文章信息
- 郝少东, 李月廷, 杨闪闪
- HAO Shaodong, LI Yueting, YANG Shanshan
- 基于数据挖掘的中药专利复方治疗胆结石的用药规律分析
- Analysis of medication rules of traditional Chinese medicine patent compound treatment for gallstones based on data mining
- 天津中医药大学学报, 2022, 41(4): 507-512
- Journal of Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 41(4): 507-512
- http://dx.doi.org/10.11656/j.issn.1673-9043.2022.04.19
-
文章历史
收稿日期: 2022-03-03
2. 北京中医药大学附属北京市中西医结合医院外科,北京 100039
2. Department of Surgery, Beijing Hospital of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100039, China
胆结石又称胆石症, 是指胆道系统发生结石的疾病, 是慢性胆囊炎的主要病因。近年来由于生活水平提高, 中国胆囊结石发病率不断上升, 发病年龄多在50岁以后, 且女性高于男性[1]。胆结石的治疗目前西医以手术为主, 但存在手术创伤、复发率高和术后并发症等问题。中医药治疗胆石症历史悠久, 疗效满意, 可避免手术损伤和预防术后结石复发, 在临床上被广为应用[2, 3]。本文基于数据挖掘技术[4], 采用中国中医科学院中医药信息研究所开发的古今医案云平台, 对治疗胆结石的中药专利复方用药配伍规律进行分析总结, 为指导胆结石的临床治疗和中药组方开发提供参考依据。
1 资料与方法 1.1 资料来源进入中国知网数据库中的专利数据库, 以"胆结石"或"胆石症"和"中药"或"中成药"或"方剂"为关键词检索治疗胆结石的中药专利复方。检索至2020年3月所有相关中药专利复方。
1.2 纳入标准和排除标准纳入标准: 以治疗胆结石为目的的中药专利复方。排除标准: 单味中药处方; 中药提取物处方; 中西药物联用的复方; 民族医药治疗胆结石的专利复方; 以不同剂型重复发表的专利复方; 药物组成中>1/2的药物为《中药学》未收录的复方。
1.3 数据规范及数据表建立选取中医专利数据库专利主权项中的复方药物, 建立Excel表。根据钟赣生主编《中药学(第十版)》(中国中医药出版社)规范药名, 如田七改为三七, 川军改为大黄, 山萸肉改为山茱萸, 六神曲、建曲改为神曲, 元胡改为延胡索, 炒白术改为白术, 法半夏改为半夏。
1.4 数据导入与核对通过古今医案云平台"医案统计分析"中"医案标准化"模块, 将整理后的Excel表按要求导入数据库, 由双人负责进行审核, 后纳入标准池进行分析。
1.5 统计分析通过"古今医案云平台(V2.2.1)"中"数据挖掘分析"模块进行数据挖掘, 对中药专利复方中的中药进行频次统计, 关联分析和聚类分析(欧氏距离, 最长距离法), 利用复杂网络分析得到核心方药组成。
2 结果共纳入274个治疗胆结石的中药专利复方, 复方中最少药物数量为2个, 最多为33个, 所有复方中共出现246味中药, 中药频次为3488次。
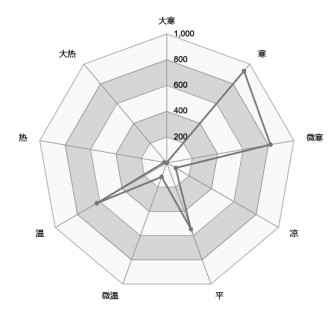
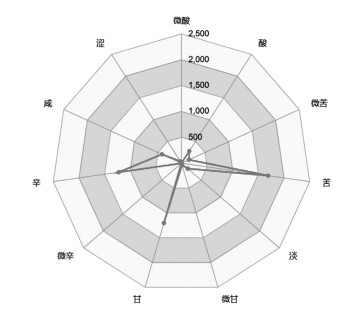
2.1 用药属性分析 2.1.1 四气五味分析对274个专利复方中药物的四气频次进行分析, 前4位分别为寒(931次)、微寒(816次)、温(627次)、平(547次), 主要以寒和微寒为主, 温、平等次之。见图 1。对药物五味频次进行分析, 前4位分别为苦(1 690次)、辛(1 226次)、甘(1 205次)、咸(414次), 主要以苦味最多, 辛、甘、咸等次之。见图 2。
|
| 图 1 药物四气分布 |
|
| 图 2 药物五味分布 |
对274个专利复方中药物的药物归经频次进行分析, 前5位分别为肝(1 728次)、脾(1 288次)、胃(1 163次)、肺(943次)、胆(647次)。归经以肝经为主, 脾、胃、肺、胆经等次之。见图 3。对药物功效频次进行分析, 前7位分别为利湿退黄、清利湿热、疏肝理气、清热解毒、解毒消肿、活血止痛、凉血解毒, 功效以清热利湿退黄、疏肝理气为主。见图 4。
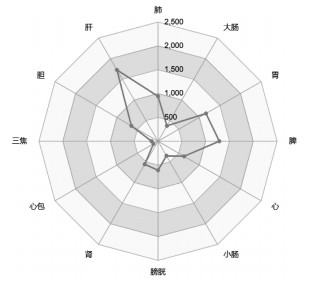
|
| 图 3 药物归经分布 |
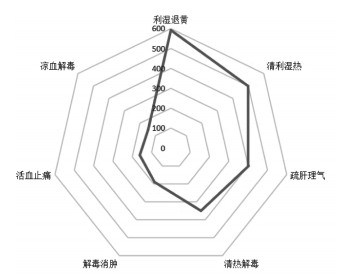
|
| 图 4 药物功效分布 |
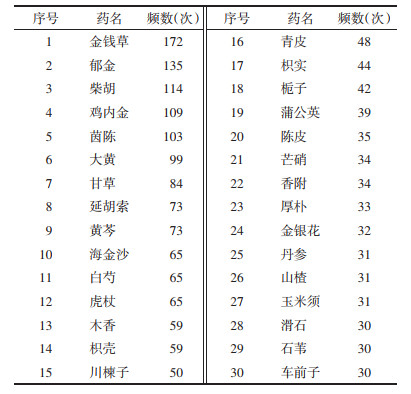
统计治疗胆结石中药专利复方中出现频次≥30的中药, 分别是: 利胆退黄药: 金钱草、虎杖、茵陈; 利水渗湿药: 玉米须、海金沙、滑石、石苇、车前子; 理气药: 木香、柴胡、枳壳、川楝子、青皮、枳实、陈皮、香附、厚朴、延胡索; 清热药: 黄芩、栀子、蒲公英、金银花; 化石排石药: 金钱草、郁金、鸡内金、海金沙; 泻下药: 大黄、芒硝。此外还有丹参、山楂、白芍、甘草。药物以清热利湿、利胆退黄、疏肝理气、通腑泻下为主。详见表 1。
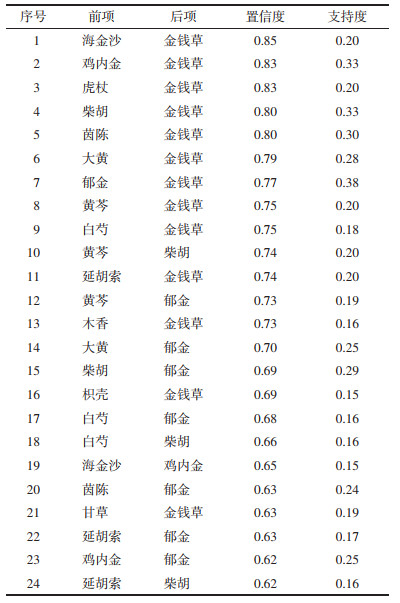
应用关联规则挖掘方法, 设置支持度为0.15, 置信度为0.60, 得到关联规则共24个。详见表 2。结果发现在治疗胆结石药物关联规则方面, 前项集中于海金沙、鸡内金、虎杖、柴胡、茵陈等, 后项集中于金钱草、柴胡、郁金等, 体现了胆结石清热利湿、利胆退黄、疏肝理气的治法。
将用药频次前20位的中药进行聚类。根据聚类分析结果, 以分组距离>10.5为界, 得到5类药物。第1类: 茵陈、大黄; 第2类: 金钱草、郁金、柴胡; 第3类: 甘草; 第4类: 鸡内金、海金沙; 第5类: 延胡索、木香、枳壳、黄芩、白芍、虎杖、青皮、枳实、栀子、川楝子、蒲公英、陈皮。图 5见开放科学(资源服务)标识码(OSID)。
2.5 复杂网络分析选择古今医案云平台复杂网络分析, 节点度设置为160, 提取治疗胆结石处方中的核心药物组合。见图 6。核心药物网络由金钱草、郁金、柴胡、鸡内金、茵陈、大黄、甘草、延胡索、黄芩、海金沙、白芍、虎杖、木香、枳壳、川楝子等24味中药组成。
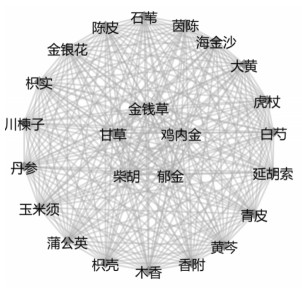
|
| 图 6 治疗胆结石核心药物组合网络图 |
胆结石归属中医"胁痛""黄疸""胆胀"等范畴, 病变脏腑主要在肝胆, 涉及脾胃。胆结石病因多为情志不遂、饮食不节、劳伤过度, 病机为肝胆湿热或气滞化火煎灼津液成石, 阻滞胆腑, 不通则痛。王学新等[5]认为晚间饱餐会使胆汁在胆囊内滞留和浓缩, 导致胆结石的发生。于梦等[6]认为胆结石的发生与运动情况、体质指数值有关。张东芳、王继新等[7-8]研究认为湿热、痰湿、气虚体质是肝胆结石患者常见的3种体质。胆结石的中西医结合诊疗共识[9]将胆结石中医证型分为肝胆湿热证、肝胆气滞证、热毒内蕴证、瘀血阻滞证和肝阴不足证, 治疗以清热祛湿、疏肝理气、清热解毒、泻火通腑、活血化瘀、滋阴清热为主。
3.1 用药信息分析用药基本信息分析显示, 中药专利复方治疗胆结石的药物以苦寒为主, 辅以辛温, 归经以肝经为主, 脾经、胃经次之, 体现了"胆病从肝论治""肝胆共主疏泄"的理论, 功效以清热利湿退黄、疏肝理气为主。赵玉清等[10]研究显示中药治疗胆总管结石以清热利湿、疏肝解郁、通腑泻下、化石排石为主, 药性以苦寒为主、辛温并用。刘名扬等[11]认为胆石症多由肝病引起, 治疗多从治肝入手。杨倩等[12]认为胆石症多由肝、脾疾病引起, 治疗上从肝、脾论治。汪得利等[13]研究显示胆石症用药多选用苦寒、辛温、甘平, 入肝胆、脾胃、肺经的药物。本研究结论基本与之相符。
3.2 用药规律分析本研究用药频次分析显示, 治疗胆结石常见的药物包括金钱草、郁金、柴胡、鸡内金、茵陈、大黄、甘草、延胡索、黄芩、海金沙等, 体现了胆结石的基本治疗方法为清热利湿、疏肝利胆、泻下通腑。关联规则分析显示在治疗胆结石药物关联规则方面, 常见药对包括海金沙-金钱草、鸡内金-金钱草、虎杖-金钱草、柴胡-金钱草、茵陈-金钱草等; 前后项药物分析显示了胆结石清热利湿、利胆退黄、疏肝理气的治法。对用药频次前20的药物进行聚类分析, 得到5类药物。第1类: 茵陈、大黄, 功效利胆退黄、泻下通腑; 第2类: 金钱草、郁金、柴胡, 功效利胆退黄、疏肝理气; 第3类: 甘草, 功效调和诸药、缓急止痛; 第4类: 鸡内金、海金沙, 功效化石排石; 第5类: 延胡索、木香、枳壳、黄芩、白芍、虎杖、青皮、枳实、栀子、川楝子、蒲公英、陈皮, 功效清热利湿、理气止痛。复杂网络分析得到治疗胆结石的24味核心中药, 包括: 金钱草、郁金、柴胡、鸡内金、茵陈、大黄、甘草、延胡索、黄芩、海金沙、白芍、虎杖、木香、枳壳、川楝子等。这些药物主要来自于治疗胆结石的经典方和经验方, 如四金汤、金铃子散、大柴胡汤、茵陈蒿汤。分析结果符合临床治疗胆结石的实际情况。
赵文霞[14]治疗胆石症常选用柴胡四金汤及加味大柴胡汤化裁。赵智强[15]治疗胆石症以柴芩五金汤为基础方, 常用柴胡、黄芩、鸡内金、海金沙、金钱草、金铃子散等。周仲瑛[16]治疗胆石症用药以柴胡、黄芩、金钱草、海金沙、郁金、鸡内金、赤芍、青皮、延胡索为主。金桂娴等[17]研究发现治疗胆结石中常用的药物包括金钱草、茵陈、蒲公英、郁金、青皮、赤芍等。丁平等[18]研究显示, 治疗胆石症常用药物有郁金、木香、大黄、金钱草、柴胡、枳壳、茵陈、黄芩、鸡内金等。现代药理研究显示: 金钱草治疗胆固醇结石和肝胆系统的炎症优势明显[19]。海金沙成分能促进胆汁中水分的分泌以增加胆汁量, 但不增加胆汁中胆红素和胆固醇的浓度[20]。郁金和生鸡内金具有消石排石的功效。茵陈及其成分能增强胆囊收缩、促进胆汁分泌、增加胆红素与胆汁酸外排而发挥利胆作用[21]。大黄具有利胆的作用, 能舒张胆管括约肌、通利胆汁[22]。柴胡醋炙后可增强疏肝止痛、利胆方面的功效[23]。这些研究结果与本次的专利复方挖掘结果相符合, 也验证了数据挖掘所产生核心药物的功效。
综上所述, 本研究利用数据挖掘技术, 揭示了治疗胆结石的中药专利复方的核心用药和药物配伍关系, 为胆结石的临床用药和新药开发提供参考。
| [1] |
何相宜, 施健. 中国慢性胆囊炎、胆囊结石内科诊疗共识意见(2018年)[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2019, 35(6): 1231-1236. HE X Y, SHI J. Consensus on diagnosis and treatment of chronic cholecystitis and gallstones in China(2018)[J]. Journal of Clinical Hepatology, 2019, 35(6): 1231-1236. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.06.011 |
| [2] |
周群, 王毅兴, 刘平, 等. 胆石症的中医药治疗研究进展[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2018, 34(11): 2458-2463. ZHOU Q, WANG Y X, LIU P, et al. Research advances in traditional Chinese medicine therapy for cholelithiasis[J]. Journal of Clinical Hepatology, 2018, 34(11): 2458-2463. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2018.11.042 |
| [3] |
王菲, 张稳, 缪雪华, 等. 中医药防治微创保胆取石术后结石复发的研究进展[J]. 天津中医药, 2019, 36(4): 413-416. WANG F, ZHANG W, MIAO X H, et al. Research progress on the prevention and treatment of stone recurrence after minimally invasive gallstone surgery with traditional Chinese medicine[J]. Tianjin Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2019, 36(4): 413-416. |
| [4] |
任建业, 许鸣, 陆嘉惠. 基于数据挖掘的中医临床用药规律和证型研究进展[J]. 中华中医药杂志, 2017, 32(10): 4579-4582. REN J Y, XU M, LU J H. Research progress on clinical medication regularity and syndrome type based on data mining[J]. China Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine and Pharmacy, 2017, 32(10): 4579-4582. |
| [5] |
王学新. 睡前胃内积食可能是引起胆囊炎、胆结石发病的主要原因[J]. 医学争鸣, 2015, 6(2): 33-35. WANG X X. Accumulation of food in stomach before going to bed at night may be the main cause of cholecystitis and gallstones[J]. Negative, 2015, 6(2): 33-35. |
| [6] |
于梦, 苏春芝, 于桂芳, 等. 基于Logistic回归分析200例胆结石患者中医体质分布规律[J]. 河北中医药学报, 2020, 35(1): 12-15. YU M, SU C Z, YU G F, et al. Distribution of 200 cholelithiasis patients' constitution of traditional Chinese medicine based on logistic regression analysis[J]. Journal of Hebei Traditional Chinese Medicine and Pharmacology, 2020, 35(1): 12-15. |
| [7] |
张东芳. 肝胆结石患者中医体质类型分析[J]. 中国卫生标准管理, 2015, 6(14): 136-137. ZHANG D F. Analysis of hepatolithiasis patients with TCM constitution type[J]. China Health Standard Management, 2015, 6(14): 136-137. |
| [8] |
王继新. 肝胆结石患者中医体质类型分析[J]. 中国现代药物应用, 2015, 9(3): 228-229. WANG J X. Analysis of TCM constitution types in patients with hepatobiliary calculi[J]. Chinese Journal of Modern Drug Application, 2015, 9(3): 228-229. |
| [9] |
李军祥, 陈誩, 梁健. 胆石症中西医结合诊疗共识意见(2017年)[J]. 中国中西医结合消化杂志, 2018, 26(2): 132-138. LI J X, CHEN J, LIANG J. Consensus on the diagnosis and treatment of integrated cholelithiasis and traditional Chinese medicine (2017)[J]. Chinese Journal of Integrated Traditional and Western Medicine on Digestion, 2018, 26(2): 132-138. |
| [10] |
赵玉清, 陈恂, 张立平. 基于数据挖掘现代中医药治疗胆总管结石用药规律分析[J]. 辽宁中医药大学学报, 2019, 21(12): 176-179. ZHAO Y Q, CHEN X, ZHANG L P. Analysis on medication regularity of modern traditional Chinese medicines in treating choledocholithiasis based on data mining technology[J]. Journal of Liaoning University of Traditional Chinese Medi- cine, 2019, 21(12): 176-179. |
| [11] |
刘名扬, 于庆生, 梁久银, 等. 胆石症从肝论治评述[J]. 安徽中医药大学学报, 2016, 35(1): 93-96. LIU M Y, YU Q S, LIANG J Y, et al. Comment on the treatment of cholelithiasis from the liver[J]. Journal of Anhui University of Chinese Medicine, 2016, 35(1): 93-96. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.2095-7246.2016.01.027 |
| [12] |
白亚楠, 杨倩, 梁亚飞, 等. 浅析杨倩主任医师以肝为轴、调中守恒治疗胆石症[J]. 河北中医药学报, 2018, 33(6): 51-54. BAI Y N, YANG Q, LIANG Y F, et al. Analysis of chief physician YANG qian's treatment of cholelithiasis by regulating the middle for conservation with liver as axis[J]. Journal of Hebei Traditional Chinese Medicine and Pharmacology, 2018, 33(6): 51-54. |
| [13] |
汪得利, 赵云燕, 陈俊良. 胆石症中医证型分布及用药规律分析[J]. 广州中医药大学学报, 2018, 35(5): 801-805. WANG D L, ZHAO Y Y, CHEN J L. Analysis of traditional Chinese medicine syndromes and medication rules of cholelithiasis[J]. Journal of Guangzhou University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2018, 35(5): 801-805. |
| [14] |
栗梦晓. 赵文霞教授临证辨治胆石症经验[J]. 中医研究, 2019, 32(12): 36-39. LI M X. Professor ZHAO Wenxia's clinical experience in differentiating and treating cholelithiasis[J]. Traditional Chinese Medicinal Research, 2019, 32(12): 36-39. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1001-6910.2019.12.15 |
| [15] |
蒋梦婷, 赵智强. 赵智强辨治胆石症[J]. 长春中医药大学学报, 2018, 34(4): 695-698. JIANG M T, ZHAO Z Q. Professor ZHAO Zhiqiang in the treatment of cholelithiasis[J]. Journal of Changchun University of Chinese Medicine, 2018, 34(4): 695-698. |
| [16] |
蒋梦婷. 基于数据挖掘的周仲瑛教授胆石症证治研究[D]. 南京: 南京中医药大学, 2019. JIANG M T. The syndrome and treatment research on the cases of cholelithiasis treating by professor Zhou zhongying based on data mining[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, 2019. |
| [17] |
金桂娴, 孙建光. 利胆排石药在胆石症中的应用概况[J]. 中国民族民间医药, 2015, 24(19): 12-13. JIN G X, SUN J G. General situation of application of cholestasis-displacing stone medicine in cholelithiasis[J]. Chinese Journal of Ethnomedicine and Ethnopharmacy, 2015, 24(19): 12-13. |
| [18] |
丁平, 王峥涛. 中药治疗胆结石的研究进展[J]. 中成药, 2019, 41(5): 1125-1128. DING P, WANG Z T. Research progress of traditional Chinese medicine in treating gallstones[J]. Chinese Traditional Patent Medicine, 2019, 41(5): 1125-1128. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1001-1528.2019.05.033 |
| [19] |
熊颖, 王俊文, 邓君. 金钱草和广金钱草的药理作用比较[J]. 中国中药杂志, 2015, 40(11): 2106-2111. XIONG Y, WANG J W, DENG J. Comparison between lysimachiae herba and desmodii styracifolii herba in pharmacological activities[J]. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica, 2015, 40(11): 2106-2111. |
| [20] |
岑庚钰, 蒙小丽, 梁远芳, 等. 海金沙化学成分和药理作用研究概况[J]. 中国民族民间医药, 2018, 27(14): 48-50. CEN G Y, MENG X L, LIANG Y F, et al. Study on the chemical composition and pharmacological activity of the Lygodium japonicum[J]. Chinese Journal of Ethnomedicine and Ethnopharmacy, 2018, 27(14): 48-50. |
| [21] |
刘玉萍, 邱小玉, 刘烨, 等. 茵陈的药理作用研究进展[J]. 中草药, 2019, 50(9): 2235-2241. LIU Y P, QIU X Y, LIU Y, et al. Research progress on pharmacological effect of artemisiae scopariae herba[J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs, 2019, 50(9): 2235-2241. |
| [22] |
金丽霞, 金丽军, 栾仲秋, 等. 大黄的化学成分和药理研究进展[J]. 中医药信息, 2020, 37(1): 121-126. JIN L X, JIN L J, LUAN Z Q, et al. Research progress on chemical constituents and pharmacology of rhubarb[J]. Information on Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2020, 37(1): 121-126. |
| [23] |
王雪芹, 赵洋, 汪新体, 等. 醋炙柴胡的化学成分及药理作用研究进展[J]. 药物评价研究, 2018, 41(1): 163-168. WANG X Q, ZHAO Y, WANG X T, et al. Research progress on chemical constituents and pharmacological actions of vinegar-baked Radix Bupleuri[J]. Drug Evaluation Research, 2018, 41(1): 163-168. |
 2022, Vol. 41
2022, Vol. 41