文章信息
- 袁大为, 唐焕峰, 王华, 等.
- YUAN Dawei, TANG Huanfeng, WANG Hua, et al.
- 穴位贴敷联合中药灌肠促进腹腔镜胆囊切除术后胃肠功能恢复临床研究
- Clinical study of acupoint application combined with Chinese medicine clysma to promote gastrointestinal function recovery after laparoscopic cholecystectomy
- 天津中医药, 2023, 40(7): 877-881
- Tianjin Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 40(7): 877-881
- http://dx.doi.org/10.11656/j.issn.1672-1519.2023.07.11
-
文章历史
- 收稿日期: 2023-05-10
腹腔镜胆囊切除术(LC)是胆囊结石、胆囊炎、胆囊息肉等多种良性胆囊病变首选的治疗手段[1],与传统的开腹手术相比较,LC具有创伤小、出血少等优势,有利于患者术后康复[2]。但该手术受术前禁食水、术中麻醉、应激反应、电刀应用、二氧化碳气腹等因素影响,患者术后往往会产生胃肠功能紊乱,表现为腹腔胀气、腹部不适、胃肠功能下降等,甚至出现肠梗阻等严重并发症[3]。中医认为胆囊疾病主要病机为肝郁气滞,木旺则乘土,故多有纳差、腹胀等脾虚表现,加之手术所致脉络受损、气血瘀滞、耗气伤阴,故LC术后胃肠功能紊乱的主要病机为气滞血瘀、脾胃虚弱。中医治疗疾病以整体观念为指导,注重辨证论治,在胃肠疾病的治疗中具有一定优势[4]。穴位贴敷通过中药对穴位的刺激作用而产生生物波效应,从而促进经络、气血运行,改善气滞血瘀和脾虚症状,促进胃肠功能恢复[5]。中药灌肠也是中医常用的外治方法,对腹部手术患者实施中药灌肠有利于加快胃肠蠕动,改善胃肠动力和胃肠功能,促进患者康复[6]。本研究应用穴位贴敷联合中药灌肠干预LC术后胃肠功能紊乱,使两种治疗方案共同发挥作用,调节脏腑功能,促进术后胃肠功能恢复。
1 资料与方法 1.1 一般资料本研究获得医院伦理委员会批准(批件编号:2021126B)后进行,选择2021年6月—2022年12月期间于秦皇岛市中医医院外科接受LC手术的良性胆囊疾病患者96例,按照随机数字表法分为观察组和对照组,各48例。观察组男23例,女25例,年龄31~70岁,平均(42.67±9.29)岁;病程2个月~11年,平均(9.06±2.71)个月;疾病类型:胆囊结石26例,胆囊炎12例,胆囊息肉10例;平均手术时间(68.72±18.51) min;平均术中出血量(9.43±3.28) mL。对照组男21例,女27例,年龄29~70岁,平均(43.09±9.41)岁;病程3个月~12年,平均(8.79±2.65)个月;疾病类型:胆囊结石22例,胆囊炎14例,胆囊息肉12例;平均手术时间(67.90±17.84) min;平均术中出血量(9.19±3.35) mL。两组年龄、性别、病程、疾病类型、手术时间、术中出血量等基线资料无统计学差异(P > 0.05),具有可比性。
纳入标准:1)符合《胆囊良性疾病外科治疗的专家共识》[1]中的相关诊断标准,诊断为胆囊结石、胆囊炎或胆囊息肉。2)首次接受LC手术治疗。3)符合《术后胃肠功能障碍防治专家共识》[7]中术后胃肠功能紊乱的诊断标准。4)美国麻醉师协会分级为Ⅰ~Ⅱ级。5)年龄25~70岁。6)自愿参加本研究,并签署协议书。
排除标准:1)合并胆管狭窄、胆总管结石、肿瘤等疾病。2)不能耐受手术的系统性疾病。3)合并溃疡性结肠炎、肠易激综合征等肠道疾病。4)精神系统疾病未有效控制。5)合并全身严重感染性疾病。6)取穴部位存在皮肤疾病。7)妊娠或哺乳期女性。
1.2 方法 1.2.1 对照组术后接受西医常规治疗,包括氧气吸入、生命体征监护,并予以维持水、电解质平衡、抗感染等,禁食水6 h,之后可进食米汤、水等无脂质流质食物,并逐渐过渡至低脂饮食。并于术后8 h开始予以中药通腑汤保留灌肠,药物组成:木香、桃仁、炒莱菔子、赤芍、枳壳各15 g,芒硝、大黄、厚朴各20 g,上述中药用清水2 000 mL(每剂)浸泡30 min,之后煎煮取得药液400 mL,每次取200 mL保留灌肠,每日2次,每次保留30 min,至恢复自主排气、排便。
1.2.2 观察组在对照组治疗基础上予以穴位贴敷,贴敷药物应用理气贴,药物组成:生大黄、延胡索、吴茱萸各30 g,厚朴、枳壳各20 g,当归、陈皮、香附、赤芍、川芎各15 g,将上述药物烘干、研末,取生姜汁、蜂蜜适量,将药物调和成膏状,贴敷于足三里(双侧)、天枢(双侧)和中脘穴,并以无菌敷贴覆盖、固定,第1次贴敷于术后6 h进行,每日贴敷1次,每次保留5 h,至恢复自主排气、排便。
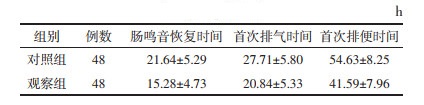
1.3 观察指标 1.3.1 胃肠功能恢复情况记录并比较两组肠鸣音恢复时间、首次排气时间和首次排便时间。术后6 h开始进行腹部听诊,于左上、左下、右上、右下腹部及脐周5个区域分别听诊1 min,每2 h听诊1次,如2个听诊区出现肠鸣音且≥3次/min则认为肠鸣音恢复。
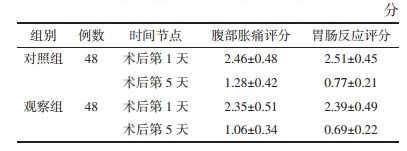
1.3.2 腹部胀痛评分和胃肠反应评分术后第1、5天后对两组进行腹部胀痛评分和胃肠反应评分。评分标准见表 1。
术后第1、5天后采集两组空腹静脉血4 mL,以3 000 r/min转速离心10 min,离心半径10 cm,收集血清,应用酶联免疫法测定血清生长抑素(SS)、血管活性肠肽(VIP)水平,仪器应用美国默赛飞世尔Multiskan FC型全自动酶标仪,试剂盒为默赛飞公司配套产品。
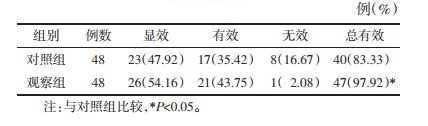
1.4 疗效评价术后第5天参照《中药新药临床研究指导原则(试行)》评价疗效:显效,恶心、呕吐、腹胀等症状消失,可正常排气、排便,睡眠时间≥3 h;有效,恶心、呕吐、腹胀等症状明显好转,排气、排便频率增加,睡眠时间 < 3 h;无效,恶心、呕吐、腹胀等症状无改善,排气、排便频率无变化,睡眠情况无改善。显效与有效例数之后为总有效。
1.5 统计学方法应用SPSS 23.0软件分析统计数据,计量资料以均数±标准差(x±s)表示,组内治疗前后比较采用配对t检验,组间比较采用独立样本t检验;计数资料以例数或率表示,组间比较采用χ2检验。P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果 2.1 两组胃肠功能恢复情况比较观察组肠鸣音恢复时间、首次排气时间和首次排便时间均少于对照组(P < 0.01)。见表 2。
|
术后第1天两组腹部胀痛评分和胃肠反应评分差异均无统计学意义(P > 0.05),术后第5天,两组腹部胀痛评分和胃肠反应评分均降低,观察组均低于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.01)。见表 3。
|
术后第1天两组血清SS、VIP水平差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05),术后第5天两组血清SS、VIP水平均降低,观察组均低于对照组,差异具有统计学意义(P < 0.01)。见表 4。
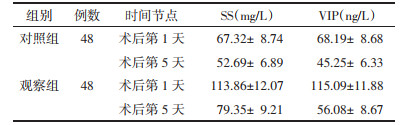
|
术后第5天,观察组治疗总有效率高于对照组,差异有统计学意义(χ2=4.414,P < 0.05),见表 5。
LC是普外科常用的手术方式,但术中受到麻醉药物的应用、手术的牵拉刺激、浆膜损伤等因素的影响,容易产生浆液渗出,进而导致胃肠功能紊乱,不利于营养物质的吸收,还会损伤肠黏膜的屏障功能,并可能伴随肠源性感染;对患者术后康复产生负面影响[8]。中医理论根据本病的临床特点将其归属为“肠结”“痞满”“呕吐”等范畴,与久病、外邪侵袭、金刃损伤等有关,胆为奇恒之腑,术前久病成疾,多伴有纳差、腹胀等脾胃虚弱症状,手术虽解除局部病变,但其病机仍存,且术中金刃损伤肌肉经络,致瘀血形成,气滞血瘀,进一步损及脾胃,脾胃升降失职,致胃肠功能紊乱[9]。
中药穴位外敷是中药方剂与经络腧穴理论相结合而产生的中医外治方法,这种方法充分发挥药物、腧穴、经络功效,共同调节脏腑功能和机体阴阳平衡,从而治疗和预防疾病[10]。根据“经脉所过,主治所及”的原则,故治疗胃肠疾病取穴应以足阳明胃经穴位为主。本研究所选足三里、天枢均为足阳明胃经穴位,其中足三里具有调理脾胃、行滞销胀、宽中理气、通经活络等作用,主治胃肠病症[11];天枢为大肠之募穴,可升降气机、调和中焦,主治腹痛、腹胀、便秘等胃肠病症[12];中脘为胃之募穴,具有健脾和胃、补齐降逆的作用,主治呃逆、呕吐、反胃等症[13]。本研究所应用中药理气贴组方由生大黄、延胡索、吴茱萸等药物组成,其中生大黄可泄下攻积、通降肠胃,吴茱萸可辛散止痛、降逆止呕。枳壳破气消痞,厚朴降气除满,可助大黄泄痞宽胀;附子可行气止痛;延胡索、川芎、赤芍活血化瘀、行气消滞、条畅气血;木香当归可补血活血,陈皮健脾益气,两药配伍可助其他药物辛散活化之力,使散而不伤气,行而不伤血。全方配伍理气活血、健脾和胃兼顾,对LC术后胃肠功能紊乱标本兼治。
中药灌肠也是临床常用的中医外治方法之一,本法将中药药液灌肠,使中药直达患处,药液有效成分可直接通过直肠黏膜吸收入血,避免了中药口服的受过效应,减轻和药物对胃肠道刺激作用[14];本研究灌肠中药通腑汤是由大承气汤化裁而来,其中芒硝、大黄可泄下导滞,攻下破积,桃仁、赤芍活血祛瘀止痛,木香、枳壳行气止痛,炒莱菔子消胀行气;厚朴可下气除满。研究表明大承气汤可改善肠道微循环,减轻肠道水肿,促进肠道平滑肌收缩和肠内容物排出,加速胃肠功能的恢复[15]。本研究发现治疗后观察组肠鸣音恢复时间、首次排气时间和首次排便时间均少于对照组,术后第5天腹部胀痛评分和胃肠反应评分均低于对照组,治疗总有效率高于对照组,表明穴位贴敷联合中药灌肠可促进胃肠功能恢复,降低腹部胀痛评分和胃肠反应评分,提高LC术后胃肠功能紊乱的治疗效果。
胃肠激素是一种调节肽,可调节消化器官运动、分泌等生物学行为,胃肠激素的分泌异常是发生胃肠功能紊乱的重要因素[16]。SS可降低迷走神经张力,减弱迷走神经兴奋性,抑制胃动素分泌,进而对胃肠运动发挥抑制作用[17]。VIP是一种舒血管肠肽,由28个氨基酸组成,主要由肠道神经元释放,具有舒张肠道平滑肌、扩张血管的作用[18]。研究表明胃肠手术患者血清SS、VIP含量会显著升高,且升高程度可较好地反应患者胃肠功能紊乱状况[19]。本研究发现治疗后观察组血清SS、VIP含量均显著低于对照组,表明穴位贴敷联合中药灌肠可能通过多靶点多途径改善胃肠激素水平,促进胃肠功能的恢复。
综上所述,穴位贴敷联合中药灌肠可降低腹部胀痛评分和胃肠反应评分,改善血清SS、VIP,促进胃肠功能恢复,治疗LC术后胃肠功能紊乱效果显著。但本研究纳入病例数较少,穴位贴敷联合中药灌肠对LC术后胃肠功能紊乱的效果需要扩大样本量进一步验证,其改善胃肠激素水平的具体机制尚需深入探讨。
| [1] |
中华医学会外科学分会胆道外科学组, 中国医师协会外科医师分会胆道外科医师委员会. 胆囊良性疾病外科治疗的专家共识(2021版)[J]. 中华外科杂志, 2022, 60(1): 4-9. Biliary Surgery Group Surgical Credit Committee Chinese Medical Association, Biliary Tract Surgeons Committee of the Surgeons Branch of the Chinese Medical Association. Consensus on the surgical management of benign gallbladder diseases (2021 edition)[J]. Chinese Journal of Surgery, 2022, 60(1): 4-9. |
| [2] |
张岩, 郑玉强. 腹腔镜胆囊切除术与开腹手术治疗胆结石的临床效果比较[J]. 中国现代普通外科进展, 2020, 23(12): 965-967. ZHANG Y, ZHENG Y Q. Comparison of clinical effects between laparoscopic cholecystectomy and open surgery in the treatment of gallstones[J]. Chinese Journal of Current Advances in General Surgery, 2020, 23(12): 965-967. |
| [3] |
刘金苗, 王玉玲. 穴位贴敷联合中药热奄包在腹腔镜胆囊切除术后胃肠功能恢复中的应用[J]. 中国中西医结合外科杂志, 2022, 28(5): 679-682. LIU J M, WANG Y L. Application of acupoint application combined with traditional Chinese medicine hot package in the recovery of gastrointestinal function after laparoscopic cholecystectomy[J]. Chinese Journal of Surgery of Integrated Traditional and Western Medicine, 2022, 28(5): 679-682. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1007-6948.2022.05.016 |
| [4] |
张静, 高晓杰, 赵华婧, 等. 董氏奇穴结合丁沉扶正汤对胃癌术后胃肠功能紊乱患者胃肠功能及血清SS、VIP表达的影响[J]. 天津中医药, 2022, 39(5): 611-615. ZHANG J, GAO X J, ZHAO H J, et al. Effect of Dongshi Qixue combined with Dingchen Fuzheng Decoction on gastrointestinal function and serum somatostain and vasoactive intestinal peptide expression in patients with gastrointestinal dysfunction after gastric cancer surgery[J]. Tianjin Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 39(5): 611-615. |
| [5] |
巩子星, 刘远, 张明明, 等. 穴位贴敷对阑尾炎腹腔镜术后恢复的影响[J]. 上海针灸杂志, 2020, 39(7): 904-908. GONG Z X, LIU Y, ZHANG M M, et al. Effect of acupoint application on the recovery after laparoscopic appendectomy[J]. Shanghai Journal of Acupuncture and Moxibustion, 2020, 39(7): 904-908. |
| [6] |
赵传印, 张跃强. 中药灌肠对腹部术后早期炎性肠梗阻胃肠动力的影响[J]. 中国中西医结合外科杂志, 2021, 27(4): 551-554. ZHAO C Y, ZHANG Y Q. Effect of traditional Chinese medicine enema on gastrointestinal motility of early postoperative inflammatory intestinal obstruction[J]. Chinese Journal of Surgery of Integrated Traditional and Western Medicine, 2021, 27(4): 551-554. |
| [7] |
李偲, 刘克玄, 邓小明, 等. 术后胃肠功能障碍防治专家共识[J]. 国际麻醉学与复苏杂志, 2021, 42(11): 1133-1142. LI C, LIU K X, DENG X M, et al. Expert consensus on prevention and treatment of postoperative gastrointestinal dysfunction[J]. International Journal of Anesthesiology and Resuscitation, 2021, 42(11): 1133-1142. |
| [8] |
刘姝璇, 蔡政东. 子午捣臼法联合柴平汤治疗腹腔镜胆囊切除术后胃肠功能紊乱临床观察[J]. 辽宁中医药大学学报, 2022, 24(3): 164-167. LIU S X, CAI Z D. Effect of ziwu daojiu method combined with Chaiping Decoction on treating gastrointestinal dysfunction after laparoscopic cholecystectomy[J]. Journal of Liaoning University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 24(3): 164-167. |
| [9] |
罗芳丽, 雷枭, 廖伯年, 等. 术后胃肠功能紊乱的中医治疗进展[J]. 中医药导报, 2022, 28(4): 197-200. LUO F L, LEI X, LIAO B N, et al. Progress on TCM treatment of postoperative gastrointestinal dysfunction[J]. Guiding Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine and Pharmacy, 2022, 28(4): 197-200. |
| [10] |
邹佳, 余俊英, 管咏梅, 等. 中药穴位贴敷的研究现状及问题分析[J]. 中华中医药杂志, 2022, 37(9): 5471-5475. ZOU J, YU J Y, GUAN Y M, et al. Research status and problem analysis of acupoint application of traditional Chinese medicine[J]. China Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine and Pharmacy, 2022, 37(9): 5471-5475. |
| [11] |
陈浩然, 方霜霜, 林新锋. 足三里穴位注射治疗术后胃肠功能障碍疗效与安全性的Meta分析[J]. 广州中医药大学学报, 2022, 39(10): 2450-2458. CHEN H R, FANG S S, LIN X F. Meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of zusanli(ST36) acupoint injection for postoperative gastrointestinal dysfunction[J]. Journal of Guangzhou University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 39(10): 2450-2458. |
| [12] |
许爱丽, 李园, 杨俭勤, 等. 天枢、上巨虚作为基础腧穴治疗胃肠疾病的研究进展[J]. 世界中医药, 2022, 17(21): 3096-3100. XU A L, LI Y, YANG J Q, et al. Research progress of treating gastrointestinal diseases with tianshu and shangjuxu as basic acupoints[J]. World Chinese Medicine, 2022, 17(21): 3096-3100. |
| [13] |
郭金玉, 孙志杰. 温艾灸足三里、中脘穴位促进腹部外科手术胃肠功能恢复临床护理观察[J]. 辽宁中医药大学学报, 2021, 23(2): 205-208. GUO J Y, SUN Z J. Clinical nursing observation on warm moxibustion at zusanli and zhongwan points to promote the recovery of gastrointestinal function in abdominal surgery[J]. Journal of Liaoning University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2021, 23(2): 205-208. |
| [14] |
张丽慧, 段培芳, 张震, 等. 疏肝解郁胶囊联合中药灌肠治疗溃疡性结肠炎患者的疗效观察[J]. 世界中西医结合杂志, 2022, 17(10): 2006-2010, 2014. ZHANG L H, DUAN P F, ZHANG Z, et al. Clinical observation of Shugan Jieyu Capsule combined with Chinese medicine en-ema in treating ulcerative colitis[J]. World Journal of Integrated Traditional and Western Medicine, 2022, 17(10): 2006-2010, 2014. |
| [15] |
谭巨丹, 瞿荣兰, 邓乾素, 等. 大承气汤保留灌肠联合穴位指针疗法缓解无创通气患者并发腹胀的疗效观察[J]. 中国中医急症, 2022, 31(7): 1218-1220. TAN J D, QU R L, DENG Q S, et al. Effect observation of Dachengqi Decoction retention enema combined with acupoint pointer therapy on alleviating abdominal distension in patients with non-invasive ventilation[J]. Journal of Emergency in Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 31(7): 1218-1220. |
| [16] |
金利红, 程华军, 虞笑娟, 等. 调中健脾汤联合米曲菌胰酶片对功能性消化不良患者胃肠激素及细胞因子水平的影响[J]. 中国中西医结合消化杂志, 2022, 30(11): 780-784. JIN L H, CHENG H J, YU X J, et al. Effects of Tiaozhong Jianpi Decoction combined with oryz-aspergilllus enzyme and pancreatin tablets on gastrointestinal hormones and cytokines in patients with functional dyspepsia[J]. Chinese Journal of Integrated Traditional and Western Medicine on Digestion, 2022, 30(11): 780-784. |
| [17] |
尹宏, 陈庆春, 苏艳蓉, 等. 重症高血压脑出血并发应激性胃溃疡影响因素及GAS、MTL、SS、CCK-8、VIP水平变化意义[J]. 分子诊断与治疗杂志, 2020, 12(2): 156-160. YIN H, CHEN Q C, SU Y R, et al. Influencing factors of severe hypertensive cerebral hemorrhage complicated with stress gastric ulcer and the significance of changes in GAS, MTL, SS, CCK-8 and VIP[J]. Journal of Molecular Diagnosis and Therapy, 2020, 12(2): 156-160. |
| [18] |
ZYGULSKA A L, FURGALA A, KASZUBA-ZWOISKA J, et al. Changes in plasma levels of cholecystokinin, neurotensin, VIP and PYY in gastric and colorectal cancer-Preliminary results[J]. Peptides, 2019, 122: 170148. |
| [19] |
FENG X M, MA X Y, SHI Y. Correlations of recurrence of gastric cancer in patients after radical surgery with serum gastrointestinal hormones, vascular endothelial growth factors and serum anti-helicobacter pylori IgG antibody[J]. Journal of BUON, 2020, 25(3): 1476-1481. |
 2023, Vol. 40
2023, Vol. 40