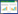文章信息
- 张亚平, 单鲁豫, 穆琦瑄, 李文慧, 王丹妮, 王跃飞, 于卉娟
- ZHANG Yaping, SHAN Luyu, MU Qixuan, LI Wenhui, WANG Danni, WANG Yuefei, YU Huijuan
- 黄曲霉毒素富集-检测-降解解毒方法的研究进展
- Research progress of aflatoxin enrichment, detection, degradation and detoxification methods
- 天津中医药大学学报, 2023, 42(5): 656-663
- Journal of Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 42(5): 656-663
- http://dx.doi.org/10.11656/j.issn.1673-9043.2023.05.18
-
文章历史
收稿日期: 2023-06-11
中医药是中华民族的瑰宝,为中华民族繁衍生息作出了巨大贡献。国家药品监管部门、产业界、科研界高度重视中药中有害物质的防控及检测,如黄曲霉毒素、硫磺、重金属等。2021年6月,国家中药材标准化与质量评估创新联盟成立,聚焦高质量中药材的加工、生产、流通环节,提出“三无一全”(无硫磺加工、无黄曲霉毒素超标、无公害、全过程可追溯)优质药材品牌理念,进一步促进高质量中药材市场供给。中药材有害菌污染是影响中药材质量的重要方面,其中黄曲霉菌极易侵染中药材,其代谢产物黄曲霉毒素具有剧毒性和致癌性,严重影响临床用药安全[1-2]。此外,黄曲霉毒素也存在于发霉的粮食、豆类、坚果及其相关食品中。
黄曲霉毒素主要是由黄曲霉菌(Aspergillus flavus)和寄生曲霉菌(Aspergillus parasiticus)在潮湿温热环境下产生的毒性次级代谢产物,是二氢呋喃香豆素化合物及其衍生物[3]。目前已发现20多种黄曲霉毒素,其中AFB1、AFB2、AFG1、AFG2、AFM1等毒素已被分离鉴定,根据化学结构主要划分为环戊烯酮型和内酯型[4](表 1)。AFB1是已知黄曲霉毒素中毒性最强的化合物,其毒性约是氰化钾的10倍、砒霜的68倍[5],被世界卫生组织列为Ⅰ类致癌物[6]。AFB1结构中存在3个毒性位点[7]:1)呋喃环上的双键(C8-C9)是黄曲霉毒素与蛋白质或核酸形成复合物的作用位点,是导致基因突变、致癌致畸的主要基团。2)香豆素内酯环上的10、11、15号位点。3)环戊烯酮环上的1、2、3、14号位点,这部分位点易被取代基团取代。长期暴露于黄曲霉毒素下会导致机体免疫抑制、先天畸形、不孕不育、内分泌紊乱、肝细胞癌变等[8]。
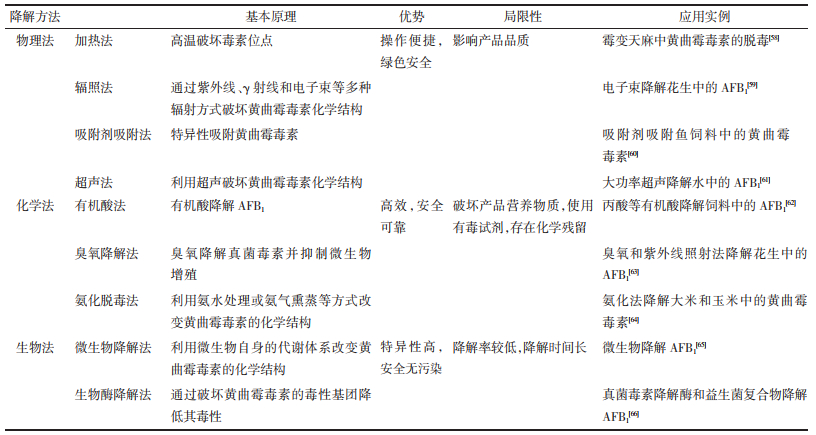
黄曲霉毒素严重危害人类健康,国家药典委员会强调,药品微生物检查是药品安全性控制的重要研究内容。《中华人民共和国药典》对中药检测黄曲霉毒素的要求日趋严格,从2010年版的5种药材增加到2020年版的24种,涵盖根茎类、果实种子类和动物类药材,检测限度为AFB1不得超过5 μg/kg,AFB1、AFB2、AFG1、AFG2的总量不得超过10 μg/kg[9-11]。科学有效地防控黄曲霉毒素侵染中药对提升中药临床用药安全具有重要意义。目前,中药中黄曲霉毒素的富集、检测及降解解毒方法研究较多,为了更好地为中药中黄曲霉毒素的研究提供参考,本文综述了近年来黄曲霉毒素的富集方法、检测分析技术、降解解毒方法的研究进展(图 1)。
|
| 图 1 黄曲霉毒素富集-检测-降解解毒方法 |
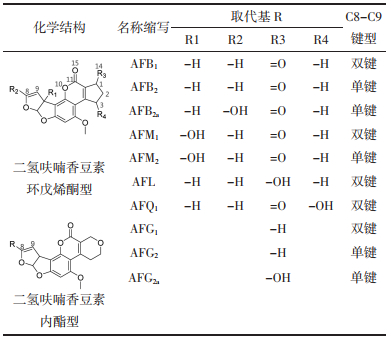
由于中药样品基质复杂且黄曲霉毒素含量较低,因此,在进行分析检测前需采取适当的样品前处理方法进行提取、富集[12]。关于黄曲霉毒素的提取方法主要有振摇提取法、超声提取法、高速均质提取法、加速溶剂萃取法等。常用的黄曲霉毒素纯化方法主要有萃取法、柱净化法、免疫亲和层析法、基质固相分散法、分子印迹固相萃取法等,新技术与新方法的应用能够特异性富集目标化合物[13]。表 2总结了黄曲霉毒素的富集方法及其基本原理、优势、应用实例[14-26]。
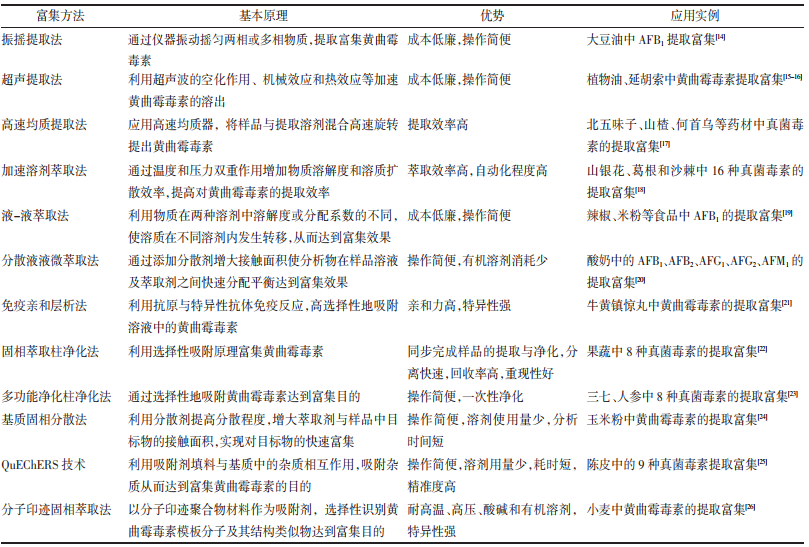
黄曲霉毒素在人体或动物体内长期蓄积会导致肝毒性、致畸、致癌[27-28]。因此,建立高效、灵敏的黄曲霉毒素检测方法对保障药品和食品安全至关重要。黄曲霉毒素的传统检测方法有薄层色谱法、高效液相色谱法、液相色谱-质谱联用法等。色谱法具有检测结果准确、灵敏度高、重复性好等优点,同时也存在样品前期处理复杂、需要专业的检测人员等局限性[13]。免疫分析法是用于快速检验的新技术,其原理是抗原-抗体特异性识别目标分析物,具有特异性强、灵敏度高、高通量等优点[29]。酶联免疫吸附法广泛应用于中药中黄曲霉毒素的检测,被收载为《中华人民共和国药典》2020年版中黄曲霉毒素测定的方法之一[11]。侧流免疫层析法、胶体金免疫层析法、化学发光免疫法、荧光免疫吸附法等可实现样品中黄曲霉毒素的现场快速检测[30-31]。近年来,基于适配体和新型纳米材料的生物传感器因具有灵敏度高、检出限低、操作简便等优势,在黄曲霉毒素检测中得到了广泛应用[32]。此外,通过引入基于适配体的不同技术实现AFB1的检测,例如电化学、表面等离子体共振、比色法等[33]。表 3对黄曲霉毒素检测方法进行了分析[34-42]。
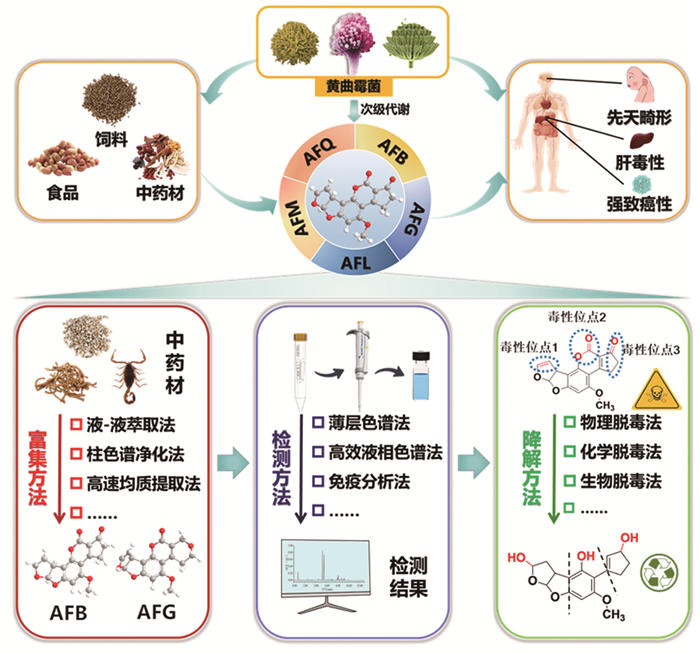
黄曲霉毒素对光和热稳定,不溶于水。中药被其侵染后脱除困难,建立有效脱除黄曲霉毒素的方法对保障中药、食品安全意义重大。常用的黄曲霉毒素降解方法有物理法、化学法、生物法(图 2)[43]。表 4对黄曲霉毒素的降解方法进行了分析。
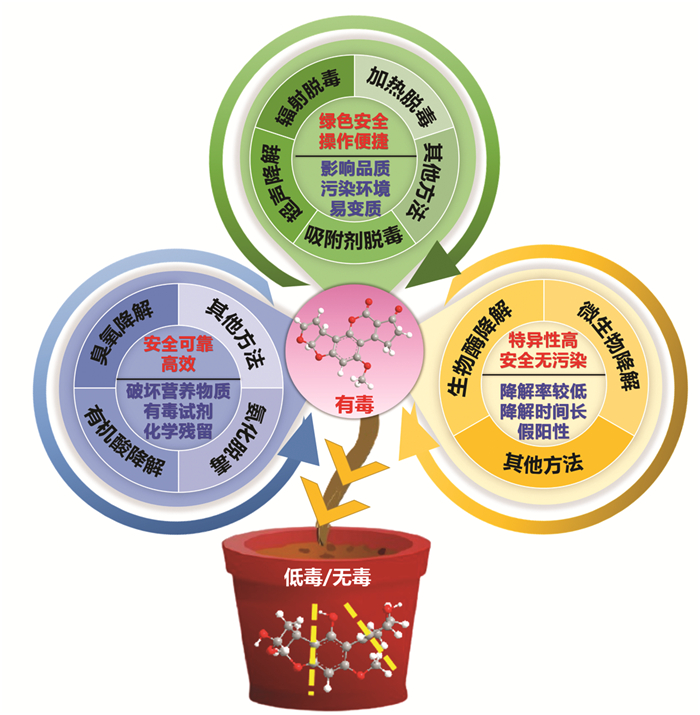
|
| 图 2 黄曲霉毒素不同降解方法的优势和局限性 |
物理方法主要采用加热、辐照、吸附剂吸附、超声等方式降低黄曲霉毒素的浓度。高温破坏毒素位点达到脱毒目的,但同时会影响中药品质,容易造成成分降解等[43-44]。吸附剂与黄曲霉毒素结合可以有效脱除黄曲霉毒素,常用的吸附剂有叶绿素、氧化磁性石墨烯和磁性石墨烯的纳米材料、黏土等[45-46]。超声降解是一种安全绿色的黄曲霉毒素脱毒方法,一般作为辅助手段与其他方法协同使用[47]。
化学方法是指采用化学试剂降解黄曲霉毒素或抑制霉菌滋生[48],主要包括有机酸法、臭氧降解法、氨化脱毒法[49]。有机酸对AFB1具有明显的降解作用[50],如柠檬酸、丙酸、苯甲酸、酒石酸等。臭氧可降解真菌毒素并抑制微生物增殖,对环境危害较小,被誉为“绿色因子”,但其本身作为强氧化剂会破坏基质中的营养物质[51]。氨化脱毒是指利用氨水处理或氨气熏蒸等方式改变黄曲霉毒素的化学结构,达到降低毒性的目的,但摄入过量的氨气会造成机体损伤[52]。微生物降解霉菌毒素是近年来研究较为广泛的一种脱毒方式,利用微生物自身的代谢体系改变黄曲霉毒素的化学结构,使之转化为其他化学衍生物,达到消除毒性或降低毒性的目的,是一种安全、高效、绿色的脱毒方式。荧光假单胞菌、鳗败血假单胞菌、葡萄球菌等菌株可有效降解黄曲霉毒素。生物酶降解是微生物降解的有效补充,通过破坏黄曲霉毒素的毒性基团降低其毒性,具有特异性强、高效性、反应条件温和等特点。红球菌[53]、枯草芽孢杆菌[54]、黑曲霉[55]等多种真菌和细菌的代谢酶能有效降解黄曲霉毒素[56-57]。
目前,关于黄曲霉毒素降解方法的研究取得了较大进展,每种降解方法都有其独特的优势[58-66],可以综合利用多元协同技术达到除去黄曲霉毒素的效果,提高其在不同研究对象中的适用性。探索绿色、环保、安全的整合降解黄曲霉毒素技术将成为未来研究的主流和重点。
4 结语黄曲霉毒素毒性极强,容易污染中药及食品,对人类健康构成严重危害。本文综述了近年来黄曲霉毒素的富集方法、检测技术及降解脱毒方法。由于黄曲霉毒素具有含量低、毒性大的特点,开发出更灵敏、更快速、更经济的检测手段具有重大迫切需求。黄曲霉毒素的早检测、早预防、早干预是有效解决黄曲霉毒素危害性的重要措施。
| [1] |
任晓航, 杜锐, 张旭, 等. 中药外源性污染物检测技术的现代研究[J]. 中草药, 2019, 50(10): 2480-2490. REN X H, DU R, ZHANG X, et al. Modern research on detection technology of exogenous pollutants in Chinese materia medica[J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs, 2019, 50(10): 2480-2490. |
| [2] |
张晓萍, 刘笑笑, 苗菊. 中药中黄曲霉毒素的研究进展[J]. 甘肃科技, 2021, 37(5): 73-77. ZHANG X P, LIU X X, MIAO J. Research progress of aflatoxin in traditional Chinese medicine[J]. Gansu Science and Technology, 2021, 37(5): 73-77. |
| [3] |
YANG L Y, WANG Z L. Advances in the total synthesis of aflatoxins[J]. Frontiers in Chemistry, 2021, 9(2): 779-785. |
| [4] |
LOI M, FANELLI F, LIUZZI V C, et al. Mycotoxin biotransformation by native and commercial enzymes: present and future perspectives[J]. Toxins, 2017, 9(4): 111. DOI:10.3390/toxins9040111 |
| [5] |
王晓艳. 畜禽饲料中黄曲霉毒素B1的危害及检测[J]. 中国动物保健, 2021, 23(5): 120-121. WANG X Y. Harm and detection of aflatoxin B1 in livestock and poultry feed[J]. China Animal Health, 2021, 23(5): 120-121. |
| [6] |
KADEMI H I, BABA I A, SAAD F T. Modelling the dynamics of toxicity associated with aflatoxins in foods and feeds[J]. Toxicology Reports, 2017, 25(4): 358-363. |
| [7] |
李瑞银, 闫金玲, 张喆萍, 等. 饲料中黄曲霉毒素B1的致毒机理及其生物脱毒技术研究进展[J]. 饲料研究, 2020, 43(10): 109-112. LI R Y, YAN J L, ZHANG Z P, et al. Research progress on toxic mechanism and biological detoxification technology of aflatoxin B1 in feed[J]. Feed Research, 2020, 43(10): 109-112. |
| [8] |
ZHOU R, LIU M Z, LIANG X L, et al. Clinical features of aflatoxin B1-exposed patients with liver cancer and the molecular mechanism of aflatoxin B1 on liver cancer cells[J]. Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology, 2019, 71(5): 103-115. |
| [9] |
国家药典委员会. 中华人民共和国药典: 2010年版[M]. 北京: 中国医药科技出版社, 2010. National Pharmacopoeia Committee. People's republic of China(PRC) pharmacopoeia: 2010 edition[M]. Beijing: China Science and Technology Press, 2010. |
| [10] |
国家药典委员会. 中华人民共和国药典: 2015年版[M]. 北京: 中国医药科技出版社, 2015. National Pharmacopoeia Committee. People's republic of China(PRC) pharmacopoeia: 2015 edition[M]. Beijing: China Science and Technology Press, 2015. |
| [11] |
国家药典委员会. 中华人民共和国药典: 2020年版[M]. 北京: 中国医药科技出版社, 2020. National Pharmacopoeia Committee. People's republic of China(PRC) pharmacopoeia: 2020 edition[M]. Beijing: China Science and Technology Press, 2020. |
| [12] |
韦芳, 廖晓芳, 刘晓菲, 等. 中药材等复杂基质中真菌毒素检测的前处理技术研究新进展[J]. 中国中药杂志, 2018, 43(17): 3431-3443. WEI F, LIAO X F, LIU X F, et al. Research progress of pretreatment technology for mycotoxin detection in Chinese materia medica and complex matrices[J]. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica, 2018, 43(17): 3431-3443. |
| [13] |
ZHANG K, BANERJEE K. A review: sample preparation and chromatographic technologies for detection of aflatoxins in foods[J]. Toxins, 2020, 12(9): 539. DOI:10.3390/toxins12090539 |
| [14] |
罗建光. 大豆油中黄曲霉毒素B1快速检测方法的研究[J]. 粮食与油脂, 2018, 31(5): 75-78. LUO J G. Study on rapid detection of aflatoxin B1 in soybean oil[J]. Cereals & Oils, 2018, 31(5): 75-78. |
| [15] |
徐洪文, 朱瑜, 徐华, 等. 高效液相色谱法测定食用植物油中6种真菌毒素[J]. 中国油脂, 2020, 45(11): 77-83. XU H W, ZHU Y, XU H, et al. Detection of six mycotoxins in edible vegetable oil by high performance liquid chromatography[J]. China Oils and Fats, 2020, 45(11): 77-83. |
| [16] |
张伟, 谌宇, 施思, 等. 黄曲霉毒素提取与净化技术用于延胡索药材中黄曲霉毒素检测[J]. 中国药师, 2019, 22(10): 1810-1814. ZHANG W, CHEN Y, SHI S, et al. Extraction and purification technology of aflatoxin used for the determination of aflatoxin in rhizoma Corydalis[J]. China Pharmacist, 2019, 22(10): 1810-1814. |
| [17] |
ZHANG L, DOU X W, KONG W J, et al. Assessment of critical points and development of a practical strategy to extend the applicable scope of immunoaffinity column cleanup for aflatoxin detection in medicinal herbs[J]. Journal of Chromatography A, 2017, 1483(11): 56-63. |
| [18] |
方真, 曲栗, 古淑青, 等. 加速溶剂萃取-QuEChERS-超高效液相色谱-串联质谱法测定药食同源性食品中16种真菌毒素[J]. 色谱, 2020, 38(7): 782-790. FANG Z, QU L, GU S Q, et al. Determination of 16 mycotoxins in drug and food homologous products by ultra performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry combined with accelerated solvent extraction and QuEChERS[J]. Chinese Journal of Chromatography, 2020, 38(7): 782-790. |
| [19] |
马海峰, 陶唐平, 方林明, 等. 液液萃取-HPLC法测定食品中黄曲霉毒素B1[J]. 食品工业, 2020, 41(5): 296-299. MA H F, TAO T P, FANG L M, et al. Determination of aflatoxin B1 in food by HPLC with liquid-liquid extraction[J]. The Food Industry, 2020, 41(5): 296-299. |
| [20] |
HAMED A M, MORENO-GONZÁLEZ D, GARCÍA-CAMPAÑA A M, et al. Determination of aflatoxins in yogurt by dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction and HPLC with photo-induced fluorescence detection[J]. Food Analytical Methods, 2017, 10(2): 516-521. DOI:10.1007/s12161-016-0611-6 |
| [21] |
刘雅丹, 李静, 张聿梅, 等. 牛黄镇惊丸中黄曲霉毒素残留检测方法研究[J]. 药学研究, 2021, 40(3): 160-163. LIU Y D, LI J, ZHANG Y M, et al. Methodology study on aflatoxin analysis in Niuhuang Zhenjing Pills[J]. Journal of Pharmaceutical Research, 2021, 40(3): 160-163. |
| [22] |
王蒙, 姜楠, 韦迪哲, 等. 自制固相萃取柱-超高效液相色谱-串联质谱法同时测定果蔬中的8种真菌毒素[J]. 食品科学, 2016, 37(10): 213-218. WANG M, JIANG N, WEI D Z, et al. A solid phase extraction-ultra performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method for the determination of 8 mycotoxins in fruits and vegetables[J]. Food Science, 2016, 37(10): 213-218. |
| [23] |
李海畅, 李磊. 多功能净化柱-UPLC/MS/MS法测定中药材中8种真菌毒素[J]. 微量元素与健康研究, 2018, 35(6): 60-61, 64. LI H C, LI L. Determination of 8 mycotoxins in Chinese herbal medicine by UPLC/MS/MS with multifunctional purification column[J]. Studies of Trace Elements and Health, 2018, 35(6): 60-61, 64. |
| [24] |
MASSAROLO K C, FERREIRA C F J, KUPSKI L, et al. Optimization of matrix solid-phase dispersion method for extraction of aflatoxins from cornmeal[J]. Food Analytical Methods, 2018, 11(12): 3342-3351. DOI:10.1007/s12161-018-1311-1 |
| [25] |
彭晓俊, 曾丽珠, 伍长春, 等. 基于QuEChERS法提取液相色谱-串联质谱法测定新会陈皮中的9种真菌毒素和农药残留[J]. 分析测试学报, 2017, 36(6): 738-743. PENG X J, ZENG L Z, WU C C, et al. Determination of nine mycotoxins and pesticide residues in Xinhui dried orange peel by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry with qu ECh ERS clean-up[J]. Journal of Instrumental Analysis, 2017, 36(6): 738-743. |
| [26] |
宋立新, 梁雨涛, 张云霞, 等. 槲皮素分子印迹聚合物的制备及其在处理粮食黄曲霉毒素中的应用[J]. 河南工业大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 42(5): 110-116. SONG L X, LIANG Y T, ZHANG Y X, et al. Preparation and application of quercetin molecularly imprinted polymers in the treatment of aflatoxins in grains[J]. Journal of Henan University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2021, 42(5): 110-116. |
| [27] |
黄晓静, 王少敏, 毛丹, 等. 曲霉属真菌毒素的毒性研究进展[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报, 2017, 8(5): 1679-1687. HUANG X J, WANG S M, MAO D, et al. Research progress on toxicity of aspergillus mycotoxins[J]. Journal of Food Safety & Quality, 2017, 8(5): 1679-1687. |
| [28] |
张禹, 王海荣. 饲料中黄曲霉毒素的危害及脱毒方法进展[J]. 饲料研究, 2021, 44(8): 157-160. ZHANG Y, WANG H R. The harm of aflatoxin in feed and the progress of detoxification methods[J]. Feed Research, 2021, 44(8): 157-160. |
| [29] |
WANG Y N, JIANG J Q, FOTINA H, et al. Advances in antibody preparation techniques for immunoassays of total aflatoxin in food[J]. Molecules, 2020, 25(18): 4113. DOI:10.3390/molecules25184113 |
| [30] |
HU S R, DOU X W, ZHANG L, et al. Rapid detection of aflatoxin B1 in medicinal materials of radix and rhizome by gold immunochromatographic assay[J]. Toxicon, 2018, 150(12): 144-150. |
| [31] |
单利楠, 豆小文, 刘好, 等. 黄曲霉毒素B1免疫快速检测技术研究进展及其在中药中的应用[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志, 2019, 25(8): 194-209. SHAN L N, DOU X W, LIU H, et al. Rapid immunoassay of aflatoxin B1 and its application in traditional Chinese medicine[J]. Chinese Journal of Experimental Traditional Medical Formulae, 2019, 25(8): 194-209. |
| [32] |
戴煌, 黄周梅, 李占明, 等. 免疫法在食品黄曲霉毒素检测中的应用[J]. 中国食品学报, 2021, 21(10): 287-304. DAI H, HUANG Z M, LI Z M, et al. Application of immunoassays in food aflatoxins detection[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology, 2021, 21(10): 287-304. |
| [33] |
WANG L, HE K Y, WANG X Q, et al. Recent progress in visual methods for aflatoxin detection[J]. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 2022, 62(28): 7849-7865. |
| [34] |
赵磊, 吴明宸, 于亚楠, 等. 酶联免疫和薄层层析法检测茶叶中黄曲霉毒素B1的评价[J]. 黑龙江医药, 2018, 31(6): 1190-1194. ZHAO L, WU M C, YU Y N, et al. Evaluation of aflatoxin B1 in tea was detected by ELISA and TLC[J]. Heilongjiang Medicine Journal, 2018, 31(6): 1190-1194. |
| [35] |
陈瑞莲. 高效液相色谱-柱前衍生法测定食用油中黄曲霉毒素B1和B2的方法研究[J]. 现代食品, 2019, 5(1): 110-113. CHEN R L. Determination of aflatoxin B1 and B2 in edible oil by pre-column derivatization-high performance liquid chromatography[J]. Modern Food, 2019, 5(1): 110-113. |
| [36] |
刘晶晶, 李耀磊, 王晶娟, 等. HPLC柱后光化学衍生荧光检测法检测3种含土鳖虫中成药的黄曲霉毒素[J]. 中国药事, 2021, 35(3): 307-314. LIU J J, LI Y L, WANG J J, et al. Determination of aflatoxins in three Chinese patent medicines containing euplyphaga steleophaga by immunoaffinity column and high performance liquid chromatography coupled with post-column photochemical derivatization[J]. Chinese Pharmaceutical Affairs, 2021, 35(3): 307-314. |
| [37] |
牛水蛟, 倪亚萍, 李启艳, 等. HPLC-MS/MS法测定化妆品中黄曲霉毒素G2、G1、B2、B1[J]. 化学试剂, 2021, 43(9): 1252-1256. NIU S J, NI Y P, LI Q Y, et al. Determination of aflatoxin G2, G1, B2 and B1 in cosmetics by HPLC-MS/MS[J]. Chemical Reagents, 2021, 43(9): 1252-1256. |
| [38] |
XIE Y L, NING M G, BAN J, et al. Novel enzyme-linked aptamer assay for the determination of aflatoxin B1 in peanuts[J]. Analytical Letters, 2019, 52(18): 2961-2973. |
| [39] |
YUGENDER GOUD K, CATANANTE G, HAYAT A, et al. Disposable and portable electrochemical aptasensor for label free detection of aflatoxin B1 in alcoholic beverages[J]. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 2016, 235(11): 466-473. |
| [40] |
范妙璇, 傅欣彤, 陈奕菲, 等. 三线定量胶体金免疫亲和试纸法定量中药饮片中黄曲霉毒素B1及B1、B2、G1、G2总量的研究[J]. 中草药, 2021, 52(17): 5275-5286. FAN M X, FU X T, CHEN Y F, et al. Quantitative study of total amount of aflatoxins B1 and B1, B2, G1 and G2 in Chinese herbal pieces by colloidal gold immunoaffinity method[J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs, 2021, 52(17): 5275-5286. |
| [41] |
LI J, ZHAO X, CHEN L J, et al. p-bromophenol-enhanced bienzymatic chemiluminescence competitive immunoassay for ultrasensitive determination of aflatoxin B1[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2019, 91(20): 13191-13197. |
| [42] |
WANG Z F, LUO P J, ZHENG B D. A rapid and sensitive fluorescent microsphere-based lateral flow immunoassay for determination of aflatoxin B1 in distillers' grains[J]. Foods, 2021, 10(9): 2109. |
| [43] |
宋承钢, 王彦多, 杨健, 等. 黄曲霉毒素脱毒研究进展[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报, 2020, 11(12): 3945-3957. SONG C G, WANG Y D, YANG J, et al. Research progress of aflatoxin detoxification[J]. Journal of Food Safety & Quality, 2020, 11(12): 3945-3957. |
| [44] |
SHEN M H, SINGH R K. Detoxification of aflatoxins in foods by ultraviolet irradiation, hydrogen peroxide, and their combination: a review[J]. LWT, 2021, 142(7): 110986. |
| [45] |
孙统政, 王娜, 田俊, 等. 黄曲霉毒素B1检测与脱毒方法最新研究进展[J]. 江苏农业学报, 2021, 37(3): 789-799. SUN T Z, WANG N, TIAN J, et al. Research progress of aflatoxin B1 detection and detoxification methods[J]. Jiangsu Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2021, 37(3): 789-799. |
| [46] |
JI J M, XIE W L. Detoxification of Aflatoxin B1 by magnetic graphene composite adsorbents from contaminated oils[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 381(11): 120915. |
| [47] |
MANOOCHEHRI M, ASGHARINEZHAD A A, SAFAEI M. Determination of aflatoxins in rice samples by ultrasound-assisted matrix solid-phase dispersion[J]. Journal of Chromatographic Science, 2015, 53(1): 189-195. |
| [48] |
刘震营, 张永清. 中药材黄曲霉毒素污染与防控[J]. 山东中医药大学学报, 2021, 45(4): 547-553. LIU Z Y, ZHANG Y Q. Aflatoxin contamination in traditional Chinese medicinal materials and its prevention and control[J]. Journal of Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2021, 45(4): 547-553. |
| [49] |
李婷, 胡小松, 巩颖, 等. 中药材中黄曲霉毒素的防控措施研究进展[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志, 2019, 25(7): 228-234. LI T, HU X S, GONG Y, et al. Research progress on prevention and control measures of aflatoxin in Chinese medicinal materials[J]. Chinese Journal of Experimental Traditional Medical Formulae, 2019, 25(7): 228-234. |
| [50] |
AIKO V, EDAMANA P, MEHTA A. Decomposition and detoxification of aflatoxin B1 by lactic acid[J]. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 2016, 96(6): 1959-1966. |
| [51] |
BAREŠOVÁ M, NAČERADSKÁ J, NOVOTNÁ K, et al. The impact of preozonation on the coagulation of cellular organic matter produced by Microcystis aeruginosa and its toxin degradation[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2020, 98(2): 124-133. |
| [52] |
刘配莲, 张刚, 陈焱, 等. 食品与饲料中黄曲霉毒素脱除技术的研究进展[J]. 中国油脂, 2021, 46(10): 92-97. LIU P L, ZHANG G, CHEN Y, et al. Progress on detoxification technology of aflatoxin in food and feed[J]. China Oils and Fats, 2021, 46(10): 92-97. |
| [53] |
吴金芳, 张雨潇, 彭仁. 红球菌的组学、遗传改造及其应用研究进展[J]. 应用与环境生物学报, 2022, 28(1): 239-246. WU J F, ZHANG Y X, PENG R. Research advance in omics, genetic modification, and application of Rhodococcus[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology, 2022, 28(1): 239-246. |
| [54] |
唐璎, 黄佳, 邓展瑞, 等. 一株枯草芽孢杆菌降解黄曲霉毒素B1产物分析[J]. 生物技术通报, 2021, 37(12): 82-90. TANG Y, HUANG J, DENG Z R, et al. Product analysis of degrading aflatoxin B1 by a strain Bacillus subtilis[J]. Biotechnology Bulletin, 2021, 37(12): 82-90. |
| [55] |
杨阳, 邱天宇, 袁晓, 等. 黑曲霉降解黄曲霉毒素B1的研究及转录组分析[J]. 食品与生物技术学报, 2021, 40(9): 16-25. YANG Y, QIU T Y, YUAN X, et al. Biodegradation of aflatoxin B1 by Aspergillus niger and transcriptome analysis[J]. Journal of Food Science and Biotechnology, 2021, 40(9): 16-25. |
| [56] |
BEN TAHEUR F, KOUIDHI B, AL QURASHI Y M A, et al. Review: biotechnology of mycotoxins detoxification using microorganisms and enzymes[J]. Official Journal of the International Society on Toxinology, 2019, 160(1): 12-22. |
| [57] |
XIA X S, ZHANG Y, LI M Y, et al. Isolation and characterization of a Bacillus subtilis strain with aflatoxin B1 biodegradation capability[J]. Food Control, 2017, 75(7): 92-98. |
| [58] |
康传志, 吕朝耕, 蒋靖怡, 等. 霉变与煎煮对硫熏天麻质量及二氧化硫残留量的影响[J]. 中华中医药杂志, 2018, 33(5): 2047-2050. KANG C Z, LYU C G, JIANG J Y, et al. Effects of mouldy and decoction on the quality and sulfur dioxide of sulfur-fumigated Gastrodia Rhizoma[J]. China Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine and Pharmacy, 2018, 33(5): 2047-2050. |
| [59] |
LIU R J, LU M Y, WANG R Q, et al. Degradation of aflatoxin B1 in peanut meal by electron beam irradiation[J]. International Journal of Food Properties, 2018, 21(1): 892-901. |
| [60] |
ZAHRAN E, RISHA E, HAMED M, et al. Dietary mycotoxicosis prevention with modified zeolite(Clinoptilolite) feed additive in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus)[J]. Aquaculture, 2020, 515(13): 734-752. |
| [61] |
LIU Y F, LI M M, LIU Y X, et al. Structures of reaction products and degradation pathways of aflatoxin B1 by ultrasound treatment[J]. Toxins, 2019, 11(9): 526. |
| [62] |
SINGH R, MANDAL A B, BISWAS A. Efficacy of propionic, benzoic and tartaric acids in preventing biosynthesis of aflatoxins in poultry feed[J]. Animal Nutrition and Feed Technology, 2017, 17(1): 157. |
| [63] |
LI H, XIONG Z F, GUI D L, et al. Effect of ozonation and UV irradiation on aflatoxin degradation of peanuts[J]. Journal of Food Processing and Preservation, 2019, 43(4): e13914. |
| [64] |
张美美, 蒋梦宇, 孙悠然, 等. 不同氨化处理黄曲霉毒素B1脱毒效果及其对奶牛瘤胃体外发酵的影响[J]. 中国畜牧兽医, 2019, 46(1): 130-139. ZHANG M M, JIANG M Y, SUN Y R, et al. Effects of different ammonia treatments on aflatoxin B1 detoxification and rumen fermentation in dairy cows[J]. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2019, 46(1): 130-139. |
| [65] |
ADEBO O A, NJOBEH P B, SIDU S, et al. Aflatoxin B1 degradation by culture and lysate of a Pontibacter specie[J]. Food Control, 2017, 80(2): 99-103. |
| [66] |
DELLAFIORA L, GALAVERNA G, REVERBERI M, et al. Degradation of aflatoxins by means of laccases from trametes versicolor: an in silico insight[J]. Toxins, 2017, 9(1): 17. |
 2023, Vol. 42
2023, Vol. 42