analysis of status of mineral medicine based on CiteSpace[J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs, 2021, 52(4): 1105-1116. |
| [8] |
谢丽华, 蔺晓源, 李昕, 等. 基于CiteSpace可视化分析中医药促神经再生研究热点与趋势[J]. 中国中药杂志, 2021, 46(17): 4555-4562. XIE L H, LIN X Y, LI X, et al. Visualization analysis of traditional Chinese medicine for neurogenesis research based on CiteSpace[J]. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica, 2021, 46(17): 4555-4562. |
| [9] |
陈芳, 张士靖. 基于知识图谱的我国医院图书馆研究热点和前沿分析[J]. 中华医学图书情报杂志, 2016, 25(8): 19-23. CHEN F, ZHANG S J. Knowledge mapping-based analysis of hot spots and frontiers in studies on domestic hospital libraries[J]. Chinese Journal of Medical Library and Information Science, 2016, 25(8): 19-23. |
| [10] |
林巧, 何庆勇, 但文超, 等. 基于CiteSpace的中医药治疗眩晕的知识图谱分析[J]. 世界科学技术-中医药现代化, 2021, 23(3): 739-749. LIN Q, HE Q Y, DAN W C, et al. Mapping knowledge domain analysis on the treatment of Vertigo with traditional Chinese medicine[J]. Modernization of Traditional Chinese Medicine and Materia Medica-World Science and Technology, 2021, 23(3): 739-749. |
| [11] |
王松, 杨涛, 胡孔法. 基于CiteSpace的中医药治疗肺癌知识图谱可视化分析[J]. 世界科学技术-中医药现代化, 2020, 22(10): 3549-3557. WANG S, YANG T, HU K F. Visualization analysis on knowledge graph of traditional Chinese medicine in treating lung cancer based on cite space[J]. Modernization of Traditional Chinese Medicine and Materia Medica-World Science and Technology, 2020, 22(10): 3549-3557. |
| [12] |
朱素梅, 覃仕娜, 覃淼, 等. 基于CiteSpace的2016—2021年国内外中药质量标志物研究文献的计量学分析[J]. 中草药, 2021, 52(9): 2575-2588. ZHU S M, QIN S N, QIN M, et al. Bibliometric analysis of literatures on quality marker of Chinese medicine at domestic and abroad from 2016 to 2021 based on CiteSpace[J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs, 2021, 52(9): 2575-2588. |
| [13] |
叶丽妮, 王宣尹, 邝梓君, 等. 基于CiteSpace的中医药治疗子宫内膜异位症知识图谱分析[J]. 世界科学技术-中医药现代化, 2021, 23(10): 3503-3510. YE L N, WANG X Y, KUANG Z J, et al. Knowledge map analysis of Chinese medicine treatment of endometriosis based on CiteSpace[J]. Modernization of Traditional Chinese Medicine and Materia Medica-World Science and Technology, 2021, 23(10): 3503-3510. |
| [14] |
陈定芳, 吴月峰, 李海英, 等. 基于CiteSpace文献计量法的中西医治疗痉挛型脑瘫文献可视化图谱分析[J]. 中草药, 2021, 52(14): 4318-4326. CHEN D F, WU Y F, LI H Y, et al. Visual atlas analysis on documents of traditional Chinese and Western medicine for treatment of spastic cerebral palsy based on CiteSpace bibliometrics[J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs, 2021, 52(14): 4318-4326. |
| [15] |
甘斌, 李华南, 章晓云, 等. 湿热证急性痛风性关节炎动物模型的建立与评价[J]. 江西中医药, 2021, 52(5): 77-80. GAN B, LI H N, ZHANG X Y, et al. Establishment and evaluation of animal model of acute gouty arthritis with damp heat syndrome[J]. Jiangxi Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2021, 52(5): 77-80. |
| [16] |
肖嫩群, 何云山, 张晨阳, 等. 葛根芩连汤对肠道湿热证泄泻小鼠肠道微生物的影响[J]. 中国微生态学杂志, 2020, 32(10): 1140-1144. XIAO N Q, HE Y S, ZHANG C Y, et al. Effect of Gegen Qinlian Decoction on intestinal microbiota in diarrhea mice with intestinal dampness-heat syndrome[J]. Chinese Journal of Microecology, 2020, 32(10): 1140-1144. |
| [17] |
胡锦洋, 蒋士生, 肖梅英, 等. 幽门螺杆菌ICR小鼠脾胃湿热证动物模型的建立[J]. 湖南中医杂志, 2020, 36(1): 140-142. HU J Y, JIANG S S, XIAO M Y, et al. Establishment of an animal model of Helicobacter pylori-related gastritis with spleen-stomach damp-heat using Institute of Cancer Research mice[J]. Hunan Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2020, 36(1): 140-142. |
| [18] |
梁丹, 李晓红, 唐耀平, 等. 食蟹猴急性酒精性脂肪肝脾胃湿热证模型的建立与评价初探[J]. 中华中医药杂志, 2021, 36(3): 1374-1378. LIANG D, LI X H, TANG Y P, et al. Preliminary study on establishment and evaluation of spleen-stomach damp-heat syndrome model of cynomolgus monkey with acute alcoholic fatty liver[J]. China Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine and Pharmacy, 2021, 36(3): 1374-1378. |
| [19] |
段继昌, 曹路, 柴晶美, 等. 湿热中阻方对脾胃湿热证小鼠氧化应激和炎症因子影响研究[J]. 吉林中医药, 2021, 41(5): 647-653. DUAN J C, CAO L, CHAI J M, et al. Study on the effect of Shire Zhongzha Fang on the oxidative stress and inflammatory factors in mice with the spleen and stomach dampness-heat syndrome[J]. Jilin Journal of Chinese Medicine, 2021, 41(5): 647-653. |
| [20] |
盛小燕, 叶勇峰, 丁懿宁, 等. 清热祛湿凉茶对脾胃湿热证大鼠血清中NO、SOD和MDA水平以及结肠中Nrf2/HO-1表达影响[J]. 中南药学, 2019, 17(10): 1631-1636. SHENG X Y, YE Y F, DING Y N, et al. Effect of Qingre Qushi herbal tea on the serum level of NO, SOD and MDA and Nrf2/HO-1 expression in rats with spleen-stomach damp-heat syndrome[J]. Central South Pharmacy, 2019, 17(10): 1631-1636. |
| [21] |
常丽萍, 阙铁生, 吕军影, 等. 温病湿热证大鼠模型复制的条件探索[J]. 时珍国医国药, 2012, 23(5): 1243-1246. CHANG L P, QUE T S, LYU J Y, et al. Exploration on the conditions of replication of rat model with damp-heat syndrome of epidemic febrile disease[J]. Lishizhen Medicine and Materia Medica Research, 2012, 23(5): 1243-1246. |
| [22] |
张俊英. 湿病湿热证湿重于热与热重于湿模型制作的初步研究[D]. 武汉: 湖北中医学院, 2009. ZHANG J Y. A preliminary study on damp-heat syndrome of seasonal febrile disease dominant damp over heat model and dominant heat over damp model-making[D]. Wuhan: Hubei University of Chinese Medicine, 2009. |
| [23] |
姚万玲, 文艳巧, 华永丽, 等. 郁金散对大肠湿热证大鼠回肠、结肠黏膜SIgA和炎性因子的影响[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2019, 50(10): 2147-2155. YAO W L, WEN Y Q, HUA Y L, et al. Effects of Yujin Powder on SIgA and inflammatory cytokines in ileal and colonic mucosa of large intestine dampness-heat syndrome rat[J]. Chinese Journal of Animal and Veterinary Sciences, 2019, 50(10): 2147-2155. |
| [24] |
张泽丹, 王凤云, 张佳琪, 等. 溃疡性结肠炎湿热证动物模型的建立与评价[J]. 中国中西医结合杂志, 2022, 42(1): 66-74. ZHANG Z D, WANG F Y, ZHANG J Q, et al. Establishment and evaluation of animal model of ulcerative colitis with damp heat syndrome[J]. Chinese Journal of Integrated Traditional and Western Medicine, 2022, 42(1): 66-74. |
| [25] |
荀蕾. 疸清颗粒干预湿热证肝内胆汁淤积大鼠的实验及临床研究[D]. 沈阳: 辽宁中医药大学, 2016. XUN L. Experimental and clinical study of danqing granule in intervening intrahepatic cholestasis in rats with damp-heat syndrome[D]. Shenyang: Liaoning University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2016. |
| [26] |
吴海滨, 佘世锋, 兰绍阳. 茵栀黄注射液对肝内胆汁淤积湿热证大鼠NTCP、BSEP表达的影响[J]. 时珍国医国药, 2015, 26(10): 2318-2321. WU H B, SHE S F, LAN S Y. Effect of Yinzhihuang injection on the expression of NTCP and BSEP in rats with damp-heat syndrome of intrahepatic cholestasis[J]. Lishizhen Medicine and Materia Medica Research, 2015, 26(10): 2318-2321. |
| [27] |
李玉静, 赵卫, 张玲, 等. 登革病毒感染湿热证小鼠模型的建立[J]. 中华中医药杂志, 2011, 26(11): 2582-2585. LI Y J, ZHAO W, ZHANG L, et al. Establishment of mouse model of Dengue Fever damp-heat syndrome[J]. China Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine and Pharmacy, 2011, 26(11): 2582-2585. |
| [28] |
刘叶, 吴智兵, 林兴栋, 等. 蒿芩清胆汤对流感病毒性肺炎湿热证模型小鼠免疫损伤的影响[J]. 上海中医药大学学报, 2011, 25(2): 51-55. LIU Y, WU Z B, LIN X D, et al. Influence of "Haoqin Qingdan Decoction" on immune injury in influenza viral pneumonia of dampness-heat syndrome in mouse[J]. Academic Journal of Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2011, 25(2): 51-55. |
| [29] |
熊辉, 曲良烨, 向黎黎, 等. 痛风性关节炎湿热证病证结合模型的建立[J]. 中医正骨, 2014, 26(3): 14-20. XIONG H, QU L Y, XIANG L L, et al. A rat model of gouty arthritis combined with dampness-heat syndrome[J]. The Journal of Traditional Chinese Orthopedics and Traumatology, 2014, 26(3): 14-20. |
| [30] |
王玉芝. 银屑病湿热证动物模型的构建[J]. 山东中医杂志, 2013, 32(7): 489-490. WANG Y Z. Construction of animal model of psoriasis with damp-heat syndrome[J]. Shandong Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2013, 32(7): 489-490. |
| [31] |
赖名慧, 刘友章. 多发性肌炎湿热证模型的制作[J]. 中华中医药杂志, 2009, 24(4): 522-525. LAI M H, LIU Y Z. Establishing model of polymyositis with damp-heat syndrome[J]. China Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine and Pharmacy, 2009, 24(4): 522-525. |
| [32] |
齐文杰, 张淑文, 王红, 等. 急性重症胰腺炎湿热证动物模型建立初探[J]. 中国中医药信息杂志, 2011, 18(2): 47-50. QI W J, ZHANG S W, WANG H, et al. Preliminary study of animal modeling of severe acute pancreatitis with damp-heat syndrome[J]. Chinese Journal of Information on Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2011, 18(2): 47-50. |
| [33] |
李成刚. 儿童湿热哮喘临床指标相关性及加味茵陈蒿汤对湿热哮喘模型鼠Th17细胞影响的研究[D]. 济南: 山东中医药大学, 2020. LI C G. Research on correlation of clinical indexes of children's damp and heat asthma and effect of Jiawei Yinchenhao Decoction on Th17 cells in mice model of damp and heat asthma[D]. Jinan: Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2020. |
| [34] |
朱闽, 徐楠, 荀建宁, 等. 建立实验性自身免疫性前列腺炎湿热证病证结合小鼠模型探讨[J]. 中华中医药学刊, 2018, 36(3): 531-534. ZHU M, XU N, XUN J N, et al. To establish mice model of experimental autoimmune prostatitis combined with dampeness-heat syndrome[J]. Chinese Archives of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2018, 36(3): 531-534. |
| [35] |
余洁英, 林育浩, 周凤华, 等. 葛根芩连汤对糖尿病湿热型小鼠心脏舒张功能的影响[J]. 中国中药杂志, 2022, 47(10): 2705-2711. YU J Y, LIN Y H, ZHOU F H, et al. Effect of Gegen Qinlian Decoction on cardiac diastolic function of diabetic mice with damp-heat syndrome[J]. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica, 2022, 47(10): 2705-2711. |
| [36] |
邹先明, 吴莹, 吴欢. 三仁汤对脾胃湿热证型胃癌癌前病变模型大鼠的作用机理[J]. 云南中医中药杂志, 2020, 41(11): 63-66. ZOU X M, WU Y, WU H. Mechanism of Sanren Decoction on gastric precancerous lesions in model rats with spleen-stomach damp-heat syndrome[J]. Yunnan Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine and Materia Medica, 2020, 41(11): 63-66. |
| [37] |
惠华英. 葛根芩连汤对肠道湿热证泄泻小鼠疗效的微生态学机理研究[D]. 长沙: 湖南中医药大学, 2020. HUI H Y. Study on microecological mechanism of Gegen Qinlian Decoction in treating diarrhea mice with intestinal damp-heat syndrome[D]. Changsha: Hunan University of Chinese Medicine, 2020. |
| [38] |
毕倩宇, 张桂菊, 崔有利, 等. 甘露消毒丹对湿热证型病毒性肺炎小鼠模型的多靶点干预作用[J]. 时珍国医国药, 2019, 30(8): 1840-1844. BI Q Y, ZHANG G J, CUI Y L, et al. Multi-target intervention effect of Ganlu Xiaodu Dan on mouse model of viral pneumonia with damp-heat syndrome[J]. Lishizhen Medicine and Materia Medica Research, 2019, 30(8): 1840-1844. |
| [39] |
武凯歌. 王氏连朴饮对脾胃湿热证大鼠HPA轴相关指标及白细胞介素影响的实验研究[D]. 广州: 南方医科大学, 2011. WU K G. The experimental study of Wang's lianpuyin on the relevant indexes of hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal axis and interleukins of the spleen and stomach damp-heat syndrome in rats[D]. Guangzhou: Southern Medical University, 2011. |
| [40] |
廖荣鑫, 文小敏, 周福生. 脾胃湿热证湿、热偏重型大鼠模型血浆淋巴细胞HSP70的表达[J]. 四川中医, 2006, 24(2): 18-19. LIAO R X, WEN X M, ZHOU F S. Expression of HSP70 in plasma lymphocytes of rat model with damp-heat syndrome of spleen and stomach[J]. Journal of Sichuan of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2006, 24(2): 18-19. |
| [41] |
张艺平, 韩鹏, 刘仕昌, 等. 清热解毒凉血化瘀治疗温病湿热证的实验研究[J]. 中国中西医结合急救杂志, 2002, 9(3): 162-165. ZHANG Y P, HAN P, LIU S C, et al. Experimental studies on the treatment of clearing away heat and removing toxic substances cooling blood to dissipate blood stasis on dampheat syndrome of seasonal febrile disease[J]. Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine in Practice of Critical Care Medicine, 2002, 9(3): 162-165. |
| [42] |
曾蓉, 喻斌, 徐寅, 等. 灭幽汤对幽门螺杆菌相关性胃炎脾胃湿热证小鼠PTEN-PI3K-Akt-FoxO凋亡信号通路的影响[J]. 现代中西医结合杂志, 2020, 29(26): 2869-2875. ZENG R, YU B, XU Y, et al. Effect of Mieyou Decoction on PTEN-PI3K-Akt-FoxO apoptotic signal pathway in the H.Pylori-associated gastritis mice with spleen-stomach damp-heat syndrome[J]. Modern Journal of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine, 2020, 29(26): 2869-2875. |
| [43] |
常丽萍, 阙铁生, 吕军影, 等. 加味藿朴夏苓汤对温病湿热证大鼠舌组织AQP-5的影响[J]. 中华中医药杂志, 2012, 27(9): 2458-2461. CHANG L P, QUE T S, LU J Y, et al. Effect of modified Huopu Xialing Decoction on AQP-5 expression of tongue tissue in rat with epidemic febrile disease of damp-heat syndrome[J]. China Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine and Pharmacy, 2012, 27(9): 2458-2461. |
2. State Key Laboratory of Component-based Chinese Medicine, Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Tianjin 301617, China;
3. Department of Medicinal Chemistry, Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Tianjin 301617, China
 2023, Vol. 40
2023, Vol. 40