文章信息
- 杨睿, 陈炫好, 李晋, 何俊, 常艳旭
- YANG Rui, CHEN Xuanhao, LI Jin, HE Jun, CHANG Yanxu
- 薄荷化学成分及药理活性研究进展
- Research development of Menthae Haplocalycis Herba on chemical composition and pharmacological activity
- 天津中医药大学学报, 2022, 41(1): 4-13
- Journal of Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 41(1): 4-13
-
文章历史
收稿日期: 2021-10-30
薄荷(Menthae Haplocalycis Herba)为唇形科植物薄荷Mentha haplocalyx Briq.的干燥地上部分,味辛,性凉,归肺、肝经,具有疏散风热、清利头目、利咽透疹、疏肝行气等功效[1]。薄荷作为常用辛凉解表药之一,主产于云南、江苏、浙江、江西、安徽等地。薄荷主要含有挥发油类、黄酮类、萜类、酚酸类、醌类、苯丙素类等化学成分,现代药理研究表明其具有抗菌、抗病毒、抗炎、抗氧化、抗肿瘤、抗生育等作用。另外,薄荷还是金花清感颗粒及连花清瘟胶囊的组成成分,可以解毒利咽、轻宣肺气,改善新型冠状病毒肺炎患者症状[2]。本文对薄荷化学成分、药理作用和毒性进行综述,为进一步深入研究薄荷提供科学依据。
1 本草考证薄荷始载于唐代《备急千金要方·食治》,名为蕃荷菜,另有别名茇括(《甘泉赋》)、菝苛(《食性本草》)、南薄荷(《本草衍义》)、猫儿薄荷(《履山巉岩本草》)、升阳菜(《滇南本草》)、蔢荷(《本草蒙荃》)等[3]。经本草考证,药用薄荷一直是唇形科植物薄荷Mentha haplocalyx Briq.的干燥地上部分,与历年各版《中华人民共和国药典》收载的薄荷品种一致。
历代本草文献对薄荷的性味、功效等内容均有记载与描述,唐代《新修本草》中记载薄荷:“味辛、苦,温,无毒。主贼风伤寒发汗,恶气心腹胀满,霍乱,宿食不消,下气。”[4]《日华子本草》提出薄荷“治中风失音,吐痰”。甄权所著《药性论》认为薄荷:“能去愤气,发毒汗,破血,止痢,通利关节。”[5]宋代本草继承唐代本草记载,并扩大了薄荷的功效主治。《本草衍义》提出薄荷可用于“小儿惊风、壮热”“治骨蒸热劳”[6],同时《履巉岩本草》首次记载薄荷“性极凉”[7]。金元时期,张元素所著《医学启源·药类法象》引用《主治秘要》言:“性凉味辛,气味俱薄,浮而升,阳也。去高颠及皮肤风热。”[8]《药类法象》又补充了薄荷“主清利头目”。明代《本草蒙筌》记载薄荷:“清六阳会首,驱诸热生风。退骨蒸解劳乏,善引药入荣卫。乃因性喜上升,小儿风涎尤为要药。”[9]《神农本草经疏》曰:“贼风伤寒,其邪在表,故发汗则解风。”[10]清代《本草新编》认为薄荷“不特善解风邪,尤善解忧郁”“入肝、胆之经,善解半表半里之邪,较柴胡更为轻清”[11]。张锡纯在《医学衷中参西录》中记载薄荷:“内透筋骨,外达肌表,宣通脏腑,贯串经络。服之能透发凉汗,为温病宜汗解者之要药。”[12]
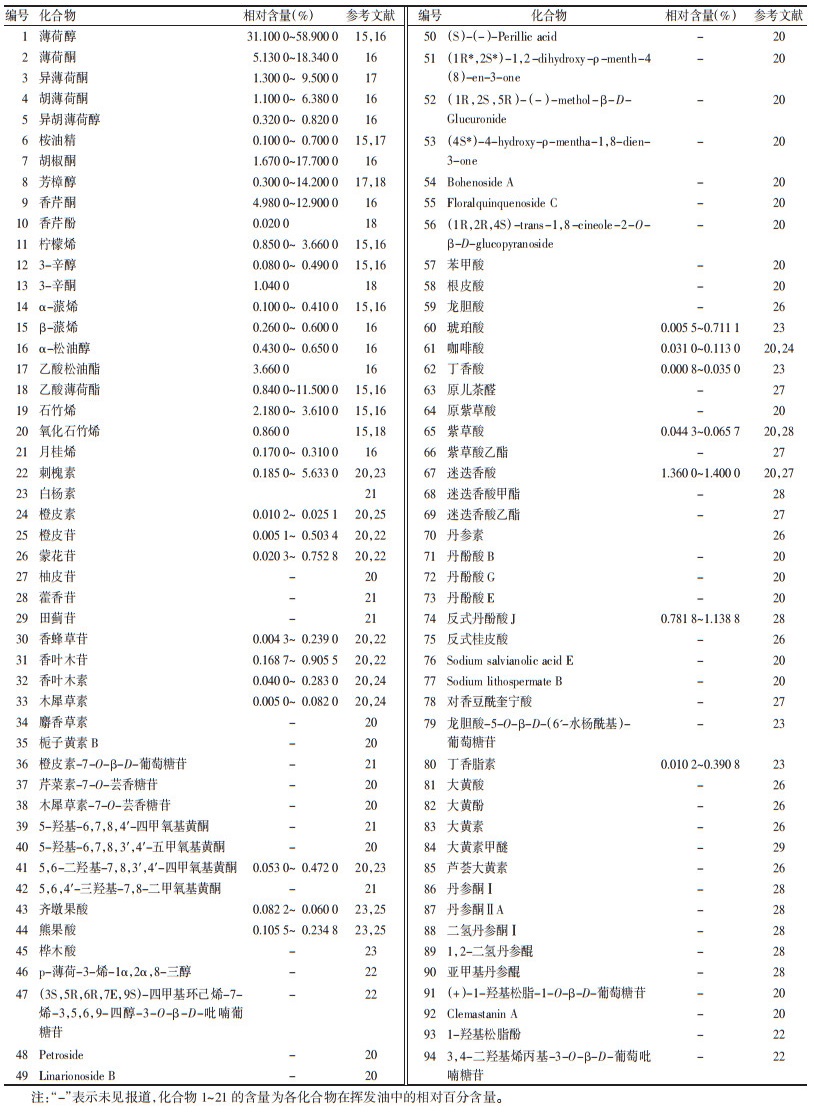
2 化学成分研究薄荷具有较高的药用价值和经济价值,目前国内外研究人员已对其化学成分进行了全面研究。薄荷的化学成分主要包括挥发油类、黄酮类、萜类、酚酸类、醌类、苯丙素类等,其中挥发油类成分是薄荷的特征性成分。薄荷主要化学成分见表 1。
挥发油类成分为薄荷的主要活性成分,包括醇、酮、酯、萜烷、萜烯等。2020年版《中华人民共和国药典》规定薄荷药材含挥发油不得少于0.80%(mL/g),薄荷饮片含挥发油不得少于0.40%(mL/g)[1]。研究表明薄荷挥发油类成分具有促进渗透、改善精神疲劳、祛痰、抗炎、抗微生物等作用[13-14]。目前薄荷挥发油类成分主要包括薄荷醇、薄荷酮、异薄荷酮、胡薄荷酮、异胡薄荷醇、胡椒酮、桉油精、芳樟醇、香芹酮、香芹酚、柠檬烯、3-辛醇、3-辛酮、α-蒎烯、β-蒎烯、α-松油醇、乙酸松油酯、乙酸薄荷酯等[15-18]。其中薄荷脑为《中华人民共和国药典》规定的薄荷含量测定的指标性成分。
2.2 黄酮类成分黄酮类成分也是薄荷的主要成分之一,薄荷中黄酮类成分具有良好的抗氧化、抗病毒、抗炎等生物活性[19],主要有刺槐素、白杨素、橙皮素、橙皮苷、蒙花苷、柚皮苷、藿香苷、田蓟苷、香蜂草苷、香叶木苷、木犀草素、香叶木素、栀子黄素B、橙皮素-7-O-β-D-葡萄糖苷、木犀草素-7-O-芸香糖苷、芹菜素-7-O-芸香糖苷、5-羟基-6,7,8,4′-四甲氧基黄酮、5-羟基-6,7,8,3′,4′-五甲氧基黄酮、5,6-二羟基-7,8,3′,4′-四甲氧基黄酮、5,6,4′-三羟基-7,8-二甲氧基黄酮等[20-25]。
2.3 萜类成分薄荷中萜类成分主要包括单萜类和五环三萜类两大类,研究表明薄荷中的萜类成分具有较好的抗炎、抗菌、抗病毒、抗肿瘤活性[22],主要有齐墩果酸、熊果酸、桦木酸、p-薄荷-3-烯-lα,2α,8-三醇、(3S,5R,6R,7E,9S)-四甲基环己烯-7-烯-3,5,6,9-四醇-3-O-β-D-吡喃葡糖苷、Petroside、Linarionoside B、(S)-(-)-Perillicacid、(1R*,2S*)-1,2-dihydroxy-ρ-menth-4(8)-en-3-one、(1R,2S,5R)-(-)-menthol β-D-Glucuronid、(4S*)-4-hydroxy-ρ-mentha-1,8-dien-3-one等[20, 22-25]。
2.4 酚酸类成分薄荷酚酸类成分主要有苯甲酸、根皮酸、龙胆酸、琥珀酸、咖啡酸、丁香酸、原儿茶醛、原紫草酸、紫草酸、紫草酸乙酯、迷迭香酸、迷迭香酸甲酯、迷迭香酸乙酯、丹参素、丹酚酸B、丹酚酸G、丹酚酸E、反式丹酚酸J、反式桂皮酸等[20, 23-28],具有抗炎、抗菌、抗病毒、抗氧化的药理作用[21, 27]。
2.5 醌类成分研究发现薄荷中含有大黄酸、大黄酚、大黄素、大黄素甲醚、芦荟大黄素、丹参酮Ⅰ、丹参酮ⅡA、二氢丹参酮Ⅰ、亚甲基丹参醌、1,2-二氢丹参醌等醌类化合物[26, 28-29]。
2.6 苯丙素类化合物薄荷中有多种苯丙素类成分,如(+)-1-羟基松脂-1-O-β-D-葡萄糖苷、Clemastanin A、1-羟基松脂酚、3,4-二羟基烯丙基-3-O-β-D-葡萄吡喃糖苷等,他们大多具有抗肿瘤、杀虫、抗炎、抗氧化、降血糖等药理作用,具有极大的应用前景[20, 22]。
2.7 其他成分除上述成分外,薄荷中还含有大量的氨基酸,如谷氨酸、天冬氨酸、苏氨酸、亮氨酸等[30]。同时薄荷中还测定出丰富的微量元素,如铁(Fe)、钙(Ca)、锌(Zn)等[31]。另外薄荷中也存在棕榈酸、油酸等脂肪酸类成分[22]。
3 药理作用薄荷是常用中药之一,主要用于治疗风热感冒、口舌生疮、咽喉肿痛、隐疹不透、肝郁不舒等。现代药理学研究表明,薄荷的化学成分具有抗炎、抗病毒、抗氧化、抗菌、保肝利胆、抗肿瘤、抗生育等多种药理活性。薄荷化学成分-药理活性-功效网络图见图 1。
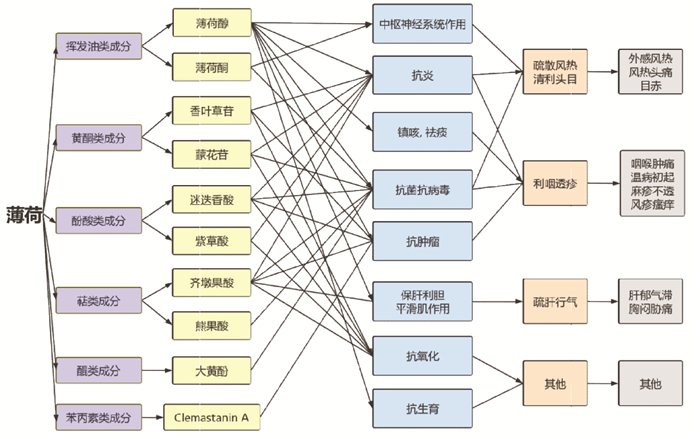
|
| 图 1 薄荷化学成分-药理活性-功效网络图 |
薄荷对多种致病细菌有抑制作用。研究表明薄荷的水、无水乙醇和乙酸乙酯提取液对枯草芽孢杆菌、大肠杆菌、沙门氏菌、金黄色葡萄球菌具有明显的抑制作用[32]。此外,从薄荷中提取得到的挥发油对革兰氏阳性菌和革兰氏阴性菌的抑菌效果显著[33]。研究人员通过体外抑菌实验发现不同化学型的薄荷挥发油均具有一定的抑菌活性,可有效抑制表皮葡萄球菌、肺炎克雷伯菌、铜绿假单胞菌等多种菌株[34]。另有研究表明薄荷挥发油中单体成分薄荷醇是其抗菌的有效成分,聚乳酸-羟基乙酸共聚物(PLGA)纳米化的L-薄荷醇通过破坏细菌细胞的细胞壁和细胞膜结构,影响细菌生长繁殖而发挥较强的抗菌作用[35-36]。
薄荷还具有一定的抗真菌作用。薄荷精油及其化合物D-香芹酮、D-柠檬烯对尖孢镰刀菌、腐皮镰孢霉菌、瓜果腐霉菌、灰霉菌等三七病原菌具有抑制作用。主要通过穿透和溶解细胞器细胞膜达到抑制真菌生长的目的[37]。
3.2 抗病毒作用近年来大量的研究证明薄荷具有抗病毒作用。陈向阳等[38]通过四甲基偶氮唑蓝(MTT)法研究发现薄荷酚类部位具有较强的抗流感病毒活性,不同的加药方式均能不同程度抑制PR8流感病毒。陈飞等[39]通过薄荷不同化学部位的体外抗病毒实验发现,薄荷的水溶性成分具有明显的抗单纯胞疹病毒活性,抑毒指数为74.3。薄荷水提液对感染呼吸道合胞病毒的小鼠具有一定治疗作用,表现出显著的体内抗病毒效果[40]。薄荷水提物对柯萨奇病毒A16型(CVA16)具有抗病毒活性,可用于手足口病的治疗[41]。
薄荷酮和胡薄荷酮是薄荷中的单体成分,实验发现其对甲型流感病毒(H1N1)有抑制作用,可能与促进干扰素-α(IFN-α)、干扰素-β(IFN-β)、白细胞介素(IL)-2的分泌,抑制IL-6与肿瘤坏死因子-α(TNF-α)的产生有关[42]。另外香芹酚还可以通过抑制病毒复制和下调Toll样受体/维甲酸诱导基因Ⅰ受体(TLR/RLR)信号通路从而抑制H1N1引起的小鼠过度免疫反应[43]。
在防控新型冠状病毒肺炎疫情期间,薄荷还被广泛应用于预防和治疗新型冠状病毒肺炎的中药处方中[44-46],如薄荷配伍的连花清瘟胶囊、金花清感颗粒被推荐用于医学观察期患者的治疗[47]。
3.3 对呼吸系统的作用发现薄荷挥发油中的薄荷醇可以通过调控瞬时受体电位M8(TRPM8)通道抑制香烟烟雾引起的呼吸道刺激[48],这种抗刺激作用可以导致呼吸道产生新的分泌物,使黏稠的痰液易于排出,表现出祛痰作用。进一步研究发现薄荷醇可以通过激活TRPM8通路抑制支气管哮喘小鼠的气道高反应性[49],同时还可以有效减轻鸡卵清蛋白(OVA)所致的哮喘气道炎症和气道高反应性,下调肺组织P物质(SP),减轻哮喘的神经源性炎症[50]。另外薄荷也是治疗咳嗽的常用药,临床上常与苏叶配伍用于治疗慢性咳嗽[51]。
3.4 抗炎作用薄荷具有一定的抗炎活性。研究发现薄荷酚类部位及其活性成分蒙花苷、迷迭香酸可以抑制脂多糖诱导的RAW264.7细胞炎症反应,主要通过抑制丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(MAPK)和核转录因子-κB(NF-κB)信号通路的活化,下调诱导型一氧化氮合酶(iNOS)、TNF-α、IL-1β和IL-6 mRNA的表达水平,进一步抑制炎性介质一氧化氮(NO)和促炎性细胞因子TNF-α、IL-1β、IL-6的分泌,从而发挥抗炎作用[27, 52]。另有研究表明薄荷醇通过降低髓过氧化物酶(MPO)活性和减少促炎细胞因子,对醋酸所致的大鼠急性结肠炎具有显著的治疗作用[53]。薄荷酮可能通过抑制NOD样受体蛋白结构域3(NLRP3)炎症小体的激活,减少干扰素-γ(IFN-γ)等促炎因子的释放进而减轻内毒素所致的小鼠肺部炎症损伤[54]。胡薄荷酮通过抑制髓样分化蛋白88(MyD88)依赖的NF-κB信号通路同样对大鼠急性肺损伤炎症模型有抑制作用[55]。临床研究也证实了龙甘薄荷汤含漱治疗慢性咽炎疗效较好[56],含薄荷脑的复方木芙蓉涂鼻软膏和薄荷油可有效缓解干燥性鼻炎相关症状[57]。
3.5 抗氧化作用薄荷提取物具有较强的抗氧化活性。研究发现薄荷正丁醇、水、乙酸乙酯、三氯甲烷提取物都具有良好的1,1-二苯基-2-三硝基苯肼(DPPH)自由基清除能力,且其作用与浓度呈正相关[58]。徐晶晶等[59]通过抗氧化谱效关系研究,发现薄荷中酚酸类、黄酮类成分具有显著的抗氧化能力,可有效清除体内自由基,并筛选出橙皮苷、蒙花苷、反式丹酚酸J、迷迭香酸等化合物为其发挥抗氧化作用的相关成分。高燕[60]研究发现野生薄荷精油也具有一定的抗氧化活性,能显著清除羟基自由基、超氧阴离子自由基、DPPH自由基,具有作为天然抗氧化剂的应用潜能。此外,薄荷多糖还可以明显提高D-半乳糖诱导的衰老小鼠体内抗氧化酶活性,表现出抗氧化、抗衰老作用[61-62]。
3.6 对中枢神经系统的作用薄荷芳香辛散,对中枢神经系统类疾病也有一定的功效。梁浩明等[63]发现鼻吸入薄荷油后有一定的抗精神疲劳作用,能显著减少小鼠强迫游泳不动时间,缩短戊巴比妥钠诱导的睡眠时间,并提高睡眠剥夺小鼠的自发活动,其作用机制可能与促进兴奋性氨基酸神经递质释放、减少抑制性神经递质的含量相关。孙凡等[64]研究发现薄荷复合精油可以通过降低乙酰胆碱酯酶(AchE)含量有效改善轻度认知障碍,其主要成分1,8-桉树脑是N-甲基-D-天冬氨酸(NMDA)拮抗剂,具有治疗阿尔茨海默病的潜能[65]。此外,从薄荷挥发油中分离得到的左旋薄荷醇被证实具有抗抑郁作用,其抗抑郁机制可能与多巴胺能、5-羟色胺能和γ-氨基丁酸能系统有关[66]。另有临床研究表明复方薄荷脑注射液具有良好的镇痛作用,可应用于肛肠手术中起到局部麻醉的作用[67]。
3.7 保肝利胆作用和松弛平滑肌作用薄荷具有一定的保肝利胆作用。Bellassoued等[68]研究发现薄荷精油对四氯化碳(CCl4)诱导的肝氧化损伤具有保护作用,可显著降低大鼠血清天门冬氨酸氨基转移酶(AST)、丙氨酸氨基转移酶(ALT)、碱性磷酸酶(ALP)、乳酸脱氢酶(LDH)和γ谷氨酰转肽酶(γ-GT)的水平。实验发现胆舒胶囊(主要成分为薄荷素油)能明显促进大鼠胆汁分泌,增加总胆汁酸含量,降低总胆固醇水平,具有显著的利胆作用[69]。
薄荷还具有松弛平滑肌的作用。陈裕等[70]实验研究发现,薄荷素油通过阻断钙离子(Ca2+)通道而抑制Oddi括约肌收缩,降低Oddi括约肌基础压。另有研究发现薄荷醇通过阻断肌膜L型Ca2+通道,抑制Ca2+内流,直接抑制胃肠道平滑肌收缩,对人结肠环行平滑肌具有解痉作用[71]。
3.8 抗肿瘤作用薄荷主要功效成分薄荷醇具有明显的抗肿瘤活性,对人结肠癌细胞、人前列腺癌细胞和人膀胱癌细胞均有一定的抗增殖作用[72]。陶兴魁等[73]用不同浓度的薄荷醇分别作用于体外培养的肝癌HepG2细胞,发现其对HepG2细胞的增殖和迁移有明显抑制作用,这一作用可能与下调IL-8、趋化因子-12(CXCL-12)mRNA和血管内皮生长因子(VEGF)的表达水平有关。同时薄荷醇还可以通过下调HepG2细胞中CYP3A4的表达而增强紫杉醇(PAC)和长春新碱(VIN)的抗肿瘤作用[74]。
3.9 抗生育作用易真珍等[75]研究发现薄荷油具有显著的抗生育能力,能够破坏雌性小鼠子宫和卵巢等生殖器官。曹玫等[76]通过实验同样发现薄荷油会损伤雄性小鼠的睾丸和附睾,影响精子的活力,从而发挥抗生育作用。同时有研究表明薄荷油颗粒剂可以抑制高原鼠兔生育能力,具有防治草原鼠害的应用前景[77]。
3.10 其他作用研究表明,薄荷50%乙醇提取物具有降低血糖的作用[78],同时薄荷对α-葡萄糖苷酶、α-淀粉酶具有一定的抑制作用,可用于治疗糖尿病[79]。文献报道了薄荷水提液对线虫有良好的抗辐射作用,可延长线虫生命[80]。薄荷精油还具有驱虫作用,对烟甲虫有强接触毒性,有作为天然杀虫剂或驱虫剂的应用价值[81]。
4 毒性研究薄荷还具有一定的毒副作用。有研究通过小鼠急性毒性实验发现薄荷挥发油的毒性较其他组分更强,进一步研究发现高剂量的薄荷挥发油和水提物对小鼠具有肝脏毒性,可造成急性肝损伤[82]。但薄荷在临床和生活中应用广泛,在规定剂量范围内使用安全性高,具有极大的应用价值。
5 结语与展望综上所述,薄荷作为临床常用中药,应用范围广且毒性较低,具有极大的开发利用价值和潜能。薄荷中所含有的萜类、黄酮类、酚酸类、醌类、挥发油类等成分具有多种药理活性,其中挥发油和黄酮类成分为其抗菌、抗病毒、抗炎、抗氧化作用的主要药效成分。今后应当深入研究薄荷的药效物质基础与作用机制,为指导临床合理应用提供科学依据。
| [1] |
国家药典委员会. 中华人民共和国药典[M]. 北京: 中国医药科技出版社, 2020: 394-395. Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission. Pharmacopoeia of people's republic of China[M]. Beijing: China Medical Science Press, 2020: 394-395. |
| [2] |
杨玉莹, 窦晓鑫, 王方园, 等. 抗新型冠状病毒肺炎"三药三方"之中医理论探讨[J]. 天津中医药, 2021, 38(6): 700-705. YANG Y Y, DOU X X, WANG F Y, et al. Discussion on traditional Chinese medicine theory of anti-COVID-19 "three drugs and three prescriptions"[J]. Tianjin Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2021, 38(6): 700-705. |
| [3] |
张燕, 吴维, 朱峰. 薄荷的本草考证及与墨旱莲的鉴别[J]. 中国乡村医药, 2016, 23(21): 44-45. ZHANG Y, WU W, ZHU F. Textual research of Mentha haplocalyx Briq. and identification with Yerbadetajo Herb[J]. Chinese Journal of Rural Medicine and Pharmacy, 2016, 23(21): 44-45. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-5180.2016.21.025 |
| [4] |
苏敬. 新修本草[M]. 合肥: 安徽科学技术出版社, 1981: 471. SU J. Newly revised materia medica[M]. Hefei: Anhui Science and Technology Press, 1981: 471. |
| [5] |
甄权. 药性论药性趋向分类论合刊本[M]. 合肥: 安徽科学技术出版社, 2006: 48. ZHEN Q. Drug property theory[M]. Hefei: Anhui Science and Technology Press, 2006: 48. |
| [6] |
寇宗奭. 本草衍义[M]. 北京: 中国医药科技出版社, 2012: 41. KOU Z S. Augmented material medical[M]. Beijing: China Medical Science Press, 2012: 41. |
| [7] |
王介. 履巉岩本草[M]. 北京: 华夏出版社, 1999: 38. WANG J. Lyuchanyan materia medica[M]. Beijing: Huaxia Publishing House, 1999: 38. |
| [8] |
张元素. 医学启源[M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 1978: 173, 176. ZHANG Y S. Origins of medicine[M]. Beijing: People's Medical Publishing House, 1978: 173. |
| [9] |
陈嘉谟. 本草蒙筌[M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 1988: 108-109, 122. CHEN J M. Materia medica companion[M]. Beijing: People's Medical Publishing House, 1988: 108-109, 122. |
| [10] |
缪希雍. 神农本草经疏[M]. 北京: 中医古籍出版社, 2002: 313, 369. MIAO X Y. Shennong's classic of materia medica[M]. Chinese Medicine Ancient books Publishing House, 2002: 313, 369. |
| [11] |
陈士铎. 本草新编[M]. 北京: 中国医药科技出版社, 2011: 124. CHEN S D. New compilation of materia medica[M]. Beijing: China Medical Science Press, 2011: 124. |
| [12] |
张锡纯. 医学衷中参西录[M]. 石家庄: 河北科学技术出版社, 2001: 310. ZHANG X C. Records of tradition Chinese and Western medicine in combination[M]. Shijiazhuang: Hebei Science & Technology Press, 2001: 310. |
| [13] |
黄兴雨, 杨黎燕, 尤静. 薄荷挥发油研究进展[J]. 化工科技, 2019, 27(3): 70-74. HUANG X Y, YANG L Y, YOU J. Research progress in volatile oil in Mentha[J]. Science & Technology in Chemical Industry, 2019, 27(3): 70-74. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1008-0511.2019.03.015 |
| [14] |
BRAHMI F, KHODIR M, MOHAMED C, et al. Chemical composition and biological activities of Mentha species[M]. Aromatic and Medicinal Plants-Back to Nature, 2017, 34(11): 47-78.
|
| [15] |
DONG W J, NI Y N, KOKOT S. Differentiation of Mint (Mentha haplocalyx Briq.) from different regions in China using gas and liquid chromatography[J]. Journal of Separation Science, 2015, 38(3): 402-409. DOI:10.1002/jssc.201401130 |
| [16] |
迟玉广, 李中阳, 黄爱华, 等. 不同产地薄荷饮片中挥发性成分的比较分析[J]. 安徽医药, 2016, 20(9): 1661-1664. CHI Y G, LI Z Y, HUANG A H, et al. A comparative analysis of volatile components in Mentha haplocalyx Briq. from different habitats[J]. Anhui Medical and Pharmaceutical Journal, 2016, 20(9): 1661-1664. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1009-6469.2016.09.013 |
| [17] |
ZHAO D, XU Y W, YANG G L, et al. Variation of essential oil of Mentha haplocalyx Briq. and Mentha spicata L. from China[J]. Industrial Crops and Products, 2013, 42(10): 251-260. |
| [18] |
魏亮, 方洪壮, 吴比, 等. 东北野生薄荷挥发油成分及抑菌活性研究[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2019, 47(10): 170-172, 178. WEI L, FANG H Z, WU B, et al. Study on the components and antibacterial activity of volatile oil from wild Mentha haplocalyx Briq. in northeast China[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 47(10): 170-172, 178. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2019.10.052 |
| [19] |
周文菊, 豆小文, 杨美华, 等. 薄荷及其饮片质量控制研究进展[J]. 中国中药杂志, 2016, 41(9): 1569-1577. ZHOU W J, DOU X W, YANG M H, et al. Quality control in Menthae Haplocalycis Herba and its decoction slices[J]. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica, 2016, 41(9): 1569-1577. |
| [20] |
XU L L, XU J J, ZHONG K R, et al. Analysis of non-volatile chemical constituents of Menthae haplocalycis herba by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-high resolution mass spectrometry[J]. Molecules, 2017, 22(10): 1756. DOI:10.3390/molecules22101756 |
| [21] |
华燕青. 薄荷化学成分及其提取方法研究进展[J]. 陕西农业科学, 2018, 64(4): 83-86. HUA Y Q. Research progress on chemical constituents and extraction methods of Menthae Haplocalycis herba[J]. Shaanxi Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2018, 64(4): 83-86. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.0488-5368.2018.04.025 |
| [22] |
钟昆芮. 薄荷化学成分及其茎叶差异性研究[D]. 北京: 北京中医药大学, 2016. ZHONG K R. Study on chemical composition and difference of stem and leaf of Menthae Haplocalycis herba[D]. Beijing: Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, 2016. |
| [23] |
徐凌玉. 薄荷化学成分及其质量评价研究[D]. 南京: 南京中医药大学, 2014. XU L Y. Studies on the chemical constituents and determination of Menthae Haplocalycis herba[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, 2014. |
| [24] |
甄亚钦, 田伟, 支雅婧, 等. UPLC-MS/MS分析薄荷配方颗粒与传统饮片中非挥发性成分的相关性[J]. 中国中药杂志, 2021, 46(5): 1134-1140. ZHEN Y Q, TIAN W, ZHI Y J, et al. Correlation study on non-volatile ingredients of herba menthae formula granules and traditional herbal pieces by UPLC-MS/MS[J]. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica, 2021, 46(5): 1134-1140. |
| [25] |
杨莉. 苏薄荷采收, 初加工及贮藏过程中关键技术的研究[D]. 南京: 南京中医药大学, 2009. YANG L. Study on the key technique during the procedure of harvesting, pretreating and storage of Mentha haplocalyx Briq[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, 2009. |
| [26] |
张昱, 马惠玲, 麦曦, 等. 基于UHPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS技术鉴定薄荷在大鼠体内的入血成分及代谢产物[J]. 中草药, 2017, 48(19): 3927-3934. ZHANG Y, MA H L, MAI X, et al. Identification of components and metabolites of Mentha haplocalyx in rats plasma by UHPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS[J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drug, 2017, 48(19): 3927-3934. DOI:10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2017.19.005 |
| [27] |
陈向阳. 薄荷酚类部位化学成分及抗炎活性研究[D]. 北京: 北京中医药大学, 2016. CHEN X Y. Study on chemical constituents and anti-inflammatory activity of Phenolic fraction of Menthae Haplocalycis herba[D]. Beijing: Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, 2016. |
| [28] |
徐晶晶. 基于抗氧化谱效关系分析的薄荷药材质量控制和评价方法研究[D]. 北京: 北京中医药大学, 2014. XU J J. Studies in quality control and evaluation method of Menthae Haplocalycis herba based on the correlation between its chromatographic fingerprint and antioxidant activity[D]. Beijing: Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, 2014. |
| [29] |
徐佳馨, 王继锋, 颜娓娓, 等. 薄荷的药理作用及临床应用[J]. 食品与药品, 2019, 21(1): 81-84. XU J X, WANG J F, YAN W W, et al. Pharmacological action and clinical application of menthae haplocalycis herba[J]. Food and Drug, 2019, 21(1): 81-84. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1672-979X.2019.01.019 |
| [30] |
孙慧娟, 王瑞, 宋芊芊, 等. 基于超快速液相色谱-质谱联用技术检测药食两用薄荷中氨基酸和核苷类成分[J]. 食品与发酵工业, 2020, 46(8): 261-266. SUN H J, WANG R, SONG Q Q, et al. Amino acid and nucleoside components in medicinal and edible Mentha haplocalyx based on UFLC-MS/MS technology[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2020, 46(8): 261-266. |
| [31] |
靳有才, 庆易薇, 阎娥, 等. 青海野生薄荷微量元素分析[J]. 青海师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 29(2): 56-58. JIN Y C, QING Y W, YAN E, et al. Determination of trace elements by wet ashing with flame atom absorpton spectrometry in wild Mentha haplocalyx from Qinghai[J]. Journal of Qinghai Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 2013, 29(2): 56-58. |
| [32] |
刘锐, 莫倩美. 不同溶剂提取的薄荷浸提物的抑菌效果研究[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2011, 39(6): 3291-3293, 3297. LIU R, MO Q M. Study on antimicrobial activities of different solvent extracts from Herba Menthae[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2011, 39(6): 3291-3293, 3297. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2011.06.057 |
| [33] |
LUO W, DU Z, ZHENG Y, et al. Phytochemical composition and bioactivities of essential oils from six Lamiaceae species[J]. Industrial Crops and Products, 2019, 133(23): 357-364. |
| [34] |
杨倩. 薄荷挥发油的化学型分析及抑菌、抗炎活性研究[D]. 镇江: 江苏大学, 2017. YANG Q. Preliminary study on the composition and biological activity of Menthae Herba[D]. Zhenjiang: Jiangsu University, 2017. |
| [35] |
KAMATOU G P, VERMAAK I, VILJOEN A M, et al. Menthol: a simple monoterpene with remarkable biological properties[J]. Phytochemistry, 2013, 96(2): 15-25. |
| [36] |
赵志伟. 薄荷精油的提取分离及L-薄荷醇PLGA抑菌作用的研究[D]. 合肥: 安徽农业大学, 2017. ZHAO Z W. Extraction and separation of essential oil from peppermint and study on antibacterial activity of L-menthol PLGA[D]. Hefei: Anhui Agricultural University, 2017. |
| [37] |
CHEN C J, LI Q Q, ZENG Z Y, et al. Efficacy and mechanism of Mentha haplocalyx and Schizonepeta tenuifolia essential oils on the inhibition of Panax notoginseng pathogens[J]. Industrial Crops and Products, 2020, 145: 112073. DOI:10.1016/j.indcrop.2019.112073 |
| [38] |
陈向阳, 吴莹, 张淑静, 等. 薄荷酚类部位抗病毒活性及特征图谱研究[J]. 中草药, 2018, 49(3): 640-645. CHEN X Y, WU Y, ZHANG S J, et al. Study on antiviral activity and characteristic spectrum of phenolic fraction of Mentha haplocalyx[J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs, 2018, 49(3): 640-645. |
| [39] |
陈飞, 姚梅悦, 张霞, 等. 薄荷抗单纯疱疹病毒有效部位筛选研究[J]. 山东中医杂志, 2015, 34(4): 289-291. CHEN F, YAO M Y, ZHANG X, et al. Reseach on screening of effective antiviral parts of mentha haplocalyx[J]. Shandong Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2015, 34(4): 289-291. |
| [40] |
陈飞. 薄荷抗呼吸道合胞病毒的有效物质基础研究[D]. 济南: 山东中医药大学, 2015. CHEN F. Study on the effective substance basis of mint against respiratory syncytial virus[D]. Jinan: Shandong Traditional Chinese Medicine University, 2015. |
| [41] |
CHEN X, WANG C, XU L, et al. A laboratory evaluation of medicinal herbs used in China for the treatment of hand, foot, and mouth disease[J]. Evidence Based Complementary & Alternative Medicine, 2013, 20(13): 504-506. |
| [42] |
何婷, 汤奇, 曾南, 等. 荆芥挥发油及其主要成分抗流感病毒作用与机制研究[J]. 中国中药杂志, 2013, 38(11): 1772-1777. HE T, TANG Q, ZENG N, et al. Study on effect and mechanism of volatile oil of Schizonepetae Herba and its essential components against influenza virus[J]. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica, 2013, 38(11): 1772-1777. |
| [43] |
ZHENG K, WU S, LV Y, et al. Carvacrol inhibits the excessive immune response induced by influenza virus A via suppressing viral replication and TLR/RLR pattern recognition[J]. Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 2020, 20(11): 113555. |
| [44] |
REN X, SHAO X X, LI X X, et al. Identifying potential treatments of COVID-19 from traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) by using a data-driven approach[J]. Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 2020, 25(8): 112932. |
| [45] |
PANYOD S, HO C T, SHEEN L Y. Dietary therapy and herbal medicine for COVID-19 prevention: a review and perspective[J]. Journal of Traditional and Complementary Medicine, 2020, 10(4): 420-427. DOI:10.1016/j.jtcme.2020.05.004 |
| [46] |
KHAN T, KHAN M A, ULLAH N, et al. Therapeutic potential of medicinal plants against COVID-19:the role of antiviral medicinal metabolites[J]. Biocatalysis and Agricultural Biotechnology, 2021, 31(2): 1-15. |
| [47] |
刘颖, 刘丽, 曹苗苗, 等. 《新型冠状病毒肺炎诊疗方案(试行第六版)》中医学观察期患者的中成药治疗文献分析[J]. 临床药物治疗杂志, 2020, 18(2): 62-66. LIU Y, LIU L, CAO M M, et al. Literature analysis of Chinese patent medicine treatment in the observation period of Clinical Management of Corona Virus Disease 2019(trial 6th edition)[J]. Clinical Medication Journal, 2020, 18(2): 62-66. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1672-3384.2020.02.013 |
| [48] |
HA M A, SMITH G J, CICHOCKI J A, et al. Menthol attenuates respiratory irritation and elevates blood cotinine in cigarette smoke exposed mice[J]. Plos One, 2015, 10(2): e0117128. DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0117128 |
| [49] |
郅琳, 臧文华, 张雪鹏. 基于TRPM8通道研究薄荷醇对哮喘小鼠气道反应性及肺组织病理学的影响[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2017, 17(24): 9-12. ZHI L, ZANG W H, ZHANG X P. Investigation for effects of menthol on airway responsiveness and lung pathology in asthmatic mice based on TRPM8 channel[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2017, 17(24): 9-12. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2017.24.002 |
| [50] |
王亚苹, 邹文静, 蔡霜, 等. 薄荷醇下调肺组织P物质改善哮喘气道炎症及气道高反应性的研究[J]. 第三军医大学学报, 2017, 39(22): 2151-2156. WANG Y P, ZOU W J, CAI S, et al. Menthol improves airway inflammation and hyperresponsiveness in asthmatic mice by reducing substance P in the lungs[J]. Journal of Third Military Medical University, 2017, 39(22): 2151-2156. |
| [51] |
张亚萍, 朱佳. 朱佳教授治疗慢性咳嗽常用药对举隅[J]. 长春中医药大学学报, 2015, 31(5): 944-946. ZHANG Y P, ZHU J. Cases of herb pairs for treatment of chronic cough of professor ZHU Jia[J]. Journal of Changchun University of Chinese Medicine, 2015, 31(5): 944-946. |
| [52] |
CHEN X, ZHANG S, XUAN Z, et al. The phenolic fraction of mentha haplocalyx and its constituent Linarin Ameliorate inflammatory response through inactivation of NF-κB and MAPKs in Lipopolysaccharide-Induced RAW264.7 Cells[J]. Molecules, 2017, 22(5): 811. DOI:10.3390/molecules22050811 |
| [53] |
GHASEMI-PIRBALUTI M, MOTAGHI E, BOZORGI H. The effect of menthol on acute experimental colitis in rats[J]. European Journal of Pharmacology, 2017, 80(5): 101-107. |
| [54] |
王凤, 温桃群, 徐锋, 等. 薄荷酮对内毒素致炎症模型小鼠的保护作用研究[J]. 中国药理学通报, 2017, 33(2): 227-234. WANG F, WEN T Q, XU F, et al. The protective effects of menthone on endotoxin-induced infalmmation in mice[J]. Chinese Pharmacological Bulletin, 2017, 33(2): 227-234. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1001-1978.2017.02.017 |
| [55] |
郭沛鑫, 解宇环, 敖丽. 胡薄荷酮对LPS致急性肺损伤大鼠肺组织NF-κB、MyD88含量的影响[J]. 天然产物研究与开发, 2013, 25(11): 1503-1506. GUO P X, XIE Y H, AO L. Effects of pulegone on the level of NF-κB, MyD88 in lung tissue of acute lung injury rats induced by LPS[J]. Natural Product Research and Development, 2013, 25(11): 1503-1506. |
| [56] |
马榕花. 龙甘薄荷汤佐治慢性咽炎50例临床观察[J]. 海峡药学, 2016, 28(9): 115-116. MA R H. 50 cases clinical observation of Longgan BoHe Decoction in treating chronic pharyngitis[J]. Strait Pharmaceutical Journal, 2016, 28(9): 115-116. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-3765.2016.09.049 |
| [57] |
张家燕, 易志刚. 复方木芙蓉涂鼻软膏、鼻康片和薄荷油治疗干燥性鼻炎的临床疗效比较研究[J]. 世界最新医学信息文摘, 2019, 19(71): 231-232. ZHANG J Y, YI Z G. Comparative study on the clinical efficacy of mutabilis coated nasal ointment, Bikang Tablets and Peppermint Oil in the treatment of dry rhinitis[J]. World Latest Medicine Information, 2019, 19(71): 231-232. |
| [58] |
庞锦伟, 胡广林, 张敬迎, 等. 薄荷提取物对自由基消除能力的研究[J]. 时珍国医国药, 2014, 25(1): 76-77. PANG J W, HU G L, ZHANG J Y, et al. Study on free radical scavenging ability of Peppermint extract[J]. Lishizhen Medicine and Materia Medica Research, 2014, 25(1): 76-77. |
| [59] |
徐晶晶, 刘斌. 基于DPPH、FRAP法的薄荷药材抗氧化谱效关系研究[J]. 北京中医药大学学报, 2015, 38(6): 405-410. XU J J, LIU B. Spectrum-effect relation in antioxidant activity of Menthae haplocalycis Herba based on DPPH and FRAP assay[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2015, 38(6): 405-410. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-2157.2015.06.009 |
| [60] |
高燕. 野生薄荷精油的提取分离及其抗氧化活性研究[D]. 石河子: 石河子大学, 2015. GAO Y. Study on the extraction and seperation of wild mint essential oil and its antioxidant activity[D]. Shihezi: Shihezi University, 2015. |
| [61] |
CHEN G, FANG C, CHEN X, et al. High-pressure ultrasonic-assisted extraction of polysaccharides from Mentha haplocalyx: structure, functional and biological activities[J]. Industrial Crops and Products, 2019, 130(14): 273-284. |
| [62] |
JIANG P, MENG W, SHI F, et al. Structural characteristics, antioxidant properties and antiaging activities of galactan produced by Mentha haplocalyx Briq[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2020, 23(4): 115936. |
| [63] |
梁浩明, 龙晓英, 卢耀文, 等. 鼻吸入薄荷油对小鼠精神疲劳行为及脑内氨基酸类神经递质的影响[J]. 中药新药与临床药理, 2015, 26(5): 649-654. LIANG H M, LONG X Y, LU Y W, et al. Effects of nasal inhalation of peppermint oil on mental fatigue behaviors and amino acid neurotransmitters in mice[J]. Traditional Chinese Drug Research and Clinical Pharmacology, 2015, 26(5): 649-654. |
| [64] |
孙凡, 石敏, 徐守宇, 等. 薄荷复合精油吸嗅对轻度认知功能障碍患者乙酰胆碱酯酶影响的研究[J]. 中国实用医药, 2019, 14(10): 19-21. SUN F, SHI M, XU S Y, et al. Study on the effect of mint compound essential oil sniffing on acetylcholinesterase in patients with mild cognitive impairment[J]. China Practical Medicine, 2019, 14(10): 19-21. |
| [65] |
AVRAM S, MERNEA M, BAGCI E, et al. Advanced structure-activity relationships applied to Mentha spicata L. subsp. spicata essential oil compounds as AChE and NMDA ligands, in comparison with donepezil, galantamine and memantine-New approach in brain disorders pharmacology[J]. CNS & Neurological Disorders-Drug Targets (Formerly Current Drug Targets-CNS & Neurological Disorders), 2017, 16(7): 800-811. |
| [66] |
WANG W, JIANG Y, CAI E, et al. L-menthol exhibits antidepressive-like effects mediated by the modification of 5-HTergic, GABAergic and DAergic systems[J]. Cognitive Neurodynamics, 2019, 13(2): 191-200. DOI:10.1007/s11571-018-9513-1 |
| [67] |
庞峻, 陈思敏, 占煜, 等. 腰俞穴中药穴位注射麻醉用于肛肠手术研究[J]. 川北医学院学报, 2016, 31(4): 513-516. PANG J, CHEN S M, ZHAN Y, et al. Anesthesia of waist-shu acupoint-injection with traditional Chinese medicine in anorectal operation[J]. Journal of North Sichuan Medical College, 2016, 31(4): 513-516. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1005-3697.2016.04.017 |
| [68] |
BELLASSOUED K, BEN H A, ATHMOUNI K, et al. Protective effects of Mentha piperita L. leaf essential oil against CCl4 induced hepatic oxidative damage and renal failure in rats[J]. Lipids in Health & Disease, 2018, 17(1): 9. |
| [69] |
HU G, YUAN X, ZHANG S, et al. Research on choleretic effect of menthol, menthone, pluegone, isomenthone, and limonene in DanShu Capsule[J]. International Immunopharmacology, 2015, 24(2): 191-197. DOI:10.1016/j.intimp.2014.12.001 |
| [70] |
陈裕, 范晓飞, 郑忠青, 等. 薄荷素油对家兔Oddi括约肌收缩性的影响[J]. 胃肠病学, 2016, 21(7): 429-432. CHEN Y, FAN X F, ZHENG Z Q, et al. Effect of peppermint oil on contractility of sphincter of Oddi in rabbits[J]. Chinese Journal of Gastroenterology, 2016, 21(7): 429-432. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1008-7125.2016.07.009 |
| [71] |
AMATO A, LIOTTA R, MULE F, et al. Effects of menthol on circular smooth muscle of human colon: analysis of the mechanism of action[J]. European Journal of Pharmacology, 2014, 740(10): 295-301. |
| [72] |
朱丽云, 张春苗, 高永生, 等. 抗癌活性植物精油的主要功效成分及作用机制研究进展[J]. 中草药, 2017, 48(6): 1229-1239. ZHU L Y, ZHANG C M, GAO Y S, et al. Advance in main functional ingredients and mechanism of anticancer plant essential oils[J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs, 2017, 48(6): 1229-1239. |
| [73] |
陶兴魁, 张兴桃, 王海潮, 等. 薄荷醇对肝癌HepG2细胞增殖、迁移及IL-8, CXCL-12, VEGF表达的影响[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志, 2019, 25(21): 60-65. TAO X K, ZHANG X T, WANG H C, et al. Effect of menthol on proliferation, migration and expressions of IL-8, CXCL-12 and VEGF in hepatoma HepG2 cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Experimental Traditional Medical Formulae, 2019, 25(21): 60-65. |
| [74] |
NAGAI K, FUKUNO S, OMACHI A, et al. Enhanced anti-cancer activity by menthol in HepG2 cells exposed to paclitaxel and vincristine: possible involvement of CYP3A4 downregulation[J]. Drug Metabolism and Personalized Therapy, 2019, 34(1): 2018-2029. |
| [75] |
易真珍, 舒扬, 赵建, 等. 薄荷油对雌性小鼠的抗生育作用[J]. 中国兽医学报, 2014, 34(8): 1380-1384. YI Z Z, SHU Y, ZHAO J, et al. Anti-fertility effect of peppermint oil on female mice[J]. Chinese Journal of Veterinary Science, 2014, 34(8): 1380-1384. |
| [76] |
曹玫, 舒杨, 赵建, 等. 薄荷油对雄性小鼠的抗生育作用研究[J]. 四川动物, 2013, 32(6): 908-911, 973. CAO M, SHU Y, ZHAO J, et al. Anti-fertility effect of peppermint oil on male mice[J]. Sichuan Journal of Zoology, 2013, 32(6): 908-911, 973. |
| [77] |
宋丽菊, 易思君, 殷中琼, 等. 薄荷油颗粒剂对高原鼠兔的抗生育作用研究[J]. 畜牧与兽医, 2017, 49(4): 54-57. SONG L J, YI S J, YIN Z Q, et al. Anti-fertility effect of peppermint oil granules on Ochotona curzoniae[J]. Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2017, 49(4): 54-57. |
| [78] |
韦邱梦, 梁寻杰, 黄小夏, 等. 薄荷提取物对小鼠血糖影响的实验研究[J]. 现代预防医学, 2017, 44(24): 4489-4492. WEI Q M, LIANG X J, HUANG X X, et al. Experimental study on the effects of peppermint extract on blood glucose in mice[J]. Modern Preventive Medicine, 2017, 44(24): 4489-4492. |
| [79] |
HE X, GENG C, HUANG X, et al. Chemical constituents from Mentha haplocalyx Briq.(Mentha canadensis L.) and their α-Glucosidase inhibitory activities[J]. Natural Products and Bioprospecting, 2019, 9(3): 223-229. DOI:10.1007/s13659-019-0207-0 |
| [80] |
李依纹. 应用线虫模型筛选抗紫外辐射的中药及薄荷提取物作用机制的研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2016. LI Y W. Screening of anti ulreaviolet radiation Chinese medicines and study on the mechanisms of Mentha haplocalyx in Caenorhabditis elegans[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2016. |
| [81] |
ZHANG W J, YANG K, YOU C X, et al. Contact toxicity and repellency of the essential oil from Mentha haplocalyx Briq. against Lasioderma serricorne[J]. Chemistry & Biodiversity, 2015, 12(5): 832-839. |
| [82] |
李晓宇, 孙蓉. 薄荷不同组分对小鼠急性毒性实验比较研究[J]. 中国药物警戒, 2012, 9(2): 65-68. LI X Y, SUN R. Experimental comparis on study on mice's acute toxicity of different composition in herba menthae[J]. Chinese Journal of Pharmacovigilance, 2012, 9(2): 65-68. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1672-8629.2012.02.001 |
 2022, Vol. 41
2022, Vol. 41