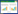文章信息
- 张孝莹, 祁纪鸽, 苏世家, 等.
- ZHANG Xiaoying, QI Jige, SU Shijia, et al.
- UHPLC-MS/MS法同时测定枳实薤白桂枝汤中10种成分
- Simultaneous determination of 10 components in Zhishi Xiebai Guizhi Decoction by UHPLC-MS/MS
- 天津中医药, 2023, 40(7): 910-915
- Tianjin Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 40(7): 910-915
- http://dx.doi.org/10.11656/j.issn.1672-1519.2023.07.16
-
文章历史
- 收稿日期: 2023-05-04
2. 组分中药国家重点实验室,天津 301617
枳实薤白桂枝汤记载于《金匮要略》一书中《胸痹心痛短气病脉证治第九》[1],由枳实、薤白、桂枝、厚朴、瓜蒌5味中药组成[2]。在中医理论中主要用于治疗胸痹,在现代临床研究发现,枳实薤白桂枝汤对各心脏类疾病具有良好的疗效,例如冠心病、心肌梗死、心绞痛等疾病[3-6]。其主要化学成分有挥发油类、有机酸类、鞣质类、香豆素等[7]。
由于枳实薤白桂枝汤中组分及化学成分复杂,而其含量测定也多为高效液相色谱法(HPLC)[8-9],文献报道的枳实薤白桂枝汤含量测定主要是测定槲皮素、橙皮苷、新橙皮苷、柚皮苷和厚朴酚等[10-12]成分,存在测定成分较少、检测限较高、检测时间长等问题,对枳实薤白桂枝汤质量控制的标准尚不完整,但随着枳实薤白桂枝汤在临床上的广泛应用,质量控制尤为必要。因此,本研究建立了专属、灵敏、快速的超高效液相色谱-质谱联用(UHPLC-MS/MS)法,并用外标法[13-14]测定枳实薤白桂枝汤中各组分的主要的代表成分槲皮素[15]、芹菜素[16]、原儿茶酸[17]、木犀草素[16]、紫丁香苷、阿魏酸、柚皮苷[18]、厚朴酚[19]、橙皮苷[20]、新橙皮苷[18]的含量,为枳实薤白桂枝汤质量标准的制定提供参考。
1 仪器与试剂QTRAP 4500高分辨液质联用仪(美国AB Sciex公司);MS205DU分析天平(瑞士METTLER TOLEDO公司);LEAGENO MICRO21 R低温高速离心机(美国Thermo公司);Concentrator plus真空浓缩仪(德国Eppendorf公司);KQ5200超声清洗器(昆山市超声仪器有限公司)。
枳实薤白桂枝汤颗粒购自天津中医药大学附属保康医院(批号20210212、20210316、20210511)。槲皮素(批号19082203)、芹菜素(批号:20042801)、原儿茶酸(批号:20052804)、木犀草素(批号:20121605)、紫丁香苷(批号:18080602)、阿魏酸(批号:18022403)、柚皮苷(批号:20121802)、厚朴酚(批号:20040301)、橙皮苷(批号:2011030)、新橙皮苷(批号:18062902)均购自成都普菲德生物技术有限公司(纯度均≥98%)。色谱纯甲醇和乙腈购自于德国默克公司。纯净水为屈臣氏纯净水购自于广州屈臣氏食品饮料有限公司。色谱纯甲酸购自上海阿拉丁生化技术公司。
2 方法和结果 2.1 分析条件 2.1.1 色谱条件Welchultimate XB-C18色谱柱(2.1 mm×100 mm,3 μm);流动相为0.1%甲酸水(A)-乙腈(B),梯度洗脱,洗脱梯度(0~2 min,20% B;2~3 min,20%~40% B;3~6 min,24%~46% B;6~8 min,46%~80% B;8~12 min,80% B;12~12.1 min,80%~20% B;12.1~15 min,20% B)。柱温40 ℃,流速0.2 mL/min,进样量3 μL。
2.1.2 质谱条件电喷雾离子源(ESI),多反应检测(MRM);紫丁香苷为正离子扫描模式。电喷雾电压为4 500 V,槲皮素、芹菜素、原儿茶酸、木犀草素、阿魏酸、柚皮苷、厚朴酚、橙皮苷、新橙皮苷为负离子扫描模式,电喷雾电压为-4 500 V;离子源气体1(GS1)为40 psi;离子源气体2(GS2)为50 psi;离子源温度500 ℃;碰撞气:Low;主要质谱参数见表 1。
精密称取槲皮素、芹菜素、原儿茶酸、木犀草素、紫丁香苷、阿魏酸、柚皮苷、厚朴酚、橙皮苷、新橙皮苷,分别置于1 mL容量瓶中,加甲醇定容至1 mL,分别配成4.98、5.04、4.90、4.95、5.05、4.97、5.06、4.94、5.02、4.96 mg/mL母液。置于4 ℃冰箱中保存备用。
2.2.2 供试品溶液制备称取0.1 g枳实薤白桂枝汤颗粒,置于25 mL锥形瓶中,加70%甲醇定容至刻度线,精密称质量,超声30 min至溶解,再精密称定,用溶剂补足减失的质量,过0.22 μm滤膜,滤液储存于-4 ℃冰箱,备用。
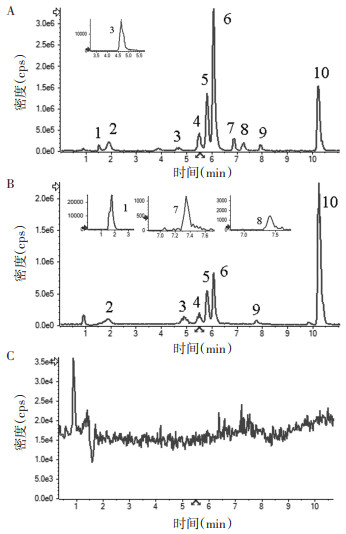
2.3 方法学验证 2.3.1 专属性考察对照品溶液(A)、枳实薤白桂枝汤样品(B)及甲醇空白溶液(C)的色谱图见图 1。由图 1可知,枳实薤白桂枝汤中10种成分分离度好,专属性良好。
|
| 注:A.对照品色谱图;B.枳实薤白桂枝汤颗粒样品色谱图;C.空白甲醇色谱图。1.紫丁香苷;2.原儿茶酸;3.阿魏酸;4.柚皮苷;5.橙皮苷;6.新橙皮苷;7.木犀草素;8.槲皮素;9.芹菜素;10.厚朴酚。 图 1 枳实薤白桂枝汤颗粒中10种成分色谱图 Fig. 1 Chromatograms of 10 components in Zhishi Xiebai Guizhi Decoction |
取“2.2.1”中各对照品母液,将各成分对照品母液用甲醇依次稀释为7个不同浓度的对照品溶液混匀,配置成槲皮素的浓度为分别1.992、3.984、5.976、9.96、14.94、29.88、49.8 ng/mL;芹菜素的浓度为0.202、0.504、1.008、2.016、4.032、6.048、10.08 ng/mL;木犀草素的浓度为0.198、0.495、0.99、1.98、3.96、5.94、9.9 ng/mL;原儿茶酸的浓度为1.96、9.8、19.6、49、98、196、490 ng/mL;紫丁香苷的浓度为2.02、10.1、20.2、50.5、101、202、505 ng/mL;阿魏酸的浓度为1.988、9.94、19.88、49.7、99.4、198.8、497 ng/mL;柚皮苷浓度为2.024、10.12、20.24、50.6、101.2、202.4、506 ng/mL;厚朴酚浓度为4.94、9.88、49.4、98.8、494、988、1 976 ng/mL;橙皮苷的浓度为10.04、20.08、50.2、100.4、200.8、502、1 004 ng/mL和新橙皮苷浓度为9.92、19.84、49.6、99.2、198.4、496、992 ng/mL。按“2.1”色谱条件下进样分析。其中以对照品浓度为横坐标(X),峰面积为纵坐标(Y),绘制标准曲线,计算回归方程。以信噪比为10∶1为定量下限(LLOQ)。10种化合物的线性回归方程及各成分LLOQ见表 2。10种成分的相关系数r均大于0.995,表明10种成分在相应的范围内线性关系良好。
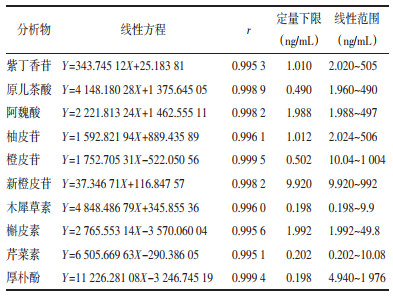
|
取对照品溶液,按“2.1”分析条件下连续进样6次,测得枳实薤白桂枝汤中10种成分槲皮素、芹菜素、原儿茶酸、木犀草素、紫丁香苷、阿魏酸、柚皮苷、厚朴酚、橙皮苷、新橙皮苷的RSD分别为1.49%、2.16%、2.86%、1.85%、1.42%、1.12%、2.36%、1.16%、1.61%、2.64%。表明仪器精密度良好。
2.3.4 稳定性实验取同一枳实薤白桂枝汤供试品溶液(批号20210212),在“2.1”分析条件下,分别在0、6、24 h进样测定,测得枳实薤白桂枝汤中10种成分槲皮素、芹菜素、原儿茶酸、木犀草素、紫丁香苷、阿魏酸、柚皮苷、厚朴酚、橙皮苷、新橙皮苷的RSD分别为0.66%、0.87%、0.33%、1.14%、0.57%、0.23%、0.18%、2.04%、0.83%、0.98%。表明溶液在24 h内稳定性良好。
2.3.5 重复性实验取同一枳实薤白桂枝汤颗粒(批号20210212),按“2.2.2供试品溶液制备”项下平行制备供试品溶液6份,在“2.1”分析条件下进行分析,测得枳实薤白桂枝汤中10种成分槲皮素、芹菜素、原儿茶酸、木犀草素、紫丁香苷、阿魏酸、柚皮苷、厚朴酚、橙皮苷、新橙皮苷的RSD分别为1.56%、0.81%、1.75%、0.46%、2.28%、2.61%、2.29%、0.83%、2.86%、1.51%。表明该方法重复性良好。
2.3.6 加标回收率实验精密称取本品0.05 g(批号20210212),加入对照品溶液(各成分理论含量与0.1 g本品相同),按“2.2.2”项下方法平行制备6份。在“2.1”分析条件下进行分析,计算各成分加样回收率和相对标准偏差(RSD)值。测得枳实薤白桂枝汤中10种成分槲皮素、芹菜素、原儿茶酸、木犀草素、紫丁香苷、阿魏酸、柚皮苷、厚朴酚、橙皮苷、新橙皮苷的加样回收率分别为100.69%、99.72%、98.41%、98.78%、100.85%、97.68%、100.12%、99.86%、98.76%、101.66%;RSD值分别为1.83%、2.94%、1.83%、1.77%、2.37%、1.39%、2.28%、1.96%、2.56%、2.98%。
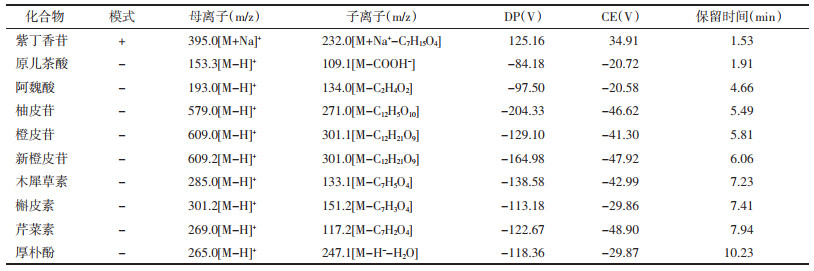
2.4 样品含量测定取“2.2.2”步骤中供试品溶液,用甲醇稀释10倍,取100 μL稀释供试品挥干,加100 μL,50%乙腈复溶,涡旋3 min,14 000 r(离心半径为8.6 cm)离心10 min,取上清液80 μL,在“2.1”色谱条件下进行分析。含量测定结果见表 3。
为了获得最佳的色谱性能和更短的保留时间,先后对水-乙腈以及0.1%甲酸水-乙腈系统进行了测试。测试结果表明采用甲醇-水水-乙腈体系时,枳实薤白桂枝汤胃力康颗粒中各个成分分离度较差,加入甲酸后各色谱峰分离度明显改善,且甲醇-0.1%甲酸水-乙腈体系洗脱时分离效果最好,0.1%甲酸水-乙腈系统洗脱时色谱效果最佳,因此选择其作为流动相。10个分析物的洗脱时间为15 min,未观察到干扰峰。
3.2 质谱条件的优化槲皮素、芹菜素、紫丁香苷、阿魏酸、厚朴酚、橙皮苷、在正负离子模式下均有响应,其中紫丁香苷在正离子模式下响应更好,检测限更低,槲皮素、芹菜素、紫丁香苷、阿魏酸、厚朴酚、橙皮苷均在负离子模式下响应更高,而原儿茶酸、木犀草素、柚皮苷、新橙皮苷只在负离子模式下有响应,经离子挑选后,选择了各成分响应最高的离子模式,大大调高了方法的适用范围。
3.3 结果分析本研究结果表明在3种批次枳实薤白桂枝汤中槲皮素、芹菜素、原儿茶酸、木犀草素、紫丁香苷、阿魏酸、柚皮苷、厚朴酚、橙皮苷以及新橙皮苷的相对标准偏差分别为3.11%、6.25%、3.67%、1.61%、24.95%、12.61%、7.55%、5.89%、4.04%和8.86%。表明在不同批次的枳实薤白桂枝汤中,槲皮素、芹菜素、原儿茶酸、木犀草素、柚皮苷、厚朴酚、橙皮苷以及新橙皮苷在不同批次间的差异较小;紫丁香苷和阿魏酸的含量存在较大差异,尤其是紫丁香苷的差异较大。因此为保证临床用药药效的专一性,有必要进一步加强枳实薤白桂枝汤的质量控制。枳实薤白桂枝汤中含有多种不同种类成分,如槲皮素、芹菜素、木犀草素、柚皮苷、橙皮苷及新橙皮苷为黄酮类化合物[21-25];原儿茶酸和阿魏酸为酚酸类化合物[26-27];紫丁香苷是苯丙素类化合物[28];厚朴酚是木脂素类化合物[29]。这些单体成分对各类心血管疾病均具有良好的药效。其中紫丁香苷和厚朴酚在枳实薤白桂枝汤中含量最高,并具有防治心肌缺血[30]和保护心脏缺血再灌注损伤、减少动脉粥样硬化变化的作用[31-32],其次含量较高的橙皮苷具有心血管保护的作用[33],阿魏酸具有降低心肌缺血和耗氧量的作用[34],柚皮苷也具有治疗心肌缺血再灌注损伤的作用[35]。枳实薤白桂枝汤以薤白和瓜蒌共为君药,其中薤白性温,可通阳散结,而瓜蒌性寒,可宽胸散结,两者均可治疗胸痹心痛。枳实和厚朴共为臣药,可共助君药宽胸散结、下气除满、通阳化痰之效。桂枝作为佐药,可通阳散寒,降逆平冲与薤白相配伍可以加强其宣通上焦的功效,又可以下达中、下二焦,温化阴气。以上5味药材相配伍合用,可以振阳气,消阴寒,使体内气机顺畅,治疗疾病[36]。因此,对枳实薤白桂枝汤颗粒中各成分的含量进行测量,为其质量控制提供参考,保证其临床疗效十分重要。
本实验建立UHPLC-MS/MS法测量枳实薤白桂枝汤中槲皮素、槲皮素、芹菜素、原儿茶酸、木犀草素、紫丁香苷、阿魏酸、柚皮苷、厚朴酚、橙皮苷以及新橙皮苷的含量。该方法快速,简单,灵敏,准确,可为评价该药品质量标准的建立提供参考。
| [1] |
张林, 曾凤. 《金匮要略》等五书中枳实薤白桂枝汤的文献考证[J]. 长春中医药大学学报, 2022, 38(4): 370-373. ZHANG L, ZENG F. Textual research on Zhishi Xiebai Guizhi Decoction based on the Synopsis of the Golden Champer five medical books[J]. Journal of Changchun University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 38(4): 370-373. |
| [2] |
王帅, 汤毅. 枳实薤白桂枝汤应用浅析[J]. 中国民间疗法, 2021, 29(18): 78-80. WANG S, TANG Y. Application of Zhishi Xiebai Guizhi Decoction[J]. China's Naturopathy, 2021, 29(18): 78-80. |
| [3] |
赵阳, 郑景辉, 徐文华, 等. 基于网络药理学方法研究枳实薤白桂枝汤治疗冠心病的作用机制[J]. 世界科学技术-中医药现代化, 2019, 21(12): 2790-2799. ZHAO Y, ZHENG J H, XU W H, et al. A network pharmacology approach to explore mechanisms of Zhishi Xiebai Guizhi Decoction for treatment of coronary heart disease[J]. World Science and Technology-Modernization of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2019, 21(12): 2790-2799. |
| [4] |
闫浩, 刘潇潇, 孙轲强, 等. 基于网络药理学和分子对接研究枳实薤白桂枝汤治疗心血管疾病的作用机制[J]. 中国药师, 2021, 24(3): 405-415, 420. YAN H, LIU X X, SUN K Q, et al. Action mechanism of Zhishi Xiebai Guizhi Decoction in the treatment of cardiovascular disease based on network pharmacology and molecular docking[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2021, 24(3): 405-415, 420. |
| [5] |
周宏园. 枳实薤白桂枝汤加味治疗冠心病不稳定型心绞痛的临床研究[D]. 济南: 山东中医药大学, 2015. ZHOU H Y. Clinical study of Zhishi Xiebai Guizhi Decoction in treating unstable angina pectoris of coronary heart disease[D]. Jinan: Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2015. |
| [6] |
金星. 枳实薤白桂枝汤治疗冠心病心绞痛的研究进展[J]. 当代医学, 2021, 27(6): 193-194. JIN X. Research progress on treatment of angina pectoris of coronary heart disease with Zhizhi Xiebai Guizhi Decoction[J]. Contemporary Medicine, 2021, 27(6): 193-194. |
| [7] |
苟玉东, 徐双, 姜晓旭, 等. 枳实薤白桂枝汤的研究进展[J]. 国医论坛, 2018, 33(3): 68-70. GOU Y D, XU S, JIANG X X, et al. Research progress of Zhizhi Xiebai Guizhi Decoction[J]. Forum on Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2018, 33(3): 68-70. |
| [8] |
盛华刚. HPLC测定枳实薤白桂枝汤颗粒中柚皮苷的含量[J]. 食品与药品, 2013, 15(2): 126-128. SHENG H G. Determination of naringin in Zhishi Xiebai Guizhi Decoction granule by HPLC[J]. Food and Drug, 2013, 15(2): 126-128. |
| [9] |
袁海建, 李卫, 祝一飞, 等. 枳实薤白桂枝汤HPLC指纹图谱及10种指标成分含量测定研究[J]. 中草药, 2020, 51(9): 2448-2459. YUAN H J, LI W, ZHU Y F, et al. Study on fingerprint of Zhishi Xiebai Guizhi Decoction by HPLC and determination of 10 index components[J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs, 2020, 51(9): 2448-2459. |
| [10] |
李明潺, 杨红素, 徐家山, 等. 基于中药Q-marker理论的经典名方枳实薤白桂枝汤关键成分发现与量质传递研究[J]. 化学试剂, 2022, 44(8): 1097-1102. LI M C, YANG H S, XU J S, et al. Study on the discovery of the index components and quantitative-qualitative transfer of classical prescription Zhishi Xiebai Guizhi Decoction based on Q-marker[J]. Chemical Reagents, 2022, 44(8): 1097-1102. |
| [11] |
徐瑞杰, 薛蓉, 梅茜, 等. 经典名方枳实薤白桂枝汤物质基准的量值传递研究[J]. 中草药, 2022, 53(9): 2650-2658. XU R J, XUE R, MEI X, et al. Research on quantitative transmitting of classical prescription Zhishi Xiebai Guizhi Decoction substance benchmarks[J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs, 2022, 53(9): 2650-2658. |
| [12] |
袁海建, 李卫, 祝一飞, 等. 枳实薤白桂枝汤HPLC指纹图谱及10种指标成分含量测定研究[J]. 中草药, 2020, 51(9): 2448-2459. YUAN H J, LI W, ZHU Y F, et al. Study on fingerprint of Zhishi Xiebai Guizhi Decoction by HPLC and determination of 10 index components[J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs, 2020, 51(9): 2448-2459. |
| [13] |
宋沛颖, 李慧勇, 那微, 等. 一测多评法测定安神宁中4个木脂素含量[J]. 药学研究, 2022, 41(10): 645-649. SONG P Y, LI H Y, NA W, et al. Determination of four lignin components in Anshenning by QAMS[J]. Journal of Pharmaceutical Research, 2022, 41(10): 645-649. |
| [14] |
王汝上, 钟铖, 陈瑞君, 等. 一测多评法测定猪胆粉中4种指标成分的含量[J]. 广州中医药大学学报, 2023, 40(4): 984-991. WANG R S, ZHONG C, CHEN R J, et al. Determination of four index components in pig bile powder by one test and multiple evaluation method[J]. Journal of Guangzhou University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 40(4): 984-991. |
| [15] |
谢进, 戴艳娇, 周佳民, 等. 6种药用植物黄酮类物质含量测定[J]. 湖南农业科学, 2020(12): 57-59. XIE J, DAI Y J, ZHOU J M, et al. Determination of flavonoids content in six medicinal plants[J]. Hunan Agricultural Sciences, 2020(12): 57-59. |
| [16] |
和焕香, 郭庆梅. 瓜蒌化学成分和药理作用研究进展及质量标志物预测分析[J]. 中草药, 2019, 50(19): 4808-4820. HE H X, GUO Q M. Research progress on chemical composition and pharmacological effects of trichosanthis fructus and predictive analysis on quality marker[J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs, 2019, 50(19): 4808-4820. |
| [17] |
孙志, 张媛媛, 周胜楠, 等. 基于UHPLC-Q-Orbitrap HRMS和生物信息学探讨瓜蒌薤白汤治疗冠心病的潜在药效物质基础和作用机制[J]. 中草药, 2022, 53(18): 5613-5624. SUN Z, ZHANG Y Y, ZHOU S N, et al. Explore potential pharmacodynamic substances basis and mechanism of Gualou Xiebai Decoction in treatment of coronary heart disease based on UHPLC-Q-Orbitrap HRMS and bioinformatics[J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs, 2022, 53(18): 5613-5624. |
| [18] |
童培珍, 李国卫, 何嘉莹, 等. 基于指纹图谱和多指标成分含量测定的枳壳与枳实药材质量差异性研究[J]. 中南药学, 2022, 20(4): 898-904. TONG P Z, LI G W, HE J Y, et al. Quality difference in aurantii fructus and aurantii fructus immatutus based on fingerprint analysis and multi-index content determination[J]. Central South Pharmacy, 2022, 20(4): 898-904. |
| [19] |
刘瑞连, 鲁翠香, 蒋孟良, 等. 不同产地厚朴中厚朴酚与和厚朴酚含量比较研究[J]. 时珍国医国药, 2022, 33(8): 1996-1997. LIU R L, LU C X, JIANG M L, et al. Comparative study on magnolol and honokiol in Magnolia officinalis from different habitats[J]. Lishizhen Medicine and Materia Medica Research, 2022, 33(8): 1996-1997. |
| [20] |
石敬依, 蔡文君, 林文栋, 等. 枳实肉和瓤的UPLC指纹图谱和多成分定量分析比较研究[J]. 中国中药杂志, 2021, 46(17): 4446-4455. SHI J Y, CAI W J, LIN W D, et al. Comparison between peel and pulp of aurantii fructus immaturus by UPLC fingerprint and multicomponent quantitative analysis[J]. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica, 2021, 46(17): 4446-4455. |
| [21] |
黄龙岳, 宁洪鑫, 姚薛超, 等. 木犀草素提取和纯化工艺的研究进展[J]. 中草药, 2021, 53(4): 1185-1192. HUANG L Y, NING H X, YAO X C, et al. Research progress on extraction and purification of luteolin[J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs, 2021, 53(4): 1185-1192. |
| [22] |
刘琴, 吕庆云. 芹菜素的提取及应用研究进展[J]. 食品研究与开发, 2020, 41(21): 208-213. LIU Q, LYU Q Y. Progress in extraction and application of apigenin[J]. Food Research and Development, 2020, 41(21): 208-213. |
| [23] |
杨稼俊, 胡爱军, 杨瑶, 等. 柚皮中柚皮苷的提取工艺研究[J]. 农产品加工, 2020(4): 36-38, 43. YANG J J, HU A J, YANG Y, et al. Study on the extraction technology of naringin from pomelo peel[J]. Aem Roducts Rocessing, 2020(4): 36-38, 43. |
| [24] |
任嘉瑜, 范娜, 彭晓邦. 枳壳橙皮苷提取工艺研究[J]. 食品安全导刊, 2021(28): 117-119. REN J Y, FAN N, PENG X B. Study on extraction technology of hesperidin from fructus aurantii[J]. China Food Safety Magazine, 2021(28): 117-119. |
| [25] |
王胜利, 于虹, 李超群, 等. 制备色谱法从槐米中同时精制芦丁和槲皮素[J]. 食品科技, 2022, 47(2): 245-250. WANG S L, YU H, LI C Q, et al. Preparation and purification of rutin and quercetin from sophora japonica by semi-preparative HPLC[J]. Food Science and Technology, 2022, 47(2): 245-250. |
| [26] |
胡杨, 李先芝, 石豪, 等. 不同提取方式对冬葵果中咖啡酸、阿魏酸含量的影响[J]. 亚太传统医药, 2022, 18(5): 57-60. HU Y, LI X Z, SHI H, et al. Effects of different extraction methods on the content of caffeic acid and feruLic acid in malvae fructus[J]. Asia-Pacific Traditional Medicine, 2022, 18(5): 57-60. |
| [27] |
赵大伟, 王佩华. 紫丁香叶中原儿茶酸提取工艺研究[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2011, 39(26): 15943-15944, 15947. ZHAO D W, WANG P H. Study on the extraction technology of protocatechuic acid from syringa oblata lindl.leaves[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2011, 39(26): 15943-15944, 15947. |
| [28] |
赵连飞. 暴马丁香小枝中紫丁香苷和橄榄苦苷的分离纯化工艺研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 东北林业大学, 2016. ZHAO L F. Study on separation and purification technology of syringin and oleuropein from the twigs of cinnamomum camphora[D]. Harbin: Northeast Forestry University, 2016. |
| [29] |
王颖, 陈文强, 邓百万, 等. 厚朴酚与和厚朴酚的药理作用及提取合成研究进展[J]. 陕西理工学院学报(自然科学版), 2018, 34(2): 58-64. WANG Y, CHEN W Q, DENG B W, et al. Advances in pharmacological effects, extraction and synthesis of magnolol and honokiol[J]. Journal of Shaanxi Shaanxi University of Technology(Natural Science Edution), 2018, 34(2): 58-64. |
| [30] |
王菲, 袁冲, 杨艳芳, 等. 紫丁香苷的植物资源、体内代谢途径及药理作用研究进展[J]. 中国药师, 2021, 24(11): 2073-2076. WANG F, YUAN C, YANG Y F, et al. Overview of plant resources, metabolic pathways and pharmacological effects of syringin[J]. China Pharmacist, 2021, 24(11): 2073-2076. |
| [31] |
张勇, 唐方. 厚朴酚药理作用的最新研究进展[J]. 中国中药杂志, 2012, 37(23): 3526-3530. ZHANG Y, TANG F. Advance in latest studies on pharmacological effects of magnolol[J]. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica, 2012, 37(23): 3526-3530. |
| [32] |
王晨虹, 商烨, 周蕊, 等. 超高效液相色谱法同时测定川木香中紫丁香苷、木香烃内酯和去氢木香内酯含量[J]. 天津中医药, 2022, 39(12): 1589-1594. WANG C H, SHANG Y, ZHOU R, et al. Simultaneous determination of syringin, costunolide and dehydrocostus lactone in vladimiriae radix by UPLC[J]. Tianjin Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 39(12): 1589-1594. |
| [33] |
钱俊臻, 王伯初. 橙皮苷的药理作用研究进展[J]. 天然产物研究与开发, 2010, 22(1): 176-180. QIAN J Z, WANG B C. New research progress in pharmacological activities of hesperidin[J]. Natural Product Research and Development, 2010, 22(1): 176-180. |
| [34] |
张欣, 高增平. 阿魏酸的研究进展[J]. 中国现代中药, 2020, 22(1): 138-147. ZHANG X, GAO Z P. Research progress in ferulic acid[J]. Modern Chinese Medicine, 2020, 22(1): 138-147. |
| [35] |
王婷婷. 柚皮苷对大鼠心肌缺血再灌注损伤的治疗作用及机制研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2021. WANG T T. Therapeutic effect and mechanism of naringin on myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats[D]. Chengdu: Southwest Jiaotong University, 2021. |
| [36] |
郭澜, 袁鑫, 王美峤, 等. 枳实薤白桂枝汤应用研究进展[J]. 河北中医, 2019, 41(6): 942-946. GUO L, YUAN Z, WANG M Q, et al. Research progress in application of Zhishi Xiebai Guizhi Decoction[J]. Hebei Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2019, 41(6): 942-946. |
2. State Key Laboratory of Component-based Chinese Medicine, Tianjin 301617, China
 2023, Vol. 40
2023, Vol. 40