文章信息
- 康华, 郝镁娟, 郭礼尚, 等.
- KANG Hua, HAO Meijuan, GUO Lishang, et al.
- 疏肝滋肾方对肝肾亏虚型卵巢储备功能下降患者性激素水平及IVF-ET治疗结局的影响
- Effects of Shugan Zishen Formula on sex hormone levels and IVF-ET treatment outcomes in patients with decreased ovarian reserve function of liver and kidney deficiency type
- 天津中医药, 2023, 40(12): 1506-1510
- Tianjin Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 40(12): 1506-1510
- http://dx.doi.org/10.11656/j.issn.1672-1519.2023.12.02
-
文章历史
- 收稿日期: 2023-08-26
卵巢储备功能下降是妇科常见疾病,是指卵巢内卵泡明显减少,卵子质量下降,产生生殖内分泌功能紊乱,降低了患者的生育能力,主要表现为月经后期、不孕、闭经、卵巢早衰、流产等[1-2]。卵巢储备功能下降发病率约为10%~26%,且发病率呈逐年上升趋势,其进展至卵巢早衰仅需1~6年,需及时给予治疗措施[3]。体外受精-胚胎移植(IVF-ET)是卵巢储备功能下降不孕女性的最终治疗策略,但多数患者IVF-ET治疗结果并不理想。中医学中尚无卵巢储备功能下降相关命名,根据其临床症状可归属为“不孕”“月经后期”等范畴,多由患者肝肾阴虚,致使肝气郁结、血海亏虚、经络瘀滞,胞宫失养所致[4],疏肝滋肾方具有补益肝肾、滋阴养血、解郁通络、调经的功效,故本次研究旨在探讨疏肝滋肾方对肝肾亏虚型卵巢储备功能下降患者性激素水平及IVF-ET治疗结局的影响,报道如下。
1 资料与方法 1.1 临床资料选择2020年11月——2021年11月于河北省沧州中西医结合医院治疗的98例卵巢储备功能下降患者,按随机数字表法随机分组,西医组49例,年龄20~39岁,平均年龄(31.23±2.48)岁,平均病程(15.24±1.37)个月,疏肝滋肾方组49例,年龄21~38岁,平均年龄(31.34±2.35)岁,平均病程(15.39±1.43)个月。西医组及疏肝滋肾方组一般资料比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),具有可比性,本研究已经过本院医学伦理委员会审核批准(伦理批号CZX2020085),患者或家属知情并同意。
1.2 纳入与排除标准 1.2.1 纳入标准符合卵巢储备功能下降诊断标准[5];分型为肝肾亏虚型[6];18~40岁;患者或家属签署知情同意书;近半年未行相关药物治疗;无肝肾功能不全;依从性良好。
1.2.2 排除标准对本次药物过敏者;合并自身免疫性疾病、传染病、恶性肿瘤者;精神障碍者;配偶精子质量异常者;染色体核型异常、手术切除单侧卵巢、生殖器官畸形者;男方因素、输卵管因素、子宫因素等引起不孕者;参与其他研究者;依从性差者。
1.3 治疗方法西医组:给予患者IVF-ET治疗,通过固定拮抗剂方案促排卵,根据患者B超、激素水平给予促性腺激素(Gn)促排卵,同时密切监测患者卵泡发育,在药物使用第5天再次给予患者拮抗剂,给予患者阴道超声检查,当发现卵泡直径在1.8 cm及以上,且数量持续≥3个卵泡时,停用Gn,给予4 000~10 000 U人绒毛膜促性腺激素(HCG)肌肉注射,36 h后行取卵术。体外培养胚胎3~6 h,行胚胎移植术,术后给予黄体酮阴道缓释凝胶支持。移植后14 d检测患者HCG水平,明确妊娠,移植后30 d后,检测阴道超声确诊临床妊娠,于孕13、28周及预产期前后2周内随访。
疏肝滋肾方组:在西医组基础上给予患者疏肝滋肾方治疗,方药组成:熟地黄20 g,女贞子15 g,白芍15 g,牡丹皮12 g,当归15 g,川芎10 g,白术15 g,茯苓15 g,生甘草5 g,由本院中药制剂室统一煎制药物,每日1剂,煎得200 mL,分早晚2次饭后服用,于IVF-ET周期前一周期的卵泡期服用。
1.4 观察指标1)性激素及生长分化因子-9(GDF-9)、抗苗勒氏管激素(AMH)、Toll样受体2(TLR2)水平:治疗前后抽取患者5 mL空腹肘静脉血,离心半径10 cm,3 000 r/min,离心10 min,采用酶联免疫吸附法测定两组患者促卵泡刺激素(FSH)、GDF-9、黄体生成素(LH)、AMH、TLR2水平。2)卵巢状态:治疗前、后(月经期第10天)给予患者阴道彩超检查,检测患者卵巢动脉收缩期峰值流速(PSV)、卵巢窦卵泡数(AFC)。3)中医证候评分:参照《中医妇科学》[7]及《中药新药临床研究指导原则(试行)》拟定评分标准[8]:主症:腰膝酸软、月经后期或稀发,量少渐至经闭;次症:目涩、头晕耳鸣、两颧潮红、手足心热、潮热盗汗、阴道干涩,心烦少寐。无症状记为0分,轻度症状记为2分,中度症状记为4分,重度症状记为6分。4)记录患者Gn使用剂量、成熟卵率(MII卵率)、获取卵泡个数、受精率、临床妊娠率、流产率。5)记录两组患者不良反应发生情况。
1.5 统计学方法将以上统计数据采用SPSS 23.0软件进行分析,以均数±标准差(x±s)表示,采用配对t检验检测组内治疗前后数据,采用成组t检验检测组间数据;计数资料采用构成比或率表示,组间比较采用χ2检验,P<0.05表示差异有统计学意义。
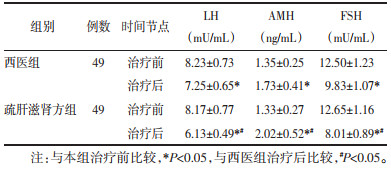
2 结果 2.1 两组患者LH、AMH、FSH水平比较治疗后,两组患者LH、FSH含量较治疗前明显降低、AMH含量较治疗前明显升高(P<0.05),以疏肝滋肾方组患者改善更明显(P<0.05),见表 1。
|
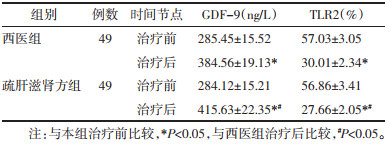
治疗后,两组患者TLR2含量较治疗前明显降低、GDF-9含量较治疗前明显升高(P<0.05),以疏肝滋肾方组患者改善更明显(P<0.05),见表 2。
|
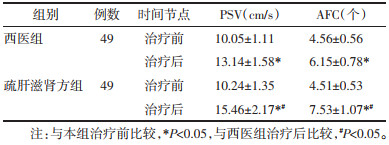
治疗后,两组患者PSV、AFC较治疗前明显升高(P<0.05),疏肝滋肾方组PSV、AFC显著高于西医组(P<0.05),见表 3。
治疗后,两组患者中医证候评分较治疗前明显降低(P<0.05),以疏肝滋肾方组患者的评分更低(P<0.05),见表 4。
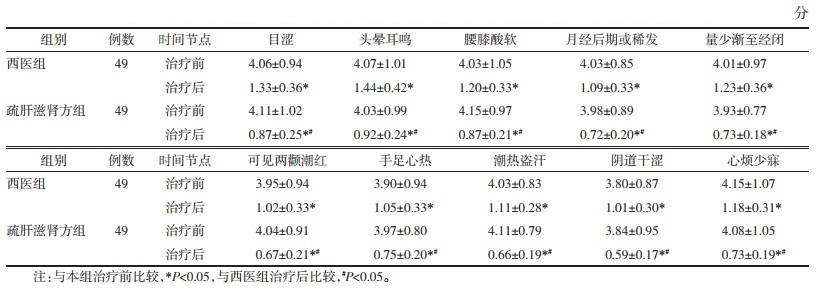
|
疏肝滋肾方组Gn使用剂量较西医组少(P<0.05),疏肝滋肾方组获取卵泡个数较西医组多(P<0.05),疏肝滋肾方组受精率、MII卵率、临床妊娠率较西医组高(P<0.05)差异均具有统计学意义,两组流产率比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),见表 5。
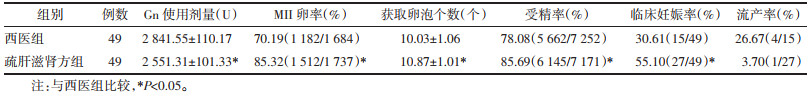
|
治疗期间两组患者均无明显不良反应。
3 讨论卵巢储备功能下降是妇科常见疾病,是导致患者不孕的常见因素,其病因复杂,是多因素共同作用的结果[9]。1)基因遗传学:约有10%的卵巢储备功能下降患者有家族史,患者主要有常染色体异常、X染色体数目异常以及基因突变等[10-11]。2)酶缺陷:卵巢DNA调聚酶活性丧失,可导致半乳糖-1-磷酸转尿苷酰酶缺乏,减少卵原细胞数量,进而可引起卵巢储备功能下降[12-13]。3)盆腔破坏因素:下卵巢囊肿剔除术中单极电凝止血可损伤卵巢血供,进而降低患者卵巢储备功能[14]。另外,环境因素、工作压力、不良生活方式、化学毒物等均可影响卵巢储备功能[15]。
根据卵巢储备功能下降的临床症状,中医将其归属为“不孕”“月经后期”等范畴,主要病机为肝肾阴虚,肾为先天之本,主生殖,藏精,精血同源,肝主疏泄,藏血,肾虚则致使精血无以生化,影响肝藏血功能;若患者思虑过度,致使肝气郁结,无以推动血行,产生气血瘀滞,胞宫难以滋养;若肝气犯脾,损伤脾胃功能,可导致气血生化乏源,经血匮乏,加重病情[16-17]。疏肝滋肾方中熟地黄为补血滋阴之要药,女贞子补益肝肾,为君,二药相须,滋阴养血;白芍养血调经、敛阴止汗、平抑肝阳,当归补血、活血化瘀、调经,为臣;牡丹皮活血化瘀、凉血,川芎行气开郁、活血化瘀,白术补气健脾、安胎,茯苓健脾宁心、安神,为佐;生甘草清热、调和诸药,为使。诸药合用,共奏补益肝肾、滋阴养血、活血通络、调经之效。
LH、FSH均为性激素,属于内分泌相关指标,在卵巢功能下降患者中呈高表达;AMH由窦前卵泡及窦状卵泡分泌产生,低表达于卵巢功能下降患者。本次研究结果表明:疏肝滋肾方组患者LH、FSH含量较西医组明显低,AMH含量较西医组明显高,说明疏肝滋肾方治疗肝肾亏虚型卵巢储备功能下降患者,可调节患者性激素水平。TLR是免疫系统识别病原的主要受体,为I型跨膜蛋白,TRL2可在MyD88作用下激活TRAF6,激活下游核因子-κB(NF-κB)信号通路,促进炎症因子表达,影响子宫微环境状态。GDF-9可调节性激素分泌量,改善卵巢储备功能,刺激卵巢发育,利于颗粒细胞增殖。疏肝滋肾方组患者TLR2含量较西医组明显低,GDF-9含量较西医组明显高,说明疏肝滋肾方治疗肝肾亏虚型卵巢储备功能下降患者,可抑制机体炎症,改善卵巢微环境,提升卵巢储备功能。疏肝滋肾方组PSV、AFC较西医组明显高,中医证候评分较西医组明显降低,说明疏肝滋肾方治疗肝肾亏虚型卵巢储备功能下降患者,可提升卵巢储备功能,缓解临床症状。疏肝滋肾方组Gn使用剂量较西医组少,获取卵泡个数较西医组多,受精率、MII卵率、临床妊娠率较西医组高,治疗期间两组患者均无明显不良反应,说明疏肝滋肾方治疗肝肾亏虚型卵巢储备功能下降患者,可减少Gn使用剂量,提升受精率、MII卵率、临床妊娠率,改善IVF-ET治疗结局,安全性好。
综上所述,疏肝滋肾方治疗肝肾亏虚型卵巢储备功能下降患者,可调节患者性激素水平,抑制机体炎症,改善卵巢微环境,提升卵巢储备功能,缓解临床症状,减少Gn使用剂量,提升受精率、MII卵率、临床妊娠率,改善IVF-ET治疗结局。
| [1] |
任慧霞, 王锦玉, 朱珂, 等. 卵巢储备功能下降患者常见中医证型与子宫、卵巢动脉血流参数关系研究[J]. 现代中西医结合杂志, 2022, 31(16): 2225-2229, 2235. REN H X, WANG J Y, ZHU K, et al. Relationship between common traditional Chinese medicine syndrome types and blood flow parameters of uterine and ovarian arteries in patients with decreased ovarian reserve[J]. Modern Journal of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine, 2022, 31(16): 2225-2229, 2235. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1008-8849.2022.16.006 |
| [2] |
周琳, 任梦雪, 秦瑜玲, 等. 基于"气血理论"论治卵巢储备功能下降性不孕[J]. 中国临床医生杂志, 2023, 51(3): 371-373. ZHOU L, REN M X, QIN Y L, et al. Treatment of infertility caused by decreased ovarian reserve function based on "qi and blood theory"[J]. Chinese Journal for Clinicians, 2023, 51(3): 371-373. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.2095-8552.2023.03.033 |
| [3] |
LEE J K, AHN S H, KIM H I, et al. Therapeutic efficacy of catheter-directed ethanol sclerotherapy and its impact on ovarian reserve in patients with ovarian endometrioma at risk of decreased ovarian reserve: a preliminary study[J]. Journal of Minimally Invasive Gynecology, 2022, 29(2): 317-323. DOI:10.1016/j.jmig.2021.08.018 |
| [4] |
冯晓玲, 贾紫千, 李娜, 等. 电针联合育阴丸对肝肾阴虚型卵巢储备功能下降患者性激素及Th2型细胞因子的影响[J]. 中国针灸, 2020, 40(9): 959-963. FENG X L, JIA Z Q, LI N, et al. Effect of electroacupuncture combined with Yuyin pill on sex hormone and Th2 cytokines in patients of decreased ovarian reserve function with liver-kidney yin deficiency[J]. Chinese Acupuncture & Moxibustion, 2020, 40(9): 959-963. |
| [5] |
武学清, 孔蕊, 田莉, 等. 卵巢低反应专家共识[J]. 生殖与避孕, 2015, 35(2): 71-79. WU X Q, KONG R, TIAN L, et al. A consensus of poor ovarian response[J]. Chinese Journal of Reproduction and Contraception, 2015, 35(2): 71-79. |
| [6] |
冯晓玲, 李力, 曲凡, 等. 早发性卵巢功能不全中西医结合诊疗指南[J]. 中医杂志, 2022, 63(12): 1193-1198. FENG X L, LI L, QU F, et al. Guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of premature ovarian insufficiency with integrated traditional Chinese and western medicine[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 63(12): 1193-1198. |
| [7] |
谈勇. 中医妇科学[M]. 4版. 北京: 中国中医药出版社, 2016: 56. TAN Y. Traditional Chinese gynecology[M]. 4th edition. Beijing: China Press of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2016: 56. |
| [8] |
郑筱萸. 中药新药临床研究指导原则: 试行[M]. 北京: 中国医药科技出版社, 2002. ZHENG X Y. Guiding principles for clinical research of new Chinese medicine: trial implementation[M]. Beijing: China Medical Science and Technology Press, 2002. |
| [9] |
JIAO X, MENG T T, ZHAI Y W, et al. Ovarian reserve markers in premature ovarian insufficiency: within different clinical stages and different etiologies[J]. Frontiers in Endocrinology, 2021, 12: 601752. DOI:10.3389/fendo.2021.601752 |
| [10] |
DUAN W X, CHENG Y Y. Sequential therapy for kidney-tonifying via traditional Chinese medicine effectively improves the reproductive potential and quality of life of women with decreased ovarian reserve: a randomized controlled study[J]. American Journal of Translational Research, 2021, 13(4): 3165-3173. |
| [11] |
郑蕾蕾, 丁辉, 李焕, 等. 卵巢储备功能下降研究进展[J]. 辽宁中医药大学学报, 2022, 24(7): 202-208. ZHENG L L, DING H, LI H, et al. Research progress of decline in ovarian reserve[J]. Journal of Liaoning University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 24(7): 202-208. |
| [12] |
邓浈仪, 陈小平, 谢波, 等. 复方左归胶囊联合穴位贴敷治疗肾虚肝郁型卵巢储备功能下降患者的临床观察[J]. 广州中医药大学学报, 2022, 39(7): 1530-1535. DENG Z Y, CHEN X P, XIE B, et al. Clinical observation on compound Zuogui capsules combined with acupoint application in the treatment of patients with kidney deficiency and liver stagnation type of diminished ovarian reserve[J]. Journal of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, 2022, 39(7): 1530-1535. |
| [13] |
朱鸿秋, 王艳娜, 谢丹, 等. 卵巢储备功能下降危险因素的分析[J]. 浙江临床医学, 2017, 19(9): 1697-1698. ZHU H Q, WANG Y N, XIE D, et al. Analysis of risk factors of ovarian reserve function decline[J]. Zhejiang Clinical Medical Journal, 2017, 19(9): 1697-1698. |
| [14] |
ZHU X X, YE J, FU Y L. Premature ovarian insufficiency patients with viable embryos derived from autologous oocytes through repeated oocyte retrievals could obtain reasonable cumulative pregnancy outcomes following frozen-embryo transfer[J]. Annals of Translational Medicine, 2021, 9(7): 539. |
| [15] |
林光耀, 张米佳, 叶涛, 等. 中西医对卵巢储备功能下降病因认识的研究进展[J]. 西南医科大学学报, 2022, 45(1): 83-87. LIN G Y, ZHANG M J, YE T, et al. Research progress in etiology of diminished ovarian reserve in traditional Chinese and Western medicine[J]. Journal of Southwest Medical University, 2022, 45(1): 83-87. |
| [16] |
刘小月, 黄海涛, 卜晓玲, 等. 金哲诊治卵巢储备功能下降经验[J]. 山东中医杂志, 2021, 40(12): 1356-1359. LIU X Y, HUANG H T, BU X L, et al. Experience of Professor JIN Zhe on treating decreased ovarian reserve[J]. Shandong Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2021, 40(12): 1356-1359. |
| [17] |
冯晓玲, 谷玥儒, 赵颜, 等. 针刺联合育阴丸对卵巢储备功能下降患者临床及超声下卵巢改变情况的观察[J]. 广州中医药大学学报, 2020, 37(9): 1684-1689. FENG X L, GU Y R, ZHAO Y, et al. Clinical observation on acupuncture combined with Yuyin pills in treating patients with decreased ovarian reserve and changes of ovarian ultrasonogram[J]. Journal of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, 2020, 37(9): 1684-1689. |
 2023, Vol. 40
2023, Vol. 40