文章信息
- 王聪颖, 韩蕊, 李晶芳, 殷宏庆, 樊佳佳, 杨珍, 宋丽丽, 张艳军
- WANG Congying, HAN Rui, LI Jingfang, YIN Hongqing, FAN Jiajia, YANG Zhen, SONG Lili, ZHANG Yanjun
- 类风湿关节炎相关间质性肺病发病机制、诊断及治疗研究进展
- Research progress in the pathogenesis, diagnosis and treatment of rheumatoid arthritis-related interstitial lung disease
- 天津中医药大学学报, 2022, 41(2): 250-257
- Journal of Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 41(2): 250-257
- http://dx.doi.org/10.11656/j.issn.1673-9043.2022.02.25
-
文章历史
收稿日期: 2021-12-01
类风湿关节炎(RA)是一种慢性炎症性自身免疫性疾病[1],主要影响关节[2]。目前中国RA的发病率约为0.34%~0.36%[3-4],特征是周围对称性关节炎,可导致关节破坏,并可能引发关节外表现(EAMS),约40%的RA病人在临床中检查出明显的EAMS。据统计10%~20%的RA死亡与肺脏疾病直接相关。在患有RA同时临床检查显示肺部受损的患者中,超过80%的死亡是因其肺部疾病造成[5]。
肺是EAMS最主要的发病部位之一,RA肺部疾病包括支气管扩张、类风湿结节、Caplan综合征、胸膜疾病,特别是间质性肺病(ILD)[6]。ILD作为RA中最常见的肺部疾病亚型之一,是一种严重的弥漫性肺实质疾病,伴有气体交换受损及肺泡间隔纤维化损伤[7],是引起RA高死亡率的最重要因素之一[8-10]。正常情况下RA患者的平均生存期为9.9年,而RA-ILD患者则为2.6年[11]。可见ILD不仅严重损害RA患者的生活质量,同时急剧缩短其生存时间。RA-ILD常表现为间质性肺炎(UIP)[12]的损伤模式,其次是非特异性间质性肺炎(NSIP)[13],其他模式并不常见。数据显示,RA的总死亡率正在下降,但RA-ILD的死亡率似乎逐年上升[14],因此有必要分析归纳出影响RA进展为RA-ILD的致病因素及其发病机制,同时总结RA-ILD的诊断方法以及治疗策略,以期为临床治疗提供参考。
1 致病因素RA自身发展为RA-ILD的可能性较小,多因各种致病因素诱导产生。促使RA发展为RA-ILD的公认致病因素包括吸烟、性别、年龄等,其中诱发ILD的关键致病因素为吸烟。
1.1 吸烟吸烟已是诱导RA发展为RA-ILD的公认致病因素。由于香烟中含有尼古丁、多环芳烃、活性氧、重金属(如镉)以及其他化合物,可通过复杂方式影响粘膜免疫,进而造成肺部炎症及病变。当RA病人存在吸烟史时,可加大患有ILD疾病的风险。Kronzer等[15]发现与从未吸烟相比,吸烟将患有RA-ILD的机率扩大了3倍以上。此外,与不吸烟者相比,每年吸烟30包或更多者,会增加6倍的患病风险。
1.2 性别尽管在RA中女性占主导地位,但RA-ILD多为男性[11]。Kelly等[16]利用高分辨率CT(HRCT)和肺功能检测共筛选出230名RA-ILD确诊病人,诊断的男女比例为1∶1.09,多因素分析发现男性与RA-ILD独立相关。性别差异同样出现在ILD的组织病理学亚型之间,男性多为UIP,而女性多为NSIP[5],但目前对于此现象可能产生原因的研究较少。
1.3 年龄据报道,年龄也可能是诱导ILD发生的致病因素[17],根据10年的年龄差异计算风险评估发现在较短时间内高龄使RA-ILD的发病风险提高了64%[18]。Zhang等[19]研究发现每增加10岁,ILD的发病风险增长59.9%,同时ILD的发病年龄多在50~69岁。年龄与RA-ILD患病风险增加之间的关联尚不完全清楚,但可能与老年RA病人(≥60岁)的EAMS发病率增加有关。
1.4 其他其他诱发RA-ILD的潜在致病因素包括胃食管反流病、肺泡表面活性蛋白异常、内质网应激、端粒长度以及气道微生物防御相关的特定基因突变等[20-21]。有研究指出,在RA-ILD患者的靶向全外显子组测序中,发现了几个端粒维持相关基因和肺泡表面活性蛋白基因突变频率增加的现象[22]。
2 RA-ILD的发病机制RA-ILD的发病机制尚不清楚,它可能通过瓜氨酸化蛋白[23]、抗瓜氨酸化蛋白抗体以及免疫细胞等诱导RA发展为RA-ILD。因此,总结与该疾病相关的发病机制可为有效预防、诊断、治疗提供一定帮助。
2.1 瓜氨酸化蛋白质最近有关吸烟、瓜氨酸化蛋白质与RA、RA-ILD之间的关联研究日益增多。吸烟是RA及RA-ILD发展的既定致病因素。烟草烟雾中的复杂成分可以直接导致肺部细胞因子及酶分泌异常,损伤呼吸上皮细胞和血管内皮细胞,并且能够增加肽酰基精氨酸脱亚胺酶(PAD)的含量,PAD会刺激肺中蛋白瓜氨酸化,两者共同作用刺激肺的局部炎症反应,造成细胞浸润及某些因子如转化生长因子以及促纤维细胞因子的释放,进一步导致肺组织损伤并促进成纤维细胞的分化及增殖。同时瓜氨酸化蛋白作为临床前水平的关键因素,它是局部免疫反应的抗原靶点,能诱导抗瓜氨酸化蛋白抗体的产生继而促使RA发病,最终导致RA-ILD[11]。研究人员发现吸烟可增强肺泡腔室和支气管黏膜中PAD2的表达,并增加前者中瓜氨酸化蛋白的表达[24],吸烟也影响了PADI4的表达,而且瓜氨酸化蛋白的表达与其呈正相关性[25]。因此当RA患者存在吸烟行为时,提高了肺部PAD水平,导致蛋白瓜氨酸化增加,刺激肺部炎症造成肺损伤,继而诱发RA-ILD。吸烟影响RA患者诱发ILD的途径见图 1。

|
| 图 1 吸烟影响RA患者诱发ILD的途径 |
有研究表明ACPA与RA-ILD的发病及其严重程度相关。ACPA为RA的特异性抗体,可通过多种可能方式引起局部黏膜、气道、肺间质损伤。这包括形成免疫复合物,促进炎症细胞因子如肿瘤坏死因子-α(TNF-α)、白细胞介素(IL-6、IL-8)的形成及释放[26]。Giles[27]观察到与没有ILD的RA患者相比,具有ILD影像学特征的RA患者中ACPA的水平较高,通常高出几倍,这意味着ACPA浓度高的RA患者更容易诱发ILD。Joshua[28]利用HRCT检测106位确诊为早期RA患者中ACPA阳性患者存在肺实质异常,提示ACPA阳性使得RA诊断时存在肺实质异常的风险增加。
2.3 免疫细胞 2.3.1 B细胞虽然RA-ILD的潜在免疫机制尚未清晰,但有报道认为B细胞可能发挥了一定作用。研究人员发现有ILD的RA患者比没有的患者记忆B细胞的数量减少[29],在RA相关的ILD中,可以检测到明显的滤泡B细胞增生,几乎完全聚集在细支气管的淋巴周围[30],提示B细胞可能在RA-ILD中具有重要作用。
2.3.2 T细胞T细胞被认为在RA的发病机制中处于重要位置,T细胞异常可能与关节外疾病表现相关,包括肺部疾病。研究人员发现RA-ILD患者外周血中T细胞与CD4+T淋巴细胞的相对计数较单纯RA患者降低[31],表明T细胞可能参与原发性RA的发病及发展过程中间质肺的形成。由于RA患者自身体内产生某些特异性抗体,这些抗体通过抗原呈递细胞上表达的Fc受体与瓜氨酸肽结合,导致促炎细胞因子如TNFα的生成,最终造成肺间质中出现弥漫性浸润。有研究表明,特别是与特发性间质性肺炎(IIP)相比,RA-ILD中CD4+和CD3+T细胞浸润的程度增加,这与疾病表现的模式无关(例如,RA-UIP或RA-NSIP)[32]。
3 诊断 3.1 临床表现RA-ILD常发生在肺间质中,包括支气管、肺泡间隔、小叶间隔、血管周围等,通常没有明显症状,或被行动不便掩盖,直至肺功能严重受损。RA-ILD最常见的胸部CT特征包括网状结节变化、胸膜增厚、磨玻璃异常,其次是间体隔膜增厚、结节、肺气肿[19]。RA-ILD患者肺脏HRCT出现异常情况,显示网状和磨玻璃异常的组合,肺功能检测如一氧化碳扩散能力和用力肺活量(FVC)异常。全身关节肿痛的同时,还伴随多种呼吸系统症状,如干咳、胸闷、气促等,晚期可引起贫血、缺氧性肺动脉高压,甚至肺源性心脏病等[33-34]。
3.2 疾病分型RA-ILD以UIP及NSIP两种亚型最为常见[26, 35]。UIP的疾病特点为蜂窝状斑片异质纤维化和活跃的成纤维细胞灶,而NSIP具有一致性,包括肺泡壁明显增厚以及不同程度的炎症及纤维化。有新的数据表明:在临床上有明显的RA-ILD时,潜在的组织病理学表型与预后有关,RA-ILD的UIP模式比非UIP模式病死率高[16, 36-37],RA-ILD患者UIP模式急性发作的发作率高于非UIP模式,RA-UIP患者的生存时间比RA-NSIP患者缩短[38]。
3.3 生物标志物 3.3.1 血清类风湿因子血清类风湿因子(RF)是针对RA发现的首批血清学生物标志物之一[12],可分为IgA-RF、IgG-RF、IgM-RF、IgE-RF。RF IgM在RA患者的肺泡壁及肺小动脉中广泛沉积,但IgG和IgA的沉积程度较低[39]。Doyle等[40]研究表明,RF水平升高与临床阳性和亚临床性RA-ILD均相关。
3.3.2 涎液化糖链抗原-6涎液化糖链抗原-6(KL-6)是一种糖类蛋白,位于Ⅱ型肺细胞和细支气管上皮细胞[41],能够促进成纤维细胞增殖和迁移,影响纤维化的形成与发展,最终导致肺间质病变[42]。杨金良等人[43]通过检测血清KL-6水平,发现较单纯RA组相比,RA-ILD组明显升高,同时发现血清KL-6与28个关节疾病活动度评分具有相关性,提示RA-ILD的发病率随关节疾病活动度的升高而升高。
3.4 抗风湿药物(DMARDS)目前对于DMARDS与ILD的发生或恶化之间的因果关系尚不确定,但是大量报告对DMARDS的安全性提出了担忧。在发病率和病死率达到20%的患者中,甲氨蝶呤可导致0.86%~6.9%的ILD或肺炎。患者的常见症状为呼吸困难、干咳、胸痛、发烧等,病死率小于1%[44]。来氟米特(LEF)也与ILD相关[45],可使先前存在的肺部疾病有加重的风险,同时对生存率有潜在的影响[46-47]。其主要机制可能是LEF引起超敏反应导致肺炎的发生[48],而间质纤维化的发展可能与A771726的作用有关。A771726是一种LEF的活性代谢产物,可诱导肺上皮细胞向肌纤维蛋白转移[49],这一现象被称为“上皮间质转移”(EMT)。EMT不仅与异常的伤口修复及组织重塑有关,而且与器官纤维化及ILD有关[50-51]。环磷酰胺(CTX)[52]是一种常用免疫抑制剂,可用于治疗RA,但存在肺毒性、心脏毒性、肝毒性等副作用[53]。有研究指出,CTX引发肺毒性的原因可能是CTX首先激活晚期糖基化终末产物受体(RAGE),再激活由RAGE介导的核因子κB(NF-κB),促进肺脏促炎细胞因子释放,从而导致急性肺损伤[54]。有人指出长期服用托珠单抗会造成RA-ILD的病情恶化[55]。一项新的研究证明,肿瘤坏死因子抑制剂(TNF-I)可能与RA中ILD不良事件相关,可诱发更严重的肺部症状,甚至导致死亡[56]。因此服用某些DMARDSs时,应考虑该药物对RA-ILD的影响,酌情服用该药物。
4 治疗 4.1 西药治疗对于RA-ILD的最佳治疗手段尚未确定,因此治疗时应综合考虑患者临床特征、肺功能以及放射学检测等,对患者的疾病严重程度及表现进行评估,根据评估结果进行抗炎、免疫抑制剂及抗纤维化治疗。由于吸烟为RA-ILD的关键致病因素,因此建议所有RA患者戒烟。对于RA-ILD患者的最初治疗策略是服用糖皮质激素,通常以口服泼尼松(0.5 mg/kg)开始,然后依据临床效果数周或数月内逐渐降低剂量[57]。N-乙酰半胱氨酸(NAC)具有扩血管、抗炎、抗氧化的作用,可用于治疗呼吸系统疾病。尹婷婷等人研究发现在常规治疗的基础上口服大剂量NAC后,RA-ILD患者的症状及肺功能得到明显改善[58]。环孢素是一种钙调磷酸酶抑制剂,对T淋巴细胞活化具有抑制作用,被广泛用于免疫性继发性间质性肺病的治疗[59-60]。霉酚酸酯、硫唑嘌呤等免疫抑制剂都已被用于治疗RA-ILD[26]。研究表明霉酚酸酯对于包含RA-ILD在内的多种结缔组织病合并ILD具有良好效果[61]。其他治疗药物还包括肿瘤坏死因子抑制剂(英夫利昔单抗、依那西普)、IL-6受体抑制剂(托珠单抗)、抗CD20单抗(利妥昔单抗)、T细胞共刺激信号阻断剂(阿巴西普)以及抗纤维化药物如吡非尼酮、尼达尼布等[62]。Vadillo等[13]发现与服用利妥昔单抗的RA-ILD患者相比,没有服用的患者更容易引起呼吸损害,因此肯定了其治疗RA-ILD的有益作用。杨金良等人发现吡非尼酮与糖皮质激素联合应用治疗RA-ILD临床效果显著,能够改善血清KL-6、ACPA的水平,促进肺功能恢复正常[63]。Wollin等[64]研究发现尼达尼布能够减轻肺纤维化小鼠的炎症及纤维化。严重肺纤维化应考虑肺移植等手术治疗。
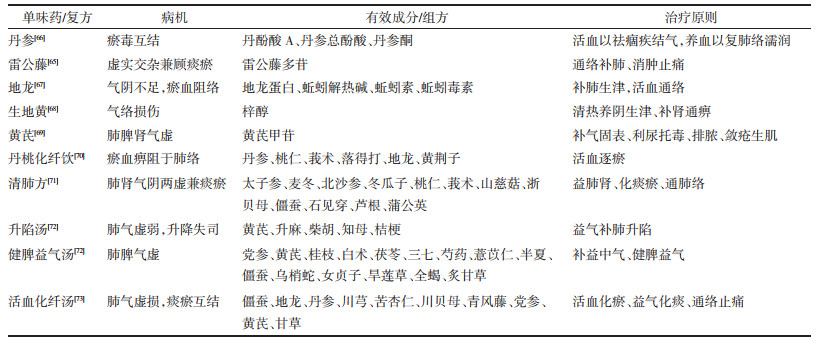
4.2 中医治疗RA-ILD的相关病名在古籍中未有记载,但依据其症状可归于痹症范畴。因其病程长,反复发作,缠绵难愈,日久病及肺脏,而成“肺痹”。中医在治疗RA-ILD过程中主要存在单味药及复方治疗,见表 1。丹参、雷公藤、地龙、生地、黄芪等常用于治疗RA-ILD。陈红等[65]发现雷公藤多苷能够改善RA-ILD病人的肺部结构,增强肺部功能,促进肺部恢复正常状态,从而产生抗肺纤维化作用。
RA-ILD是一种关注度日益增高且病情严重的疾病,对于RA-ILD还存在以下问题:1)对于致病因素而言,虽然吸烟为主要影响因素,但存在多种因素相互交错的现象,导致RA-ILD的病因复杂,无法做到对因治疗。2)RA-ILD的肺部病变可能早于RA症状也可能伴随产生,同时特异性抗体及免疫功能等个人因素导致发病机制复杂,应综合临床指标及具体情况进行对症治疗。3)对于RA-ILD的检测手段及评估需要进一步加强。4)RA-ILD的治疗需要新的突破,例如将中医的整体观念及辩证论治的思想与西医检测手段相结合用于RA-ILD的诊断及中西药联合治疗等。这些问题有待后续研究者解决。
| [1] |
SMOLEN J S, ALETAHA D, BARTON A, et al. Rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Nature Reviews Disease Primers, 2018, 4: 18001. DOI:10.1038/nrdp.2018.1 |
| [2] |
FIRESTEIN G S. Evolving concepts of rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Nature, 2003, 423(6937): 356-361. DOI:10.1038/nature01661 |
| [3] |
韩宇飞, 高明利, 刘东武. 类风湿性关节炎的发病机制研究进展综述[J]. 中国卫生标准管理, 2021, 12(1): 162-165. HAN Y F, GAO M L, LIU D W. Review on the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis[J]. China Health Standard Manage-ment, 2021, 12(1): 162-165. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1674-9316.2021.01.061 |
| [4] |
古结乃特汗·拜克里木, 巴燕·艾克海提, 卫荣. 类风湿性关节炎活动期中医证型与免疫学指标相关性[J]. 中医学报, 2017, 32(8): 1551-1554. GUJIENAITEHAN B K L M, BAYAN A K H T, WEI R. Cor-relation study between TCM syndrome types and laboratory indexes in active stage of rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Acta Chi-nese Medicine, 2017, 32(8): 1551-1554. |
| [5] |
SOLOMON J J, BROWN K K. Rheumatoid arthritis-associ-ated interstitial lung disease[J]. Open Access Rheumatology, 2012, 18(4): 21-31. |
| [6] |
JUGE P A, LEE J S, LAU J, et al. Methotrexate and rheuma-toid arthritis associated interstitial lung disease[J]. The Euro-pean Respiratory Journal, 2021, 57(2): 2000337. DOI:10.1183/13993003.00337-2020 |
| [7] |
TERASAKI Y, TERASAKI M, KANAZAWA S, et al. Effect of H2 treatment in a mouse model of rheumatoid arthritis-as sociated interstitial lung disease[J]. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine, 2019, 23(10): 7043-7053. DOI:10.1111/jcmm.14603 |
| [8] |
CHEN J, DOYLE T J, LIU Y L, et al. Biomarkers of rheumatoid arthritis -associated interstitial lung disease[J]. Arthritis & Rheumatology (Hoboken, N J), 2015, 67(1): 28-38. |
| [9] |
章平衡. 基于FAK/Calpain通路探讨新风胶囊抑制血小板活化改善类风湿关节炎肺功能机制[D]. 合肥: 安徽中医药大学, 2019. ZHANG P H. Mechanism research of Xinfeng capsule on inhibiting platelet activation to improve pulmonary function in rheumatoid arthritis based on FAK/calpain pathway[D]. Hefei: Anhui University of Chinese Medicine, 2019. |
| [10] |
HYLDGAARD C, HILBERG O, PEDERSEN A B, et al. A population-based cohort study of rheumatoid arthritis-asso-ciated interstitial lung disease: Comorbidity and mortality[J]. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 2017, 76(10): 1700-1706. DOI:10.1136/annrheumdis-2017-211138 |
| [11] |
CAVAGNA L, MONTI S, GROSSO V, et al. The multifaceted aspects of interstitial lung disease in rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Bio Med Research International, 2013, 2013(5): 759760. |
| [12] |
AMIGUES I, RAMADURAI D, SWIGRIS J J. Current per-spectives on emerging biomarkers for rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease[J]. Open Access Rheu-matology: Research and Reviews, 2019, 11(2): 229-235. |
| [13] |
VADILLO C, NIETO M A, ROMERO-BUENO F, et al. Com-ment on: Efficacy of rituximab in slowing down progression of rheumatoid arthritis-related interstitial lung disease: Data from the NEREA Registry[J]. Rheumatology, 2020, 59(8): 2099-2108. DOI:10.1093/rheumatology/kez673 |
| [14] |
IQBAL K, KELLY C. Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis-as-sociated interstitial lung disease: A perspective review[J]. Therapeutic Advances in Musculoskeletal Disease, 2015, 7(6): 247-267. DOI:10.1177/1759720X15612250 |
| [15] |
KRONZER V L, HUANG W X, DELLARIPA P F, et al. Lifestyle and clinical risk factors for incident rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease[J]. The Journal of Rheumatology, 2021, 48(5): 656-663. DOI:10.3899/jrheum.200863 |
| [16] |
KELLY C A, SARAVANAN V, NISAR M, et al. Rheuma-toid arthritis-related interstitial lung disease: Associations, prognostic factors and physiological and radiological char-acteristics-a large multicentre UK study[J]. Rheumatology, 2014, 53(9): 1676-1682. DOI:10.1093/rheumatology/keu165 |
| [17] |
杨金良, 任占芬, 罗寰, 等. 类风湿关节炎合并肺间质性病变的临床特点及与抗环瓜氨酸肽抗体的相关性研究[J]. 临床肺科杂志, 2020, 25(7): 1062-1065. YANG J L, REN Z F, LUO H, et al. Clinical characteristics of rheumatoid arthritis with pulmonary interstitial lesions and its correlation with anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide anti-bodies[J]. Journal of Clinical Pulmonary Medicine, 2020, 25(7): 1062-1065. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1009-6663.2020.07.020 |
| [18] |
KODURI G, NORTON S, YOUNG A, et al. Interstitial lung disease has a poor prognosis in rheumatoid arthritis: Results from an inception cohort[J]. Rheumatology, 2010, 49(8): 1483-1489. DOI:10.1093/rheumatology/keq035 |
| [19] |
ZHANG Y F, LI H B, WU N W, et al. Retrospective study of the clinical characteristics and risk factors of rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease[J]. Clinical Rheu-matology, 2017, 36(4): 817-823. DOI:10.1007/s10067-017-3561-5 |
| [20] |
MCFARLANE I M, ZHAZ S Y, BHAMRA M S, et al. Asse-ssment of interstitial lung disease among black rheumatoid arthritis patients[J]. Clinical Rheumatology, 2019, 38(12): 3413-3424. DOI:10.1007/s10067-019-04760-6 |
| [21] |
NEWTON C A, OLDHAM J M, LEY B, et al. Telomere length and genetic variant associations with interstitial lung disease progression and survival[J]. The European Respiratory Jour-nal, 2019, 53(4): 1801641. DOI:10.1183/13993003.01641-2018 |
| [22] |
JUGE P A, BORIE R, KANNENGIESSER C, et al. Shared genetic predisposition in rheumatoid arthritis-interstitial lung disease and familial pulmonary fibrosis[J]. The Euro-pean Respiratory Journal, 2017, 49(5): 1602314. DOI:10.1183/13993003.02314-2016 |
| [23] |
赵智明. PAD酶参与CIA小鼠肺损伤诱发类风湿关节炎的可能机制及青藤碱的作用[D]. 南京: 南京中医药大学, 2018. ZHAO Z M. The possible mechanism of PAD enzyme in rheumatoid arthritis induced by lung injury in CIA mice and the effect of sinomenine[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, 2018. |
| [24] |
MAKRYGIANNAKIS D, HERMANSSON M, ULFGREN A K, et al. Smoking increases peptidylarginine deiminase 2 enzyme expression in human lungs and increases citrullina-tion in BAL cells[J]. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 2008, 67(10): 1488-1492. DOI:10.1136/ard.2007.075192 |
| [25] |
SAMARA K D, TRACHALAKI A, TSITOURA E, et al. Upregulation of citrullination pathway: from autoimmune to idiopathic lung fibrosis[J]. Respiratory Research, 2017, 18(1): 218. DOI:10.1186/s12931-017-0692-9 |
| [26] |
FARQUHAR H, VASSALLO R, EDWARDS A L, et al. Pul-monary complications of rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Seminars in Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, 2019, 40(2): 194-207. DOI:10.1055/s-0039-1683995 |
| [27] |
GILES J T, DANOFF S K, SOKOLOVE J, et al. Association of fine specificity and repertoire expansion of anticitrulli-nated peptide antibodies with rheumatoid arthritis associat-ed interstitial lung disease[J]. Annals of the Rheumatic Dis-eases, 2014, 73(8): 1487-1494. DOI:10.1136/annrheumdis-2012-203160 |
| [28] |
JOSHUA V, HENSVOLD A H, REYNISDOTTIR G, et al. Association between number and type of different ACPA fine specificities with lung abnormalities in early, untreated rheumatoid arthritis[J]. RMD Open, 2020, 6(2): e001278. DOI:10.1136/rmdopen-2020-001278 |
| [29] |
SHIMIZU T, NAGAFUCHI Y, HARADA H, et al. Decreased peripheral blood memory B cells are associated with the presence of interstitial lung disease in rheumatoid arthritis: A case-control study[J]. Modern Rheumatology, 2021, 31(1): 127-132. DOI:10.1080/14397595.2020.1719596 |
| [30] |
ATKINS S R, TURESSON C, MYERS J L, et al. Morphologic and quantitative assessment of CD20 + B cell infiltrates in rheumatoid arthritis-associated nonspecific interstitial pneu-monia and usual interstitial pneumonia[J]. Arthritis and Rheumatism, 2006, 54(2): 635-641. DOI:10.1002/art.21758 |
| [31] |
LAI N L, JIA W, WANG X, et al. Risk factors and changes of peripheral NK and T cells in pulmonary interstitial fibrosis of patients with rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Canadian Respiratory Journal, 2019, 2019: 7262065. |
| [32] |
TURESSON C, MATTESON E L, COLBY T V, et al. In-creased CD4+ T cell infiltrates in rheumatoid arthritis-asso-ciated interstitial pneumonitis compared with idiopathic in-terstitial pneumonitis[J]. Arthritis and Rheumatism, 2005, 52(1): 73-79. DOI:10.1002/art.20765 |
| [33] |
ANTIN-OZERKIS D, EVANS J, RUBINOWITZ A, et al. Pulmonary manifestations of rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Clin Chest Med, 2010, 31(3): 451-478. DOI:10.1016/j.ccm.2010.04.003 |
| [34] |
沈洲立, 唐小蓉, 沈思辰, 等. 类风湿关节炎合并间质性肺疾病相关生物标志物的研究进展[J]. 医学综述, 2020, 26(13): 2507-2512. SHEN Z L, TANG X R, SHEN S C, et al. Research ad-vances of related biological markers on rheumatoid arthritis with interstitial lung disease[J]. Medical Recapitulate, 2020, 26(13): 2507-2512. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-2084.2020.13.003 |
| [35] |
O'DWYER D N, ARMSTRONG M E, COOKE G, et al. rheumatoid arthritis associated interstitial lung disease[J]. European Journal of Internal Medicine, 2013, 24(7): 597-603. DOI:10.1016/j.ejim.2013.07.004 |
| [36] |
KIM H C, CHOI K H, JACOB J, et al. Prognostic role of blood KL-6 in rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease[J]. PLoS One, 2020, 15(3): e0229997. DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0229997 |
| [37] |
JOHNSON C. Recent advances in the pathogenesis, predic-tion, and management of rheumatoid arthritis-associated in-terstitial lung disease[J]. Current Opinion in Rheumatology, 2017, 29(3): 254-259. DOI:10.1097/BOR.0000000000000380 |
| [38] |
SOLOMON J J, CHUNG J H, COSGROVE G P, et al. Pre-dictors of mortality in rheumatoid arthritis-associated inter-stitial lung disease[J]. The European Respiratory Journal, 2016, 47(2): 588-596. DOI:10.1183/13993003.00357-2015 |
| [39] |
GAUHAR U A, GAFFO A L, ALARCON G S. Pulmonary manifestations of rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Semin Respir Crit Care Med, 2007, 28(4): 430-440. DOI:10.1055/s-2007-985664 |
| [40] |
DOYLE T J, PATEL A S, HATABU H, et al. Detection of rheumatoid arthritis-interstitial lung disease is enhanced by serum biomarkers[J]. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, 2015, 191(12): 1403-1412. DOI:10.1164/rccm.201411-1950OC |
| [41] |
CHO E J, PARK K J, KO D H, et al. Analytical and clinical performance of the nanopia Krebs von den Lungen 6 assay in Korean patients with interstitial lung diseases[J]. Annals of Laboratory Medicine, 2019, 39(3): 245-251. DOI:10.3343/alm.2019.39.3.245 |
| [42] |
肖铁铮, 徐英. 通痹颗粒治疗RA-ILD的疗效分析[J]. 河北医药, 2020, 42(10): 1537-1540. XIAO T Z, XU Y. Therapeutic effects of Tongbi Granule on RA-ILD and its effects on the levels of TGF-β1 and KL-6[J]. Hebei Medical Journal, 2020, 42(10): 1537-1540. |
| [43] |
杨金良, 郑学军, 任占芬, 等. 血清KL-6、SP-A在类风湿关节炎合并肺间质病变患者中的表达及临床意义[J]. 重庆医学, 2020, 49(9): 1442-1445. YANG J L, ZHENG X J, REN Z F, et al. Expression and clinical significance of serum KL-6 and SP-A in patients with rheumatoid arthritis complicating interstitial lung dis-ease[J]. Chongqing Medicine, 2020, 49(9): 1442-1445. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1671-8348.2020.09.016 |
| [44] |
袁菱, 童德银, 沈巍, 等. 抗类风湿关节炎药物相关性肺损伤研究进展[J]. 西北药学杂志, 2018, 33(3): 425-428. YUAN L, TONG D Y, SHEN W, et al. Research progress in anti-rheumatoid arthritis drugs induced lung injury[J]. Northwest Pharmaceutical Journal, 2018, 33(3): 425-428. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1004-2407.2018.03.034 |
| [45] |
JU J H, KIM S I, LEE J H, et al. Risk of interstitial lung dis-ease associated with leflunomide treatment in Korean patients with rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Arthritis and Rheuma-tism, 2007, 56(6): 2094-2096. DOI:10.1002/art.22666 |
| [46] |
CHIKURA B, LANE S, DAWSON J K. Clinical expression of leflunomide-induced pneumonitis[J]. Rheumatology, 2009, 48(9): 1065-1068. DOI:10.1093/rheumatology/kep050 |
| [47] |
SAWADA T, INOKUMA S, SATO T, et al. Leflunomide-in-duced interstitial lung disease: prevalence and risk factors in Japanese patients with rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Rheuma-tology, 2009, 48(9): 1069-1072. DOI:10.1093/rheumatology/kep052 |
| [48] |
NEIL M, ALASTAIR I J, MICHAEL L C, et al. Hypersensi-tivity pneumonitis associated with leflunomide therapy[J]. The Journal of Rheumatology, 2007, 34(9): 1934-1937. |
| [49] |
BERNSTEIN E J, BARR R G, AUSTIN J H M, et al. Rheumatoid arthritis -associated autoantibodies and sub-clinical interstitial lung disease: The Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis[J]. Thorax, 2016, 71(12): 1082-1090. DOI:10.1136/thoraxjnl-2016-208932 |
| [50] |
HINZ B, PHAN S H, THANNICKAL V J, et al. The myofi-broblast: One function, multiple origins[J]. The American Journal of Pathology, 2007, 170(6): 1807-1816. DOI:10.2353/ajpath.2007.070112 |
| [51] |
NAMBA T, TANAKA K I, ITO Y, et al. Induction of EMT-like phenotypes by an active metabolite of leflunomide and its contribution to pulmonary fibrosis[J]. Cell Death & Dif-ferentiation, 2010, 17(12): 1882-1895. |
| [52] |
沈艳玲, 吴辉, 黄环, 等. CTX联合BUS对小鼠卵巢及早期肺损伤的研究[J]. 中国现代医生, 2015, 53(5): 14-16, 19, 161. SHEN Y L, WU H, HUANG H, et al. The effects of cyclophos-phamide and busulfan on ovarian injuries and early lung in-jury[J]. China Modern Doctor, 2015, 53(5): 14-16, 19, 161. |
| [53] |
SUN Y, ITO S, NISHIO N, et al. Acrolein induced both pul-monary inflammation and the death of lung epithelial cells[J]. Toxicology Letters, 2014, 229(2): 384-392. DOI:10.1016/j.toxlet.2014.06.021 |
| [54] |
EL-EMAM S Z. Sesamol alleviates the cytotoxic effect of cyclophosphamide on normal human lung WI-38 cells via suppressing RAGE/NF-κB/autophagy signaling[J]. Natural Products and Bioprospecting, 2021, 11(3): 333-343. DOI:10.1007/s13659-020-00286-6 |
| [55] |
KAWASHIRI S Y, KAWAKAMI A, SAKAMOTO N, et al. A fatal case of acute exacerbation of interstitial lung disease in a patient with rheumatoid arthritis during treatment with tocilizumab[J]. Rheumatology International, 2012, 32(12): 4023-4026. DOI:10.1007/s00296-010-1525-z |
| [56] |
HUANG Y, LIN W, CHEN Z, et al. Effect of tumor necrosis factor inhibitors on interstitial lung disease in rheumatoid arthritis: Angel or demon?[J]. Drug Design, Development and Therapy, 2019, 13: 2111-2125. DOI:10.2147/DDDT.S204730 |
| [57] |
常文静, 蔡辉. 类风湿关节炎相关间质性肺病的研究进展[J]. 现代医学, 2020, 48(8): 1093-1099. CHANG W J, CAI H. Advances in research on rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease[J]. Modern Med-ical Journal, 2020, 48(8): 1093-1099. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1671-7562.2020.08.032 |
| [58] |
尹婷婷, 顾晓燕, 冯卫忠, 等. N-乙酰半胱氨酸联合肺康复治疗对类风湿关节炎相关间质性肺病患者运动耐力及生活质量的影响[J]. 实用药物与临床, 2017, 20(3): 290-293. YIN T T, GU X Y, FENG W Z, et al. Effect of N-acetylcys-teine combined with pulmonary rehabilitation on the exer-cise endurance and quality of life of patients with rheuma-toid arthritis-interstitial lung disease[J]. Practical Pharmacy and Clinical Remedies, 2017, 20(3): 290-293. |
| [59] |
陈皓然, 吴秋惠, 王鸯鸯, 等. 皮肌炎和多发性肌炎相关间质性肺炎的药物治疗[J]. 中南药学, 2020, 18(5): 811-815. CHEN H R, WU Q H, WANG Y Y, et al. Drug therapy of dermatomyositis/polymyositis-associated interstitial lung disease[J]. Central South Pharmacy, 2020, 18(5): 811-815. |
| [60] |
宋周烨, 徐媛, 葛卫红, 等. 结缔组织病相关间质性肺病患者环孢素血药浓度监测与评价[J]. 中国临床药学杂志, 2019, 28(2): 110-114. SONG Z Y, XU Y, GE W H, et al. Monitoring and evalua-tion of cyclosporine blood concentration in patients with connective tissue disease -associated interstitial lung dis-ease[J]. Chinese Journal of Clinical Pharmacy, 2019, 28(2): 110-114. |
| [61] |
李小燕, 徐亮. 类风湿关节炎合并间质性肺病研究进展[J]. 安徽医学, 2011, 32(10): 1787-1789. LI X Y, XU L. Research progress of rheumatoid arthritis complicated with interstitial lung disease[J]. Anhui Medical Journal, 2011, 32(10): 1787-1789. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-0399.2011.10.055 |
| [62] |
何欣, 黄玉琴, 青玉凤, 等. 类风湿关节炎相关性肺间质病变治疗进展[J]. 临床荟萃, 2021, 36(1): 75-79. HE X, HUANG Y Q, QING Y F, et al. Progress in the treat-ment of rheumatoid arthritis-related pulmonary interstitial lesions[J]. Clinical Focus, 2021, 36(1): 75-79. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2021.01.016 |
| [63] |
杨金良, 郑学军, 赵亚君, 等. 吡非尼酮联合糖皮质激素治疗类风湿关节炎合并肺间质纤维化的效果及对血清KL-6、ACPA的影响[J]. 广东医学, 2018, 39(23): 3552-3556. YANG J L, ZHENG X J, ZHAO Y J, et al. Clinical observa-tion of pifenidone combined with glucocorticoid in the treat-ment of rheumatoid arthritis complicated with pulmonary in-terstitial fibrosis and its effect on serum KL-6 and ACPA[J]. Guangdong Medical Journal, 2018, 39(23): 3552-3556. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1001-9448.2018.23.025 |
| [64] |
WOLLIN L, MAILLET I, QUESNIAUX V, et al. Antifibrotic and anti-inflammatory activity of the tyrosine kinase in-hibitor nintedanib in experimental models of lung fibrosis[J]. The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeu-tics, 2014, 349(2): 209-220. DOI:10.1124/jpet.113.208223 |
| [65] |
陈红, 王小超, 陶丽菊, 等. 雷公藤多苷联合泼尼松治疗类风湿关节炎肺间质病变的临床疗效[J]. 世界中医药, 2020, 15(4): 586-589, 594. CHEN H, WANG X C, TAO L J, et al. Analysis of clinical efficacy of Tripterygium wilfordii glycosides combined with prednisone in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis with in-terstitial lung disease[J]. World Chinese Medicine, 2020, 15(4): 586-589, 594. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1673-7202.2020.04.023 |
| [66] |
燕小宁, 张娜. 丹参下调早中期肺间质纤维化模型大鼠肺组织中VEGF的表达[J]. 临床医药实践, 2015, 24(6): 438-441. YAN X N, ZHANG N. Danshen reduced VEGF expression in the lung tissues of model rats with pulmonary fibrosis[J]. Proceeding of Clinical Medicine, 2015, 24(6): 438-441. |
| [67] |
陈宏, 张伟, 郭建波, 等. 地龙提取物通过抑制TGF-β1信号通路发挥抗肺纤维化作用研究[J]. 陕西中医, 2021, 42(4): 427-429. CHEN H, ZHANG W, GUO J B, et al. Analysis on the an-tifibrotic effect of earthworm extract by inhibiting TGF-β1 signaling pathway[J]. Shaanxi Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2021, 42(4): 427-429. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-7369.2021.04.005 |
| [68] |
张兴, 陈麒, 张一乐, 等. 生地提取物对肺纤维化大鼠血气分析影响及抗纤维化机制研究[J]. 云南中医学院学报, 2019, 42(01): 19-23. ZHANG X, CHEN Q, ZHANG Y L, et al. Study on the effect of Shengdi extract on blood gas analysis and anti -fibrosis mechanism of pulmonary fibrosis rats[J]. Journal of Yunnan University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2019, 42(01): 19-23. |
| [69] |
栾智华, 张东坡, 刘必旺, 等. 黄芪甲苷对肺纤维化小鼠VEGF/VEGFR2信号通路的影响[J]. 时珍国医国药, 2019, 30(7): 1611-1613. LUAN Z H, ZHANG D P, LIU B W, et al. Effect of Astragaloside Ⅳ on VEGF/VEGFR2 Signal Pathway in Mice with Pul-monary Fibrosis[J]. Lishizhen Medicine and Materia Medica Research, 2019, 30(7): 1611-1613. |
| [70] |
陈晓云, 苏励, 顾军花, 等. 活血化瘀法治疗类风湿性关节炎并肺间质病变[J]. 中华中医药杂志, 2010, 25(4): 629-631. CHEN X Y, SU L, GU J H, et al. Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis with interstitial lung disease by in removal stasis[J]. China Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine and Phar-macy, 2010, 25(4): 629-631. |
| [71] |
陈湘君, 顾军花, 茅建春, 等. 陈湘君教授治疗类风湿关节炎并发间质性肺炎经验应用总结[C]. 黄山: 中华中医药学会第十六届全国风湿病学术大会, 2012. CEHN X J, GU J H, MAO J C, et al. Summary of Professor CHEN Xiangjun's experience in treating rheumatoid arthri-tis complicated with interstitial pneumonia[C]. proceedings of the 16th national rheumatism academic conference of the Chinese society of Chinese medicine, Huangshan, Anhui, China, 2012. |
| [72] |
蒋军艳, 郑聪, 刘柳, 等. 类风湿关节炎合并肺间质病变的中医研究进展[J]. 风湿病与关节炎, 2018, 7(9): 77-80. JIANG J Y, ZHENG C, LIU L, et al. Research progress of rheumatoid arthritis with interstitial lung disease in tradi-tional Chinese medicine[J]. Rheumatism and Arthritis, 2018, 7(9): 77-80. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.2095-4174.2018.09.020 |
| [73] |
赵珊. 活血化纤汤治疗类风湿关节炎合并间质性肺炎的临床研究[D]. 南宁: 广西中医药大学, 2017. ZHAO S. Clinical research on Huoxue Huaxian Decoction in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis complicated with in-terstitial pneumonia[D]. Nanning: Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, 2017. |
 2022, Vol. 41
2022, Vol. 41