文章信息
- 陈希西, 韩嵩, 樊根豪, 张露丹, 吕春晓, 黄宇虹
- CHEN Xixi, HAN Song, FAN Genhao, ZHANG Ludan, LYU Chunxiao, HUANG Yuhong
- 活血化瘀类中药现代药理学研究进展
- Research progress of modern pharmacology of traditional Chinese medicine for promoting blood circulation and removing stasis
- 天津中医药, 2023, 40(2): 250-257
- Tianjin Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 40(2): 250-257
- http://dx.doi.org/10.11656/j.issn.1672-1519.2023.02.20
-
文章历史
- 收稿日期: 2022-10-20
2. 天津中医药大学, 天津 301617;
3. 青岛黑卓博林置地有限公司, 青岛 266555
活血化瘀是中医重要的治疗原则和理论基础。活血化瘀类中药药性多为辛、苦、温。味辛则能散能行,味苦则通泄,且均入血分,故能行血活血,消散瘀滞[1]。根据其功效特点可分为活血止痛药、活血调经药、破血消癥药等[2]。目前国内外对于活血化瘀类中药的研究主要以化学成分的药理活性为中心、以靶点为导向,整理多集中于临床疗效和临床药理作用,缺少与其功效对应的现代药理学机制研究的系统归纳总结。文章对活血化瘀类药物中与活血止痛药、活血调经药和破血消癥药功效相关的有效成分的现代药理学研究进行归纳总结,以期为活血化瘀类药物现代药理学研究及临床组方用药提供思路和参考。
1 活血止痛药本类药物主要有川芎、延胡索、郁金、姜黄等,这些药物即入血分,又入气分,有活血行气,止痛的功效。
1.1 活血行气药理学作用 1.1.1 影响血小板活化、聚集川芎、郁金的活性成分可能通过调控血小板活化聚集等方向的靶点和信号通路发挥活血行气的作用。川芎活性成分—四甲基吡嗪(TMP)可以上调腺苷酸环化酶(AC)/环磷酸腺苷(cAMP)信号通路、抑制磷酸化蛋白激酶(p-Akt)蛋白表达,进而抑制P2Y12受体介导的血小板活化[3]。郁金的活性成分则通过干预促红细胞生成素(Epo)/促红细胞生成素受体(EpoR)通路、下调P-选择素(CD62P),抑制血小板的活化和聚集,进而发挥活血化瘀作用的机制[4]。
1.1.2 影响血管生成延胡索、姜黄的活性成分可能通过调控影响血管生成等方向的靶点和信号通路发挥活血行气的作用。延胡索生物碱提取物可以抑制血管内皮生长因子(VEGF)/血管内皮生长因子受体2(VEGFR-2)信号通路抑制血管生成;并通过减弱VEGFR-2的下游信号介质酪氨酸激酶(SRC)/蛋白激酶B(AKT)、蛋白激酶C(PKC)/细胞外调节蛋白激酶(ERK)和蛋白酪氨酸激酶-2(JAK2)/信号转导及转录激活蛋白3(STAT3)的活化来阻断血管的生成[5]。延胡索活性成分—四氢巴马汀(THP),通过调节精氨酸的生物合成,影响瓜氨酸-精氨酸的流量-精氨酸的生物合成和内皮VEGFR-2的表达,从而促进血管生成[6]。另外有研究发现,姜黄活性成分—姜黄素可以影响白细胞介素-17(IL-17)信号通路治疗心房颤动(AF),同时发现姜黄素对AF作用机制相关的关键基因包括Ⅰ型胶原Α1(COL1α1)、磷酸烯醇式丙酮酸羧激酶(PCK1)、骨形态发生蛋白-10(BMP10)、IL-33和c-fos诱导生长因子(FIGF)等[7]。
1.2 止痛药理学作用川芎、延胡索的活性成分可能通过调控抑制神经递质、镇痛等方向的靶点和信号通路发挥止痛的作用。TMP可以抑制即刻早期基因(c-fos)/ERK信号通路,阻碍三叉神经系统中与疼痛相关的神经递质的表达,达到治疗偏头痛的目的[8]。延胡索活性成分THP、紫堇碱(DHC)可以抑制电压门控钠离子通道(VGSC)中Nav1.7亚型,发挥镇痛作用[9]。
1.3 其他药理学作用 1.3.1 保护神经川芎活性成分和姜黄素可能调控保护神经、改善脑缺血等方向的靶点和信号通路。川芎活性成分—洋川芎内酯H(SNH)既可以调控丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(MAPK)通路,抑制大鼠嗜铬细胞瘤(PC12)细胞凋亡,从而发挥保护神经[10];同时还具有改善脑缺血,保护受损神经细胞的作用[11]。与之不同,姜黄的有效成分姜黄素主要通过激活环AMP反应元件结合蛋白(CREB)/脑源性神经营养因子(BDNF)信号通路保护大鼠神经[12]。有研究发现,其类似物可以显着降低小鼠大脑中乙酰胆碱酯酶(AChE)和丁酰胆碱酯酶(BChE)水平、增加乙酰胆碱(Ach)水平,说明姜黄素类似物可能通过抑制胆碱酯酶的活性,发挥保护神经和预防阿尔茨海默病(AD)的作用[13]。
1.3.2 其他作用川芎活性成分可能通过调控保护支气管黏膜、抗肿瘤转移等方向的靶点和信号通路发挥行气、化瘀的作用。川芎活性成分TMP可以抑制核因子-κB-p65(NF-κB-p65)/肿瘤坏死因子(TNF-α)信号通路保护支气管黏膜上皮细胞[14]。而其他48个活性成分如藁本内酯(AHP)等与肺癌脑转移的血管内皮生长因子A(VEGFA)等7个核心靶点有较强亲和能力,通过实验验证川芎可能通过抑制磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶(PI3K)/蛋白激酶B(AKT)和VEGF通路起到抗肺癌脑转移的作用[15]。
2 活血调经药本类药物主要有丹参、红花、桃仁、益母草、牛膝等,这些药物大多辛散苦泄,归肝经,入血分,有活血通脉,通经的功效。
2.1 活血通脉药理学作用 2.1.1 影响血管生成丹参和桃仁的活性成分可能通过调控抑制血管生成等方向的靶点和信号通路发挥其活血通脉的作用。丹参活性成分—丹参酮ⅡA(Tan IIA)可以抑制转化生长因子-β(TGF-β)/β连环蛋白(β-catenin)和缺氧诱导因子-1α(HIF-1α)/β-catenin/VEGF通路,抑制血管生成[16]。而桃仁活性成分—苦杏仁苷则通过抑制TGF-β/Smad信号通路,抑制肝星状细胞(HSCs)活化和肝窦内皮细胞(LSECs)去分化以改善血管生成[17]。
2.1.2 防治心脑血管疾病丹参、红花和桃仁的活性成分可能通过调控降低心肌细胞凋亡、改善心肌缺血和改善血脂水平等方向的靶点和信号通路发挥其活血通脉的作用,从而防治心脑血管疾病。Tan ⅡA通过抑制Toll样受体4(TLR4)/髓样分化因子88(MyD88)/核因子κB(NF-κB)信号通路[18]和NF-κB和p38-MAPK信号通路[19],分别发挥其减少心肌细胞凋亡,预防左心室重构(VR),进而改善心肌梗死(MI)和预防动脉粥样硬化的作用。而丹参另一活性成分—丹参素通过促进PI3K/Akt/哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白(mTOR)、肿瘤抑制基因p53通路和细胞外信号调节酶1/2(ERK1/2)磷酸化,抑制心肌细胞的自噬、减轻心肌细胞损伤和凋亡,改善心肌缺血再灌溉损伤[20]。红花的活性成分的药理学作用机制与丹参有所不同,其活性成分可能通过抑制大鼠肉瘤(Ras)/Raf/MEK/ERK1/2和希佩尔-林道抑癌基因(VHL)/HIF-1α/VEGF通路调控血管平滑肌细胞的增殖和迁移,进而防治心脑血管疾病[21]。其活性成分之一的西红花苷可以激活核因子红细胞2-相关因子2(Nrf-2)信号通路,上调Nrf-2的蛋白表达,提高肝脏抗氧化酶活性[22]。而其另一活性成分—羟基红花黄色素A(HAS)则通过影响PI3K/Akt信号通路发挥其对脑缺血模型大鼠神经保护的作用[23]。桃仁可降低TRIB3基因及Toll样受体[24],抑制PI3K/AKT信号通路的激活[25],改善糖尿病血管纤维化大鼠的动脉纤维化,从而改善糖尿病的动脉病变。其活性成分苦杏仁苷主要通过抑制NF-κB/环氧合酶2(COX-2)通路,降低冠心病(CHD)模型大鼠炎症因子表达水平,改善血脂水平[26]。
2.2 通经药理学作用益母草主要活性成分益母草碱可能通过调控改善子宫功能等靶点和通路发挥活血调经的作用。益母草碱既可以抑制p38丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(p38 MAPK)/PI3K/AKT信号通路,阻止大鼠子宫蜕膜组织血管生成,促进药物流产大鼠的蜕膜绒毛组织排出,进而增加子宫出血量[27];同时又可以与骨髓间充质干细胞联合使用,调控TGF-β/Smad3信号转导通路,抑制TGF-β与Smad3蛋白的表达,抑制子宫内膜纤维化的形成,改善子宫粘连[28]。
2.3 其他药理学作用 2.3.1 保护神经桃仁、益母草和牛膝的活性成分可能通过调控营养神经、促进神经元生长和抑制神经凋亡方向的靶点和通路。桃仁活性成分Amygdalin可以激活ERK1/2通路营养神经,诱导神经突触生长,发挥保护神经的作用[29]。而益母草活性成分益母草碱可以增强BDNF/TrkB/CREB信号通路,促进体内和体外神经元生长[30]。另外还可以通过激活Nrf-2/血红素加氧酶1(HO1)信号通路发挥血脑屏障保护作用,减轻血脑屏障渗透性,启动脑梗死模型小鼠梗死后血管新生,维持血脑屏障功能[31]。牛膝活性成分—牛膝多肽K(ABPPk)可以促进体外培养的原代雪旺细胞(SCs)在不同时间的增殖,抑制其凋亡[32],激活PI3K/AKT和ERK1/2信号通路[33],帮助周围神经再生和功能恢复;还可以抑制PI3K/Akt依赖的NADPH氧化酶(NOX)/活性氧(ROS)通路,降低脂多糖(LPS)激活的BV2小胶质细胞中的神经炎症,为神经炎症的干预和治疗提供新的角度[34]。
2.3.2 影响癌细胞丹参和红花的活性成分可能通过调控促进癌细胞凋亡、迁徙等相关的靶点和信号通路。Tan ⅡA可以通过激活Jun N端激酶(JNK)通路抑制人喉表皮样癌细胞和人喉癌细胞活力,促进癌细胞凋亡[35]。近期研究发现,TanⅡA与顺铂(DDP)组合可能通过PI3K/Akt信号通路抑制细胞增殖、迁移和侵袭,诱导细胞凋亡[36]。丹参另一活性成分—丹参酮Ⅰ(Tan-Ⅰ)既抑制PI3K/Akt/mTOR通路,诱导卵巢癌细胞自噬,同时激活凋亡相关蛋白Caspase-3,促进卵巢癌细胞凋亡[37];又阻碍JAK/STAT3信号通路,下调p-JAK1/2和STAT3蛋白水平,抑制骨肉瘤(OS)的生长和转移[38]。红花有效成分—红花多糖(SPS)通过提高小鼠体内肿瘤坏死因子-α(TNF-α)和IL-6的水平,增强免疫调节活性;同时发现SPS可以抑制PI3K/Akt通路抑制肿瘤生长,诱导人非小细胞肺癌细胞的凋亡[39]。
2.3.3 其他作用红花和牛膝的活性成分可能通过调控抑制肺部炎症通路、改善血液黏稠度等方向的靶点和通路。红花活性成分Crocin和HAS分别通过抑制大鼠肺中单核细胞趋化蛋白-1(MCP-1,又称CCL2)/受体CCR2炎症通路的表达[40]和调节PI3K/AKT/BCL2/BAX通路[41],发挥改善肺动脉高压(PAH)和降低大鼠的血液黏度,改善股骨头的病理性损伤的作用。牛膝活性成分—牛膝多糖(ABPS)通过抑制TGF-β1/Smad通路,降低血清基质金属蛋白酶组织抑制因子-1(TIMP-1)、血管内皮细胞生长因子(VEGF)、骨桥蛋白(OPN)水平,提高慢性阻塞性肺疾病模型大鼠肺功能[42]。
3 破血消癥药本类药物主要有莪术、三棱、水蛭等,药性峻猛,这类药物归肝经,入血分,有破血逐瘀的功效。
3.1 破血逐瘀的药理作用莪术和水蛭的活性成分可能通过调控抗血小板聚集、保护心肌等方向的靶点和通路发挥其破血逐瘀的作用。莪术有效成分—莪术二酮和莪术醇分别通过抑制AMP-activated protein kinase-vinculin/talin-integrin αIIbβ3信号通路[43]和激活Nrf2/HO1信号通路[44],发挥其抑制血小板聚集和抗凋亡、保护损伤心肌细胞的作用。水蛭有效成分—水蛭素和透明质酸酸(HA)则分别通过抑制布鲁顿酪氨酸激酶(Btk)介导的未知的IgG复合物对血小板Fc受体(FcγRIIA)的刺激[45]和被水蛭透明质酸酶(LHase)降解[46],发挥其降低高自发性血小板聚集(SPA)及促进血管生成活性的作用。
3.2 其他药理作用 3.2.1 影响癌细胞莪术、三棱的活性成分可能通过调控抑制癌细胞生长、增值和转移等方向的靶点和通路。莪术醇可以抑制PI3K/AKT信号通路的活动,抑制人卵巢癌细胞生长[47]和胃癌细胞的增殖[48];同时可以抑制JAK1/STAT3信号通路,抑制肺癌细胞的增殖、侵袭,进而促进肺癌细胞的凋亡[49]。另外还发现莪术醇可以调控miR-152-3p/PI3K/AKT和ERK/NF-κB信号通路,抑制黑色素瘤的增殖和转移[50]。而三棱散水提物可能通过阻断NF-KB信号通路抑制胃癌细胞增殖,促进其凋亡,从而发挥抗胃癌作用[51];其活性成分可能通过影响p53信号通路发挥抗胃癌的潜在作用[52]。
3.2.2 其他作用水蛭的活性成分可能通过调控抗纤维化等方向的靶点和通路。水蛭素可以抑制1-磷酸鞘氨醇(S1PS1P)/S1PR2/S1PR3信号通路,降低蛋白酶激活受体1(PAR1)表达,减弱了近端肾小管上皮(HK-2)细胞纤维化[53]。因此水蛭素可能是一种很有前途的肾间质纤维化(RIF)治疗剂。
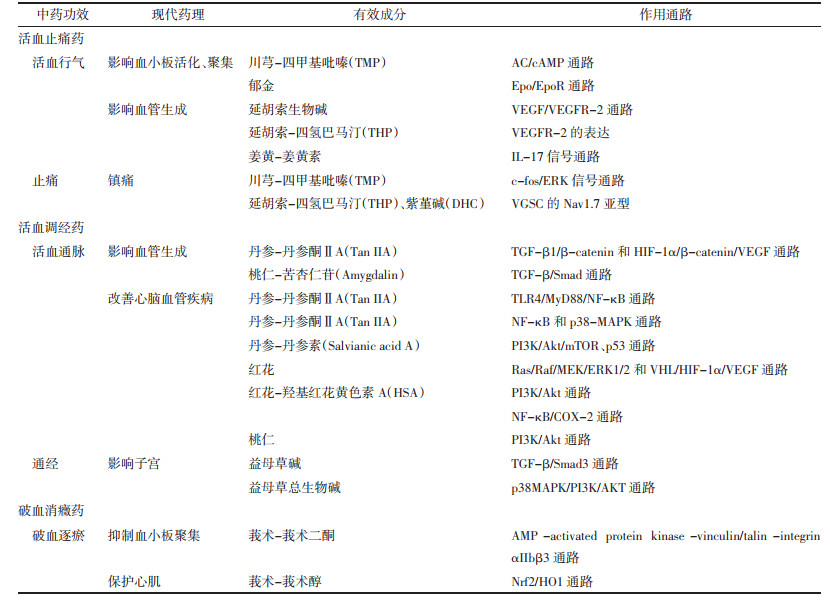
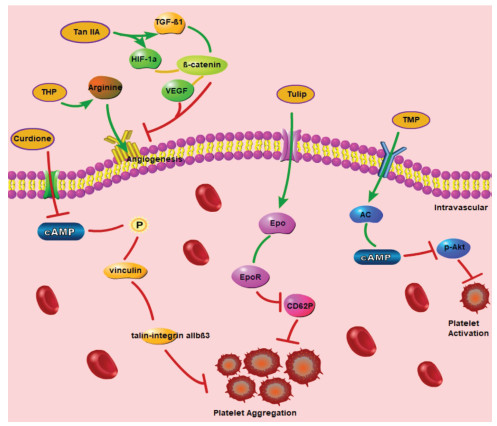
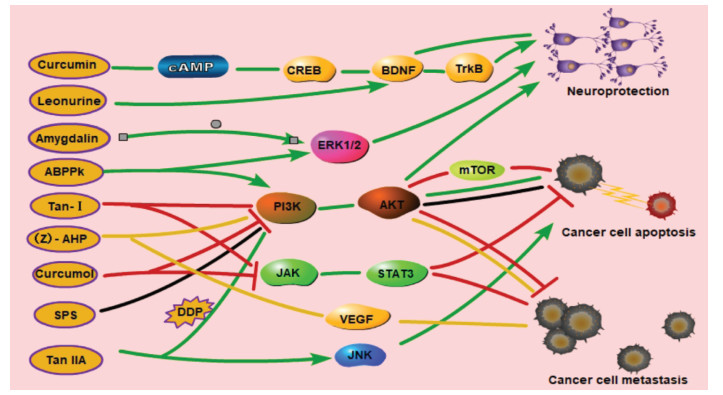
4 讨论随着现代分子生物技术、代谢组学等科研技术的进步,学者们对活血化瘀中药的研究已从宏观层面转向了细胞、分子等微观层面。文章以活血化瘀中药主要功效分类为纲,总结归纳与其功效对应的现代药理学研究结果,确证了中药按照功效分类的科学性。发现单一中药的活性成分多样、功能不同,同一活性成分亦可以影响多条通路,如活血调经药中丹参的活性成分包括TanⅡA、Salvianic acid A和Tan-Ⅰ等,Salvianic acid A和Tan-Ⅰ均影响PI3K/Akt/mTOR通路,前者改善心肌缺血,后者促进癌细胞凋亡;TanⅡA可以影响TGF-β1/β-catenin、HIF-1α/β-catenin/VEGF、NF-κB和p38-MAPK等信号通路,分别发挥影响血管生成、改善心肌梗死和预防动脉粥样硬化等作用,与中药多靶点、多通路、整体调控的特点相符。通过对活血化瘀类中药现代药理学作用机制总结归纳,见表 1,并绘制了相关机制通路图,见图 1、2,提示活血止痛药可能主要影响体内血小板活化聚集及血管生成,其中VEGF/VEGFR-2通路研究较多;活血调经药可能主要作用于影响血管生成和防止心脑血管疾病,例如改善脑梗、保护心肌等,其中PI3K/Akt通路和NF-κB靶点研究较多;破血消癥药可能主要作用于抑制血小板活化和保护心肌。说明VEGF/VEGFR-2、PI3K/Akt通路及NF-κB靶点可能为活血化瘀中药的潜在靶点,为进一步研究活血化瘀中药提供新角度。
|
|
| 图 1 活血化瘀药物有效成分影响血小板活化、聚集和血管生成相关通路 Fig. 1 Active components of drugs for promoting blood circulation and removing blood stasis affect platelet activation, aggregation and angiogenesis-related pathways |
|
| 图 2 活血化瘀药物有效成分作用保护神经、促进癌细胞凋亡和抑制癌细胞转移相关通路 Fig. 2 Active ingredients of the drugs for promoting blood circulation and removing blood stasis protect nerves, promote cancer cell apoptosis and inhibit cancer cell metastasis-related pathways |
目前对活血化瘀中药的现代药理学研究主要集中于单一药材活性成分研究,对于中药复方在细胞、分子水平上的阐释较少,这可能与中药复方成分复杂多样有关。下一步可以通过现代药理学研究方法发掘中药复方作用靶点和通路与单一药材区别,验证中医中药的科学性和安全性,为中医中药临床应用提供科学依据和思路。
| [1] |
潘祥龙, 郝二伟, 谢金玲, 等. 活血化瘀中药调节血瘀证的分子机制研究进展[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志, 2018, 24(24): 227-234. PAN X L, HAO E W, XIE J L, et al. Molecular mechanism of blood-activating and stasis-removing Chinese medicine in regulating blood stasis syndrome[J]. Chinese Journal of Experimental Traditional Medical Formulae, 2018, 24(24): 227-234. DOI:10.13422/j.cnki.syfjx.20182434 |
| [2] |
高学敏. 中药学[M]. 北京: 中国中医药出版社, 2010: 311. GAO X M. Chinese Materia Medica[M]. Beijing: China Traditional Chinese Medicine Press, 2010: 311. |
| [3] |
官宝怡. 川芎嗪通过P2Y12受体信号通路抗血小板活化的作用机制研究[D]. 北京: 中国中医科学院, 2020. GUAN B Y. The antiplatelet mechanism of tetramethylpyrazine via P2Y12 receptor-mediated signaling athway[D]. Beijing: China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, 2020. |
| [4] |
CHEN Z, LI W, QUAN L, et al. The effects of curcumae longae Radix, Curcuma phaeocaulis Radix and their processed products on epo/EpoR pathway and CD62p[J]. Frontiers in Pharmacology, 2018, 9: 736. DOI:10.3389/fphar.2018.00736 |
| [5] |
WAN L, ZHAO Y, ZHANG Q, et al. Alkaloid extract of Corydalis yanhusuo inhibits angiogenesis via targeting vascular endothelial growth factor receptor signaling[J]. BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine, 2019, 19(1): 359. DOI:10.1186/s12906-019-2739-6 |
| [6] |
CUI H R, et al. Tetrahydropalmatine triggers angiogenesis via regulation of arginine biosynthesis[J]. Pharmacological Research, 2021, 163: 105242. DOI:10.1016/j.phrs.2020.105242 |
| [7] |
YUE H H, ZHAO X S, LIANG W T, et al. Curcumin, novel application in reversing myocardial fibrosis in the treatment for atrial fibrillation from the perspective of transcriptomics in rat model[J]. Biomedecine & Pharmacotherapie, 2022, 146: 112522. |
| [8] |
LI H, BAI F, CONG C, et al. Effects of ligustrazine on the expression of neurotransmitters in the trigeminal ganglion of a rat migraine model[J]. Ann Transl Med, 2021, 9(16): 1318. DOI:10.21037/atm-21-3423 |
| [9] |
XU Y J, et al. Analgesic effect of the main components of Corydalis yanhusuo(Yanhusuo in Chinese) is caused by inhibition of voltage gated sodium channels[J]. Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 2021, 280: 114457. DOI:10.1016/j.jep.2021.114457 |
| [10] |
LUO Y Y, et al. Senkyunolide H protects against MPP+-induced apoptosis via the ROS-mediated mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway in PC12 cells[J]. Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology, 2019, 65: 73-81. DOI:10.1016/j.etap.2018.12.007 |
| [11] |
JIANG Y Y, et al. Senkyunolide H protects PC12 cells from OGD/R-induced injury via cAMP-PI3K/AKT signaling pathway[J]. Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 2022, 282: 114659. DOI:10.1016/j.jep.2021.114659 |
| [12] |
GHOLAMI M, HOZURI F, ABDOLKARIMI S, et al. Pharmacological and molecular evidence of neuroprotective curcumin effects against biochemical and behavioral sequels caused by methamphetamine: possible function of CREB-BDNF signaling pathway[J]. Basic and Clinical Neuroscience, 2021, 12(3): 325-338. |
| [13] |
HUSSAIN H, AHMAD S, SHAH S W A, et al. Neuroprotective potential of synthetic mono-carbonyl curcumin analogs assessed by molecular docking studies[J]. Molecules (Basel, Switzerland), 2021, 26(23): 7168. DOI:10.3390/molecules26237168 |
| [14] |
LIN X, ZHU Y, LE G H. Tetramethylpyrazine alleviates tight junction disruption of bronchial mucosal epithelial cells caused by interleukin-17 via inhibiting nuclear factor-κB-p65/tumor necrosis factor-α signaling pathway[J]. Journal of Interferon & Cytokine Research: the Official Journal of the International Society for Interferon and Cytokine Research, 2021, 41(11): 415-424. |
| [15] |
徐廉松, 黄富豪, 张语涵, 等. 川芎通过多成分、多靶点、多信号通路和多生物学功能发挥抗肺癌脑转移作用[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2021, 41(9): 1319-1328. XU L S, HUANG F H, ZHANG Y H, et al. Chuanxiong Rhizoma inhibits brain metastasis of lung cancer through multiple active ingredients acting on multiple targets, pathways and biological functions[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2021, 41(9): 1319-1328. |
| [16] |
SUI H, et al. Tanshinone ⅡA inhibits β-catenin/VEGF-mediated angiogenesis by targeting TGF-β1 in normoxic and HIF-1α in hypoxic microenvironments in human colorectal cancer[J]. Cancer Letters, 2017, 403: 86-97. DOI:10.1016/j.canlet.2017.05.013 |
| [17] |
XIAO Z, JI Q, FU Y D, et al. Amygdalin ameliorates liver fibrosis through inhibiting activation of TGF-β/smad signaling[J]. Chinese Journal of Integrative Medicine, 2021, 1-9. |
| [18] |
WU D M, WANG Y J, HAN X R, et al. Tanshinone ⅡA prevents left ventricular remodelling via the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signalling pathway in rats with myocardial infarction[J]. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine, 2018, 22(6): 3058-3072. DOI:10.1111/jcmm.13557 |
| [19] |
FANG J, et al. Tanshinone ⅡA attenuates TNF-α induced PTX3 expression and monocyte adhesion to endothelial cells through the p38/NF-κB pathway[J]. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 2018, 121: 622-630. DOI:10.1016/j.fct.2018.09.063 |
| [20] |
YANG X, YANG R, LI X, et al. Danshensu attenuates aldosterone-induced cardiomyocytes injury through interfering p53 pathway[J]. Molecular Medicine Reports, 2017, 16(4): 4994-5000. DOI:10.3892/mmr.2017.7137 |
| [21] |
马嘉翼, 褚松龄. 羟基红花黄色素A改善缺血性脑卒中机制的研究进展[J]. 中国现代应用药学, 2019, 36(8): 1012-1017. MA J Y, CHU S L. Mechanism of hydroxysafflor yellow A meliorating ischemia stroke: a literature review[J]. Chinese Journal of Modern Applied Pharmacy, 2019, 36(8): 1012-1017. |
| [22] |
MARD S A, et al. Protective effects of crocin and zinc sulfate on hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats: A comparative experimental model study[J]. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, 2017, 96: 48-55. |
| [23] |
谭燕萍, 周福宜, 梁慧超, 等. 羟基红花黄色素A对脑缺血再灌注损伤大鼠脑组织中PDGF含量及PI3K、Akt蛋白表达的影响[J]. 广东药科大学学报, 2018, 34(3): 335-339. TAN Y P, ZHOU F Y, LIANG H C, et al. Effect of hydroxysafflor yellow A on PDGF content and PI3K and Akt expression in brain tissue of rats with cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury[J]. Journal of Guangdong Pharmaceutical University, 2018, 34(3): 335-339. |
| [24] |
周玉, 刘国涛, 卢增珍, 等. 中药桃仁对糖尿病大血管纤维化大鼠TRIB3基因及Toll样受体信号通路的影响[J]. 中华中医药杂志, 2019, 34(12): 5670-5674. ZHOU Y, LIU G T, LU Z Z, et al. Effects of peach kernel on TRIB3 gene and Toll like receptor signaling pathway in rats with diabetic macrovascular fibrosis[J]. China Journal of Traditional Chinese Medi- cine and Pharmacy, 2019, 34(12): 5670-5674. |
| [25] |
周玉, 刘国涛, 卢增珍, 等. 桃仁对糖尿病大血管纤维化大鼠蛋白激酶B信号通路的影响[J]. 中国中西医结合外科杂志, 2019, 25(1): 61-67. ZHOU Y, LIU G T, LU Z Z, et al. Effect of peach kernel on protein kinase B signaling pathway in diabetic macrovascular fibrosis rats[J]. Chinese Journal of Surgery of Integrated Traditional and Western Medicine, 2019, 25(1): 61-67. |
| [26] |
吴飞飞, 张邢炜. 桃仁提取物经NF-κB/COX-2通路对冠心病模型大鼠的保护作用[J]. 武汉大学学报(医学版), 2020, 41(5): 725-731. WU F F, ZHANG X W. Protective effect of peach kernel extract on coronary heart disease model rats through nuclear factor-kappaB/cyclooxygenase-2 pathway[J]. Medical Journal of Wuhan University, 2020, 41(5): 725-731. |
| [27] |
马静静, 刘宇, 梁艳, 等. 益母草总生物碱对药物流产大鼠蜕膜绒毛组织排出的促进作用及其机制[J]. 吉林大学学报(医学版), 2021, 47(6): 1476-1484. MA J J, LIU Y, LIANG Y, et al. Promotion effect of total alkaloids of Leonurus on decidual villus excretion in drug abortion rats and its mechanism[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(6): 1476-1484. |
| [28] |
王冰玉, 姬霞. 骨髓间充质干细胞移植联合益母草碱治疗宫腔粘连[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2016, 20(32): 4771-4777. WANG B Y, JI X. Leonurine combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in the treatment of intrauterine adhesions[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(32): 4771-4777. |
| [29] |
YANG C B, ZHAO J, CHENG Y Y, et al. Bioactivity-guided fractionation identifies amygdalin as a potent neurotrophic agent from herbal medicine Semen Persicae extract[J]. BioMed Research International, 2014, 2014: 306857. |
| [30] |
HONG Z Y, YU S S, WANG Z J, et al. SCM-198 ameliorates cognitive deficits, promotes neuronal survival and enhances CREB/BDNF/TrkB signaling without affecting aβ burden in AβPP/PS1 mice[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2015, 16(8): 18544-18563. DOI:10.3390/ijms160818544 |
| [31] |
解燕昭. 益母草碱对实验性脑梗死小鼠血脑屏障保护作用及相关机制研究[D]. 石家庄: 河北医科大学, 2016. XIE Y Z. Effect of leonurine on protection of blood brain barrier in experimental ischemic stroke and the related mechanism research[D]. Shijiazhuang: Hebei Medical University, 2016. |
| [32] |
TANG L L, ZHANG M, LIU X Y, et al. Effects and molecular mechanisms of Achyranthes bidentata polypeptide k on proliferation of Schwann cells[J]. Annals of Translational Medicine, 2021, 9(20): 1581. |
| [33] |
LI M Y, ZHU Y, PENG W Q, et al. Achyranthes bidentata polypeptide protects schwann cells from apoptosis in hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative stress[J]. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 2018, 12: 868. |
| [34] |
WANG Y, GE X, YU S, et al. Achyranthes bidentata polypeptide alleviates neurotoxicity of lipopolysaccharide-activated microglia via PI3K/Akt dependent NOX2/ROS pathway[J]. Annals of Translational Medicine, 2021, 9(20): 1522. |
| [35] |
XU H, HAO Y L, XU L N, et al. Tanshinone sensitized the antitumor effects of irradiation on laryngeal cancer via JNK pathway[J]. Cancer Medicine, 2018, 7(10): 5187-5193. |
| [36] |
LIAO X Z, GAO Y, HUANG S, et al. Tanshinone ⅡA combined with cisplatin synergistically inhibits non-small-cell lung cancer in vitro and in vivo via down-regulating the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt signalling pathway[J]. Phytotherapy Research: PTR, 2019, 33(9): 2298-2309. |
| [37] |
ZHOU J, JIANG Y Y, CHEN H, et al. Tanshinone I attenuates the malignant biological properties of ovarian cancer by inducing apoptosis and autophagy via the inactivation of PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway[J]. Cell Prolif, 2020, 53(2): e12739. |
| [38] |
WANG W G, LI J S, DING Z Y, et al. Tanshinone I inhibits the growth and metastasis of osteosarcoma via suppressing JAK/STAT3 signalling pathway[J]. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine, 2019, 23(9): 6454-6465. |
| [39] |
LI J Y, YU J, DU X S, et al. Safflower polysaccharide induces NSCLC cell apoptosis by inhibition of the Akt pathway[J]. Oncology Reports, 2016, 36(1): 147-154. |
| [40] |
SHENG Y L, GONG X W, ZHAO J, et al. Effects of crocin on CCL2/CCR2 inflammatory pathway in monocrotaline-induced pulmonary arterial hypertension rats[J]. The American Journal of Chinese Medi- cine, 2022, 50(1): 241-259. |
| [41] |
曾晓会, 卓俊城, 杨帆, 等. 羟基红花黄色素A联合扁桃苷对激素性股骨头坏死大鼠的作用研究[J]. 中药新药与临床药理, 2019, 30(11): 1284-1290. ZENG X H, ZHUO J C, YANG F, et al. Pharmacological effects of hydroxysafflor yellow A combined with amygdalin on steroid-induced avascular necrosis of femoral head in rats[J]. Traditional Chinese Drug Research and Clinical Pharmacology, 2019, 30(11): 1284-1290. |
| [42] |
吴娜娜, 李梅霞, 韩晓环. 基于TGF-β1/Smad通路研究牛膝多糖对慢阻肺模型大鼠的作用机制[J]. 中医学报, 2021, 36(9): 1943-1948. WU N N, LI M X, HAN X H. Study the mechanism of Achyranthes bidentata polysaccharide on COPD model rats based on TGF-β1/smad pathway[J]. Acta Chinese Medicine, 2021, 36(9): 1943-1948. |
| [43] |
FANG H, et al. Curdione inhibits thrombin-induced platelet aggregation via regulating the AMP-activated protein kinase-vinculin/talin-integrin αⅡbβ3 sign pathway[J]. Phytomedicine, 2019, 61: 152859. |
| [44] |
WU Z M, ZAI W J, CHEN W, et al. Curdione ameliorated doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity through suppressing oxidative stress and activating Nrf2/HO-1 pathway[J]. Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology, 2019, 74(2): 118-127. |
| [45] |
DUAN R D, GOLDMANN L, LI Y, et al. Spontaneous platelet aggregation in blood is mediated by FcγRⅡA stimulation of bruton's tyrosine kinase[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2021, 23(1): 76. |
| [46] |
LYU M X. Characterisation of separated end hyaluronan oligosaccharides from leech hyaluronidase and evaluation of angiogenesis[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2016, 142: 309-316. |
| [47] |
赵楠, 韩凤娟, 刘岩, 等. 莪术醇诱导人卵巢癌SKOV3细胞凋亡及对PI3K/Akt信号通路相关蛋白的影响[J]. 中国中医急症, 2020, 29(8): 1411-1414, 1443. ZHAO N, HAN F J, LIU Y, et al. Curcumol induced apoptosis of human ovarian cancer SKOV3 cells and its effect on PI3K-Akt signaling pathway related proteins[J]. Journal of Emergency in Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2020, 29(8): 1411-1414, 1443. |
| [48] |
HUANG X F, QIAN J, LI L C, et al. Curcumol improves cisplatin sensitivity of human gastric cancer cells through inhibiting PI3K/AKT pathway[J]. Drug Development Research, 2020, 81(8): 1019-1025. |
| [49] |
张琰, 马娜, 王芳, 等. 莪术醇抑制JAK1/STAT3信号通路对肺癌细胞增殖、凋亡和侵袭的影响[J]. 临床医学研究与实践, 2021, 6(34): 10-15. ZHANG Y, MA N, WANG F, et al. Effects of curcumol on proliferation, apoptosis and invasion of lung cancer cells by inhibiting JAK1/STAT3 signaling pathway[J]. Clinical Research and Practice, 2021, 6(34): 10-15. |
| [50] |
NING N, LIU S, LIU X, et al. Curcumol inhibits the proliferation and metastasis of melanoma via the miR-152-3p/PI3K/AKT and ERK/NF-κB signaling pathways[J]. Journal of Cancer, 2020, 11(7): 1679-1692. |
| [51] |
吉爱军, 陆建伟, 刘沈林, 等. 三棱散对人胃癌SGC-7901细胞增殖作用的影响[J]. 辽宁中医杂志, 2016, 43(1): 114-117. JI A J, LU J W, LIU S L, et al. Anti-proliferation and pro-apoptosis effect of Sanleng Powder extract on human gastric carcinoma cell SGC-7901[J]. Liaoning Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2016, 43(1): 114-117. |
| [52] |
唐杰, 阳帆, 李洋, 等. 三棱抗胃癌的潜在药物靶点及作用机制研究[J]. 湘南学院学报(医学版), 2020, 22(4): 11-16. TANG J, YANG F, LI Y, et al. Study on potential drug targets and mechanism of Sparganium in treating gastric cancer[J]. Journal of Xiangnan University (Medical Sciences), 2020, 22(4): 11-16. |
| [53] |
LIN Q, LONG C L, WANG Z G, et al. Hirudin, a thrombin inhibitor, attenuates TGF-β-induced fibrosis in renal proximal tubular epithelial cells by inhibition of protease-activated receptor 1 expression via S1P/S1PR2/S1PR3 signaling[J]. Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine, 2022, 23(1): 3. |
2. Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Tianjin 301617, China;
3. Qingdao Heizhuo Bolin Land Co., Ltd., Qingdao 266555, China
 2023, Vol. 40
2023, Vol. 40