文章信息
- 韩国英, 李霖, 李楠, 张晗
- HAN Guoying, LI Lin, LI Nan, ZHANG Han
- 基于糖皮质激素受体信号通路中药抗抑郁作用及机制的研究进展
- Advances in the antidepressant effects and mechanisms of traditional Chinese medicine based on glucocorticoid receptor signaling pathway
- 天津中医药大学学报, 2023, 42(1): 121-126
- Journal of Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 42(1): 121-126
- http://dx.doi.org/10.11656/j.issn.1673-9043.2023.01.22
-
文章历史
收稿日期: 2022-09-25
抑郁症是由多种因素引起的一种情绪障碍类疾病,主要表现为情绪低落、思维迟钝及意志活动减退等症状,具有较高的发病率、致残率和病死率。据统计,2017年全球抑郁症患者人数已达3.22亿,占世界人口的4.4%,严重威胁人类健康[1]。
抑郁症属中医“郁证”范畴,早在《黄帝内经》中就有关于郁证的论述。《素问·举痛论》中提及“余知百病生于气也,怒则气上,喜则气缓,悲则气消,恐则气下,惊则气乱,思则气结”,认为情志不畅导致的气机失调会引起郁证。其中肝气郁结是诱发抑郁症的核心病机,治疗多从疏肝解郁方面着手,并采用逍遥散、柴胡疏肝散等方剂加减进行调节。目前临床上治疗抑郁症主要以传统西药为主,但这些药物多存在起效缓慢和认知障碍等不良反应,因此寻找和开发更加有效且不良反应较小的抗抑郁药物是亟待解决的问题[2]。中药对于抑郁症的治疗不但有丰富的经验和大量的临床研究支持,还具有独特的疗效,如临床上多从中药单体或在经典方剂的基础上加减对抑郁症患者进行对症治疗。抑郁症的发病机制主要包括单胺类神经递质假说、受体假说、下丘脑-垂体-肾上腺(HPA)轴假说及脑源性神经营养因子(BDNF)假说[3]。HPA轴假说是近年来的研究热点之一,其中糖皮质激素受体(GR)是HPA轴的末端效应器,参与应激诱导的肾上腺分泌糖皮质激素(GC)的负反馈调节。应激激活HPA轴,刺激下丘脑分泌促肾上腺皮质激素释放激素(CRH),进而引起垂体分泌促肾上腺皮质激素(ACTH),ACTH通过血液到达肾上腺刺激皮质分泌GC。长期应激会促使肾上腺分泌大量GC,从而引起HPA轴亢进,使GR处于持续激活状态,导致GR功能失调,HPA轴负反馈调节作用失控,最终诱发或加剧抑郁症的发生与发展。本文就GR与抑郁症的关系及中药基于GR途径抗抑郁作用与机制进行综述。
1 GR与抑郁症GR是一种配体依赖的核转录因子,有GRα和GRβ两种亚型。无GC存在的情况下,GR与热休克蛋白90(HSP90)以蛋白复合物的形式稳定存在于细胞质中,此时GR处于非活性状态。GC存在的情况下,GC可以自由通过细胞膜进入细胞与GR结合发生构象改变,蛋白复合物迅速解离后GR进入细胞核,与糖皮质激素反应元件(GRE)结合,主动或被动地调节靶基因的转录和蛋白质的合成,进而发挥生物学效应。目前大部分研究也证实GR参与了抑郁症的机制,例如,运动可以通过GR上调大鼠内侧前额叶皮质中的多巴胺(DA)水平,并以DA2型受体(D2R)依赖的方式发挥抗抑郁作用[4];GR拮抗剂米非司酮(RU486)可通过抑制GR的激活逆转皮质醇(CORT)诱导的抑郁大鼠胶质纤维酸性蛋白(GFAP)表达的降低及胶质纤维酸性蛋白(GFAP)数量的减少[5];选择性GR调节剂CORT 118335可减少GC的过度分泌,进而下调海马CA1区癌基因蛋白(c-Fos)表达发挥抗抑郁作用[6];中药通过上调GR表达抑制HPA轴的过度激活,发挥抗抑郁作用[7-9]。
2 中药基于GR相关信号通路抗抑郁作用及机制的实验研究 2.1 BDNF信号通路BDNF在大脑中广泛分布,是神经营养因子家族的一员,在调节神经元的生长、发育和功能方面发挥着重要作用。研究发现,GR-BDNF的串话作用可以抑制BDNF诱导的树突生长、突触蛋白表达和神经元细胞钙离子(Ca2+)内流[10]。GR功能受损导致其对BDNF调节失控参与了抑郁症的发生和发展。大黄素和厚朴酚可以通过抑制HPA轴活性及上调海马中GR与BDNF的mRNA及蛋白表达发挥抗抑郁作用[11-12]。
2.1.1 基于GR-BDNF-神经肽Y(NPY)信号通路的抗抑郁中药NPY对调节情绪、学习与记忆、压力和焦虑具有重要作用,其表达受BDNF调控,是BDNF的下游靶点。杨琴等[13]研究发现百合疏肝安神汤可显著增加海马齿状回(DG)和CA3区的神经元数量,减少杏仁核神经元的损伤及上调GR、BDNF及NPY的蛋白表达水平,通过调控GR-BDNF-NPY的表达从而增加海马神经再生,改善抑郁症状。
2.1.2 基于FK506结合蛋白(FKBP)s-GR-BDNF信号通路的抗抑郁中药FKBP4和FKBP5是FKBPs的家族成员,是热休克蛋白90(HSP90)的分子伴侣蛋白,具有调节多种生物过程的功能,如类固醇受体作用、转录活性、蛋白质构象和蛋白质运输等[14]。GR与HSP90形成GR-HSP90-FKBP4复合物,进入细胞浆后GR-HSP90-FKBP4复合物中的FKBP4被FKBP5替换,FKBP5与GR结合竞争性地抑制GC与GR的结合,导致无法形成受体-配体复合物,从而抑制受体-配体复合物向细胞核的转移,使其不能发挥核转录因子的作用。因此,FKBP5的过度表达降低了GR对GC的敏感性,减少了GR向细胞核的转移并抑制了GR功能[15-16]。芍药苷具有潜在的神经保护作用,可用于治疗抑郁症[17]、帕金森氏病[18]及脑缺血[19]。研究表明,芍药苷可显著降低HPA轴亢进,与增加GR核易位和降低FKBP5的蛋白表达有关[20]。于鲁璐等[21]研究发现,丹参多酚酸可通过下调抑郁大鼠FKBP5表达,促进GR进入细胞核的活性,提高GR靶基因BDNF的表达水平,从而发挥改善海马神经突触可塑性的作用。逍遥散是基于疏肝解郁法治疗抑郁症的经典方剂[22-24],曹国平[25]研究发现逍遥散可上调FKBP4表达,下调FKBP5表达,抑制GR进入细胞核,增加细胞膜上GR的数量,同时提高GR表达,从而上调BDNF表达,改善其海马神经可塑性,提示该方可通过调节FKBPs-GR-BDNF通路实现对海马神经元的保护。
2.1.3 基于GR-磷酸化环磷酸腺苷反应元件结合蛋白(pCREB)-BDNF信号通路的抗抑郁中药BDNF的启动子区域包含环磷酸腺苷反应元件(CRE)序列,因此会受到CRE结合蛋白(CREB)的调控,pCREB与BDNF结合后可增强其转录水平[26]。当GC-GR复合物与CREB结合时,GC可能干扰该过程并阻止其磷酸化,从而阻止CRE调节BDNF的表达。蒲郁胶囊常用于抑郁症的治疗[27],王玉露等[28]采用酶联免疫吸附(ELISA)法检测小鼠血清中CORT、ACTH水平,蛋白免疫印迹(Western Blot)法检测海马中GR、pCREB、CREB及BDNF的蛋白表达,结果显示蒲郁胶囊能够降低HPA轴的活性,并通过调节GR-pCREB-BDNF信号通路改善慢性温和不可预知应激(CUMS)诱导的小鼠抑郁行为。
2.2 GR-磷酸化GR(p-GR)-血清/糖皮质激素调节激酶1(SGK1)信号通路SGK1是一种丝氨酸/苏氨酸蛋白激酶,具有调节神经元活性、增殖和凋亡的作用,并参与学习记忆和行为认知等过程。研究表明,SGK1可通过调节GR磷酸化及核易位介导皮质酮诱导的海马神经发生障碍[29]。长期暴露于高浓度GC会增加SGK1在Ser422和Thr256处的磷酸化水平,进而增强SGK1的活性,诱导Ser203和Ser211处GR的磷酸化,增强GR的核易位。黄芩苷作为黄芩中的主要活性成分,其抗抑郁作用被广泛证实[30-33],刘勇永等[31]研究发现黄芩苷可以通过调节SGK1介导的GR磷酸化使GR功能正常,以促进海马神经新生,改善抑郁状态。孟盼等[34]研究发现百事乐胶囊可显著增加海马中GR、p-GR的表达及降低海马中SGK1的表达,提示百事乐胶囊可以通过促进GR-p-GR-SGK1信号级联反应改善抑郁大鼠的学习记忆能力,进而发挥抗抑郁作用。
2.3 磷酸酪氨酸衔接蛋白2(APPL2)-GR信号通路APPL2是一种细胞内的衔接蛋白,具有调节细胞生长的作用。研究发现GR特异性阻断剂RU486可逆转APPL2基因过表达对小鼠海马神经新生的抑制[35]。GAO等[36]研究发现黄芩苷可通过抑制APPL2介导的GR过度激活促进海马、脑室下区及嗅球的神经发生,并改善嗅觉功能和抑郁症状,提示黄芩苷的抗抑郁机制与APPL2-GR通路有关。
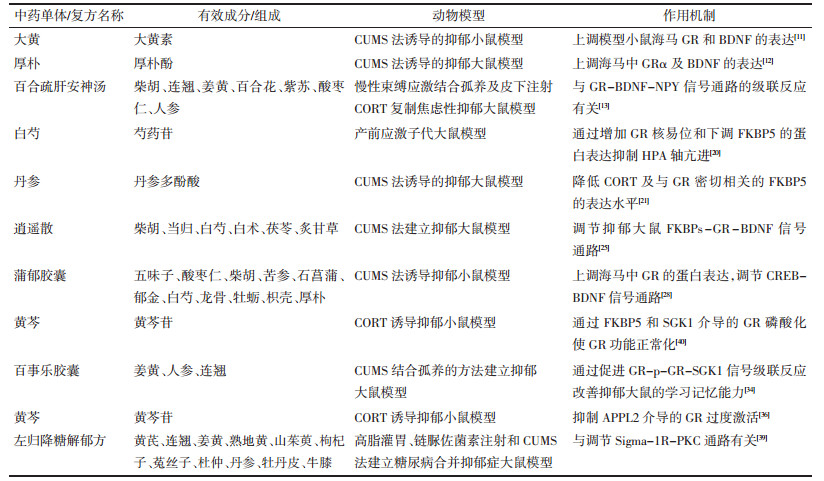
2.4 sigma-1受体(sigma-1R)-PKC信号通路sigma-1R是一种受体型分子伴侣,参与多种神经代谢系统的调节,是治疗抑郁症的重要靶点[37]。sigma-1R被激活后,会从内质网转移至细胞质膜,并调节膜表面的蛋白激酶C(PKC)信号通路,使其从胞质游离态转移为膜结合态,直接或间接地磷酸化膜相关蛋白GR,进而参与促肾上腺皮质激素释放因子(CRF)的转录过程[38]。杨蕙等[39]研究发现左归降糖解郁方可通过上调糖尿病合并抑郁大鼠下丘脑中sigma-1R的蛋白表达和增加PKC及GR的磷酸化水平对sigma-1R-PKC通路进行调节,增加GR的表达,进而控制CRF含量,最终发挥降低血糖和抗抑郁的双重疗效。基于GR相关信号通路中药治疗抑郁症的作用机制见表 1。
HPA轴作为神经内分泌免疫调节的重要环节,其功能变化会直接影响机体健康状况。各类应激因素引起的HPA轴功能的紊乱,主要表现为HPA轴功能亢进,而HPA轴功能亢进是导致抑郁症的主要作用机制之一。HPA轴功能亢进造成GC、ACTH、CRH及CORT水平升高,CORT水平升高可损伤海马、蓝斑等,使抑郁症患者出现认知功能障碍、情绪消沉、失眠等症状[40]。
GR作为GC效应的执行者,不仅参与机体的能量代谢,而且对多种基因具有转录调控作用,并直接接受激素的反馈调节,在调节HPA轴的负反馈方面起着重要作用。在慢性应激初期,大量激活的GR负反馈作用于HPA轴,抑制GC的合成和分泌,然而持续应激产生的高浓度GC导致其与GR的结合能力降低,引起GR活性下降,导致HPA轴功能紊乱并持续亢进,最终诱发或加重抑郁症的发生和发展。综上所述,中药单体及复方可以通过多个靶点、多条通路发挥抗抑郁作用,其作用与GR相关的信号通路有关,如GR-BDNF-NPY、FKBPs-GR-BDNF、GR-pCREB-BDNF、GR-p-GR-SGK1及APPL2-GR等。关于抗抑郁的机制,多从动物行为学、神经内分泌轴及神经营养因子等方面进行研究,显示出中药在抗抑郁方面的良好发展前景,但也存在不足之处。一方面,目前尚难明确慢性不可预知性应激、慢性束缚应激及体外注射CORT等造模方式对于研究中药对GR信号通路的影响哪种更具优势,这一问题值得思考并需要大量实验验证。另一方面,中药虽然成分多样性、作用机制多靶点,但在治疗疾病时存在起效慢的缺点。而化学药物虽然存在作用靶点单一、抗抑郁谱短、易复发等缺点,但其起效迅速是相对于中药的一大优势。因此,未来可考虑将中药与化学药物联合运用,以提高临床疗效、减少用药量及降低不良反应,这将为抗抑郁药物的研发提供新思路,为抑郁症的治疗提供更多选择。
| [1] |
FRIEDRICH M J. Depression is the leading cause of disability around the world[J]. JAMA, 2017, 317(15): 1517. |
| [2] |
PAPAKOSTAS G I. Treatment of SSRI-resistant depression: a meta-analysis comparing within-versus across-class switches[J]. Biological Psychiatry, 2008, 63(7): 699-704. DOI:10.1016/j.biopsych.2007.08.010 |
| [3] |
张潇, 田俊生, 刘欢, 等. 抗抑郁中药新药研发进展[J]. 中国中药杂志, 2017, 42(1): 29-33. ZHANG X, TIAN J S, LIU H, et al. Progress of new antidepressant drugs development[J]. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica, 2017, 42(1): 29-33. DOI:10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20161222.056 |
| [4] |
CHEN C, NAKAGAWA S, KITAICHI Y, et al. The role of medial prefrontal corticosterone and dopamine in the antidepressant-like effect of exercise[J]. Psychoneuroendocrinology, 2016, 69(1): 1-9. |
| [5] |
LOU Y X, LI J, WANG Z Z, et al. Glucocorticoid receptor activation induces decrease of hippocampal astrocyte number in rats[J]. Psychopharmacology, 2018, 235(9): 2529-2540. DOI:10.1007/s00213-018-4936-2 |
| [6] |
NGUYEN E T, STREICHER J, BERMAN S, et al. A mixed glucocorticoid/mineralocorticoid receptor modulator dampens endocrine and hippocampal stress responsivity in male rats[J]. Physiology & Behavior, 2017, 178(1): 82-92. |
| [7] |
张彦, 祝晨陈. 金丝桃苷对慢性不可预知温和刺激大鼠抑郁行为的影响[J]. 中国新药与临床杂志, 2017, 36(3): 150-156. ZHANG Y, ZHU C C. Effect of hyperin on depressive behavior of rats induced by chronic unpredicted mild stress[J]. Chinese Journal of New Drugs and Clinical Remedies, 2017, 36(3): 150-156. DOI:10.14109/j.cnki.xyylc.2017.03.007 |
| [8] |
CAI L, LI R, TANG W J, et al. Antidepressant-like effect of geniposide on chronic unpredictable mild stress-induced depressive rats by regulating the hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal axis[J]. European Neuropsychopharmacology: the Journal of the European College of Neuropsychopharmacology, 2015, 25(8): 1332-1341. DOI:10.1016/j.euroneuro.2015.04.009 |
| [9] |
ZHENG X X, CHENG Y, CHEN Y W, et al. Ferulic acid improves depressive-like behavior in prenatally-stressed offspring rats via anti-inflammatory activity and HPA axis[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2019, 20(3): 493. DOI:10.3390/ijms20030493 |
| [10] |
KUMAMARU E, NUMAKAWA T, ADACHI N, et al. Glucocorticoid prevents brain-derived neurotrophic factor-mediated maturation of synaptic function in developing hippocampal neurons through reduction in the activity of mitogen-activated protein kinase[J]. Molecular Endocrinology, 2008, 22(3): 546-558. DOI:10.1210/me.2007-0264 |
| [11] |
LI M, FU Q, LI Y, et al. Emodin opposes chronic unpredictable mild stress induced depressive-like behavior in mice by upregulating the levels of hippocampal glucocorticoid receptor and brain-derived neurotrophic factor[J]. Fitoterapia, 2014, 98(1): 1-10. |
| [12] |
WANG C M, GAN D N, WU J G, et al. Honokiol exerts antidepressant effects in rats exposed to chronic unpredictable mild stress by regulating brain derived neurotrophic factor level and hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal axis activity[J]. Neurochemical Research, 2018, 43(8): 1519-1528. DOI:10.1007/s11064-018-2566-z |
| [13] |
杨琴, 杜青, 赵洪庆, 等. 百合疏肝安神汤对焦虑性抑郁症模型大鼠前额叶-边缘结构及GR/BDNF/NPY表达的影响[J]. 中国临床药理学与治疗学, 2017, 22(10): 1090-1098. YANG Q, DU Q, ZHAO H Q, et al. Effects of compound Baihe Shugan anshen on stucture and expressions of GR, BDNF and NPY on prefrontal cortex-edge structure in anxious depression model rats[J]. Chinese Journal of Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics, 2017, 22(10): 1090-1098. |
| [14] |
ZGAJNAR N R, DE LEO S A, LOTUFO C M, et al. Biological actions of the Hsp90-binding immunophilins FKBP51 and FKBP52[J]. Biomolecules, 2019, 9(2): 52. DOI:10.3390/biom9020052 |
| [15] |
CATTANEO A. Stress-induced mechanisms in mental illness: a role for glucocorticoid signalling[J]. The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 2016, 160(12): 169-174. |
| [16] |
MENKE A, KLENGEL T, RUBEL J, et al. Genetic variation in FKBP5 associated with the extent of stress hormone dysregulation in major depression[J]. Genes, Brain and Behavior, 2013, 12(3): 289-296. DOI:10.1111/gbb.12026 |
| [17] |
李萍, 李艺杰, 薛玲, 等. 芍药苷对Bayk8644诱导大鼠抑郁焦虑样行为的改善作用及机制研究[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2020, 40(6): 489-495. LI P, LI Y J, XUE L, et al. Effect and mechanism of paeoniflorin on depression and anxiety behavior induced by Bayk8644 in rats[J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2020, 40(6): 489-495. |
| [18] |
ZHENG M Z, LIU C M, FAN Y J, et al. Neuroprotection by paeoniflorin in the MPTP mouse model of parkinson's disease[J]. Neuropharmacology, 2017, 116: 412-420. DOI:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2017.01.009 |
| [19] |
KO C H, HUANG C P, LIN Y W, et al. Paeoniflorin has anti-inflammation and neurogenesis functions through nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury rats[J]. Iranian Journal of Basic Medical Sciences, 2018, 21(11): 1174-1178. |
| [20] |
LI Y C, ZHENG X X, XIA S Z, et al. Paeoniflorin ameliorates depressive-like behavior in prenatally stressed offspring by restoring the HPA axis-and glucocorticoid receptor-associated dysfunction[J]. Journal of Affective Disorders, 2020, 274(4): 471-481. |
| [21] |
于鲁璐, 甄凤亚, 韩冰, 等. 丹参多酚酸对慢性应激抑郁大鼠脑内细胞因子和糖皮质激素系统的影响[J]. 中国神经精神疾病杂志, 2018, 44(9): 531-535. YU L L, ZHEN F Y, HAN B, et al. Salvianolic acid reverses cytokines, glucocorticoid system changes in prefrontal cortex and Hippocampus in rats with chronic stress[J]. Chinese Journal of Nervous and Mental Diseases, 2018, 44(9): 531-535. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1002-0152.2018.09.005 |
| [22] |
HOU Y J, LIU Y Y, LIU C Y, et al. Xiaoyaosan regulates depression-related behaviors with physical symptoms by modulating Orexin A/OxR1 in the hypothalamus[J]. Anato-mical Record, 2020, 303(8): 2144-2153. DOI:10.1002/ar.24386 |
| [23] |
SONG M, ZHANG J J, LI X J, et al. Effects of Xiaoyao San on depressive-like behaviors in rats with chronic unpredictable mild stress through HPA axis induced astrocytic activities[J]. Frontiers in Psychiatry, 2020, 11(10): 533-545. |
| [24] |
JIAO H Y, YANG H J, YAN Z Y, et al. Traditional Chinese formula Xiaoyao San alleviates depressive-like behavior in CUMS mice by regulating PEBP1-GPX4-mediated ferroptosis in the Hippocampus[J]. Neuropsychiatric Disease and Treatment, 2021, 17(9): 1001-1019. |
| [25] |
曹国平. 基于FKBPs/GR/BDNF通路探讨逍遥散对抑郁模型大鼠海马神经可塑性损伤修复的机制研究[D]. 广州: 广州中医药大学, 2017. CAO G P. Study of the mechanism of Xiaoyao Powder on hippocampal nerve plasticity injury repairment in chronic stress rats based on FKBPs/GR/BDNF pathway[D]. Guangzhou: Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, 2017. |
| [26] |
庞妍, 杨敬华, 刘秋芳, 等. 出生前后染镧对大鼠海马CREB和BDNF影响[J]. 中国公共卫生, 2014, 30(2): 204-206. PANG Y, YANG J H, LIU Q F, et al. Effects of exposure to lanthanum during perinatal period on CREB phosphorylation and BDNF expression in Hippocampus of rats[J]. Chinese Journal of Public Health, 2014, 30(2): 204-206. |
| [27] |
贾铷, 芦锰, 陈燕, 等. 解郁胶囊对药物所致抑郁模型小鼠的影响[J]. 中医学报, 2018, 33(2): 278-281. JIA R, LU M, CHEN Y, et al. Evaluation of the antidepressant effect of Jieyu Capsule in pharmacological depression models[J]. Acta Chinese Medicine, 2018, 33(2): 278-281. |
| [28] |
王玉露, 芦锰, 王月月, 等. 蒲郁胶囊对抑郁小鼠行为学、HPA轴及海马CREB-BDNF通路表达的影响[J]. 中国中药杂志, 2020, 45(20): 4971-4977. WANG Y L, LU M, WANG Y Y, et al. Effect of Puyu Capsules on behavior, HPA axis and CREB-BDNF pathway expression in Hippocampus of depressed mice[J]. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica, 2020, 45(20): 4971-4977. |
| [29] |
ANACKER C, CATTANEO A, MUSAELYAN K, et al. Role for the kinase SGK1 in stress, depression, and glucocorticoid effects on hippocampal neurogenesis[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2013, 110(21): 8708-8713. |
| [30] |
LI Y C. Chronic treatment with baicalin prevents the chronic mild stress-induced depressive-like behavior: involving the inhibition of cyclooxygenase-2 in rat brain[J]. Progress in Neuro-Psychopharmacology and Biological Psychiatry, 2013, 40(5): 138-143. |
| [31] |
刘勇永, 芦晔, 楚立, 等. 黄芩苷对抑郁症模型小鼠海马钙结合蛋白D28K表达的影响[J]. 中国新药与临床杂志, 2019, 38(2): 107-111. LIU Y Y, LU Y, CHU L, et al. Effects of baicalin on expression of calbindin-D28K in Hippocampus of depression model mice[J]. Chinese Journal of New Drugs and Clinical Remedies, 2019, 38(2): 107-111. |
| [32] |
沈继朵, 胡春月, 魏玉, 等. 黄芩苷对皮质酮诱导抑郁小鼠海马NT-3表达水平的影响[J]. 中国民族民间医药, 2016, 25(20): 13-15. SHEN J D, HU C Y, WEI Y, et al. Effects of baicalin on the expression of NT-3 in Hippocampus of mice with depression induced by corticosterone[J]. Chinese Journal of Ethnome-dicine and Ethnopharmacy, 2016, 25(20): 13-15. |
| [33] |
ZHANG K, PAN X, WANG F, et al. Baicalin promotes hippocampal neurogenesis via SGK1 and FKBP5 mediated glucocorticoid receptor phosphorylation in a neuroendocrine mouse model of anxiety/depression[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 12(6): 30-51. |
| [34] |
孟盼, 赵洪庆, 雷昌, 等. 百事乐胶囊对抑郁模型大鼠海马GR/p-GR/SGK1表达的影响[J]. 中国医院药学杂志, 2017, 37(8): 694-697. MENG P, ZHAO H Q, LEI C, et al. Effects of Baishile Capsules on GR/p-GR/SGK1 expression in Hippocampus of depression rat model[J]. Chinese Journal of Hospital Pharmacy, 2017, 37(8): 694-697. |
| [35] |
GAO C, CHEN X M, XU A M, et al. Adaptor protein APPL2 affects adult antidepressant behaviors and hippocampal neurogenesis via regulating the sensitivity of glucocorticoid receptor[J]. Molecular Neurobiology, 2018, 55(7): 5537-5547. |
| [36] |
GAO C, DU Q H, LI W T, et al. Baicalin modulates APPL2/glucocorticoid receptor signaling cascade, promotes neurogenesis, and attenuates emotional and olfactory dysfunctions in chronic corticosterone-induced depression[J]. Molecular Neurobiology, 2018, 55(12): 9334-9348. |
| [37] |
DI T T, ZHANG S Y, HONG J, et al. Hyperactivity of hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis due to dysfunction of the hypothalamic glucocorticoid receptor in Sigma-1 receptor knockout mice[J]. Frontiers in Molecular Neuroscience, 2017, 10(2): 287. |
| [38] |
BROSSAUD J, ROUMES H, HELBLING J C, et al. Retinoic acid increases glucocorticoid receptor phosphorylation via cyclin-dependent kinase 5[J]. Molecular and Cellular Neurosciences, 2017, 82(1): 96-104. |
| [39] |
杨蕙, 韩远山, 柳卓, 等. 左归降糖解郁方对糖尿病并发抑郁症大鼠下丘脑信号通路的影响[J]. 中国现代应用药学, 2019, 36(11): 1333-1337. YANG H, HAN Y S, LIU Z, et al. Effect of Zuogui Jiangtang Jieyu Formulation on signaling pathway in hypothalamus of diabetic rats with depression[J]. Chinese Journal of Modern Applied Pharmacy, 2019, 36(11): 1333-1337. |
| [40] |
LI Y C, WANG L L, PEI Y Y, et al. Baicalin decreases SGK1 expression in the hippocampus and reverses depressive-like behaviors induced by corticosterone[J]. Neuroscience, 2015, 311(2): 130-137. |
 2023, Vol. 42
2023, Vol. 42